Anti-Virus Management Service (AVMS)
1. Overview
Networx Security Services - Overview
The Networx contracts require a basic level of security management for its contractors that ensures compliance with Federal Government generally accepted security principles and practices, or better. The contracts employ adequate and reasonable means to ensure and protect the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of Networx services, Operational Support Systems (OSS), and Government information transported or stored in the contractors Networx services infrastructure. These requirements are detailed in Section C.3.3.2 of the Networx contracts.
In addition to this mandatory level of security, the Networx contracts provide additional security services that may be ordered on a fee-for-service basis. These are:
- Managed Tiered Security Service (MTSS)
- Managed Firewall Service (MFS)
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Service (IDPS)
- Vulnerability Scanning Service (VSS)
- Anti-Virus Management Service (AVMS)
- Incident Response Service (INRS)
- Managed E-Authentication Service (MEAS)
- Secure Managed E-Mail Service (SMEMS)
The AVMS offering is described below.
3. Technical Summary
AVMS is a service that was not offered on the original FTS2001 contracts. AVMS enables the detection and removal of viruses by scanning Agency systems and traffic for patterns, activities, and behaviors that may signal the presence of malicious code. Anti-virus applications are constantly active in attempting to detect patterns, activities, and behaviors that may signal the presence of viruses. AVMS enables Agencies to procure anti-virus capabilities that protect their network infrastructure.
AVMS provides the most current anti-virus software and tools. It includes traffic scanning, anti-virus software/hardware, monitoring of anti-virus advisories, management, and maintenance. The service monitors traffic for malicious content, and complements the anti-virus software already implemented on Agency desktops.
AVMS connects to and interoperates with the Agency networking environment, including Demilitarized Zones (
As part of its AVMS service, the contractor provides the software and hardware components, including servers and gateways as required by the Agency. The Agency may order either or both of the two following components:
A managed gateway-based anti-virus service which provides a gateway that scans web and email traffic for worms, viruses, and malicious content. A server-based anti-virus service that scans all files and software housed on a specific server, including the operating system. This host-level scanning is provided at Agency-specified time intervals.
The diagram below illustrates a sample implementation of these components, as applicable. Illustrative hardware such as firewalls and edge routers are not provided as part of the AVMS.
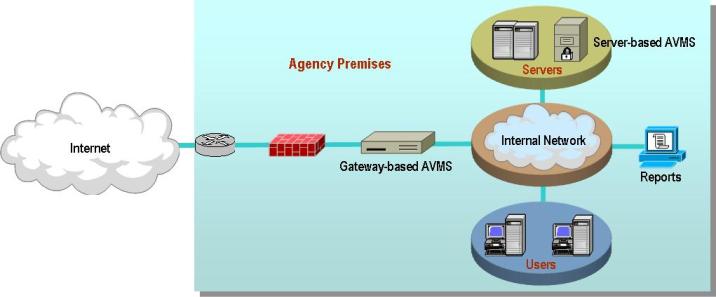
AVMS also offers a load balancing feature which distributes traffic across multiple gateway anti-virus servers, to meet the requirements of large high-volume implementations.
4. Technical Detail
AVMS provides Agency's internal networks with a layer of protection against cyber attacks. This includes providing Agencies with anti-virus capabilities to protect their network infrastructure. It also equips Agencies with up-to-date anti-virus systems and tools for timely virus protection.
AVMS will support the full range of technical capabilities that are available in commercial offerings. These include a design for the appropriate anti-virus solution for an Agency's specific needs. The contractor will monitor the system on a 24X7 basis for infection, will allow real-time and on-demand virus scanning, will screen incoming and outgoing traffic for possible infection, will protect against all known threats, and will provide various methods of alerting the Agency to detected threats. These and other service capabilities are detailed in Section C.2.10.4.1.4 Technical Capabilities of the Networx contracts.
AVMS is required to support the User-to-Network Interfaces (UNIs) defined in the following Networx Internet Protocol (IP) services;
- Internet Protocol Service (IPS)
- Premises-Based IP VPN Services (PBIP-VPNS)
- Network-Based IP VPN Services (NBIP-VPNS)
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for AVMS. The specific details can be found within each Contractors Networx contract files and pricing notes for AVMS
For more information on the general AVMS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.10.4 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.10.4 for pricing.
5. AVMS Price Description
AVMS Price Basics
AVMS is a service that was not offered on the original FTS2001 contracts. AVMS provides the following components:
- A managed gateway-based anti-virus service which provides a gateway that scans web and email traffic for worms, viruses, and malicious content.
- A server-based anti-virus service that scans all files and software housed on a specific server, including the operating system. This host-level scanning is provided at Agency-specified time intervals.
Price components required for service are:
- Basic service (NRC and/or MRC) consisting of either:
- Managed Gateway-Based AVMS (NRC + MRC per user).
- Server-Base2d (NRC + MRC per server).
- Anti-Virus Load Balancing feature ordered as needed by the Agency.
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement AVMS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
Example 1: Managed Gateway-Based AVMS
- Choose CLIN 360001 Managed Gateway-Based AVMS NRC per user
- Choose CLIN 360101 Managed Gateway-Based AVMS MRC per user
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement AVMS. Illustrative hardware such as firewalls and edge routers are not provided as part of the AVMS.
Example 2: Server-Based AVMS
- Choose CLIN 360002 Server-Based AVMS NRC per server
- Choose CLIN 360102 Server-Based AVMS MRC per server
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement AVMS. Illustrative hardware such as servers are not provided as part of the AVMS.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for AVMS. The specific details can be found within each Contractors Networx contract files and pricing notes for AVMS.
For more information on the general AVMS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.10.4 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.10.4 for pricing.
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
2. Technical Description
ATMS Technical Summary
ATMS is a transport service that provides reliable and secure delivery of data, voice, and video content in packets referred to as ATM cells. These cells (composed of 53 byte fixed length containers) are delivered via links between ATM switches to comprise a network. ATMS may be delivered as Native ATM or as Emulated ATM but not both, depending on the Agency's requirements. The service footprint covers CONUS, OCONUS, and Non-Domestic locations. The service's performance and reliability in delivering converged data, video and voice applications, makes it an attractive alternative to Private Line or Frame Relay (FR) networks.
The example shown below illustrates some of the key technical requirements satisfied by ATMS. Agencies with both Routine and Critical Service Level Agreements (SLAs) are connected to the contractor's backbone network through contractor-provided access services that include dial-up Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN), Digital Subscriber Line (DSL), Ethernet, Frame Relay Service (FRS), Private Line Service (PLS), other Agency ATMS, and dial-backup. ATMS can accommodate connections at customer locations via Agency's routers, ATM edge switches, multiplexing/switching devices, PBXs, and host computers. Critical Agency locations requiring high availability may purchase multiple edge switches to provide switch diversity. Inverse Multiplexing capability for ATM (IMA) can provide a scalable and cost-effective solution for customers who choose to optimize WAN resources among existing T1s (NxDS1), without having to purchase DS3 or OC3 circuits.
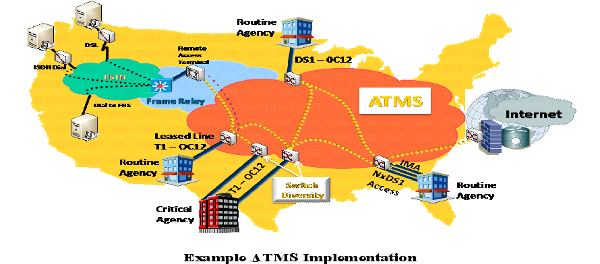
ATMS Technical Detail
The ATMS solution provides a connection-oriented, transmission service with scalable port speeds of DS-1, DS-3, OC-3, and OC-12. In addition, ATMS provides E-1 and E-3 port speeds for terminations outside the United States. ATMS provides service continuity to FTS2001 contracts.
ATMS supports the following technical capabilities as described in Section C.2.3.2.1.4 of the Networx contracts:
- Quality of Service (QoS) and/or Class of Service (CoS) levels per Permanent Virtual Connection (PVC).
- Bandwidth on demand via scalable CoS.
- Provisioning as a point-to-point virtual connection.
- Network management systems accessibility for querying status, performance statistics, equipment configuration, and fault detection by the Agency's network management staff.
- Multiple PVC speeds from 64 Kbps up to and including OC-12
- Symmetrical PVCs.
- Virtual Path/Virtual Channel (VP/VC) addressing.
- Local access / Local loops.
ATMS allows Agencies to interconnect sites served by ATMS, FRS, PLS, and Ethernet services. Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is an enhancement to IP/ATM networks that is offered on ATMS. An MPLS backbone creates virtual circuits between MPLS-enabled endpoints on the network in order to speed up connections.
ATMS features are described in Section C.2.3.2.2.1 of the Networx contracts that include:
- Circuit Emulation Services
- Disaster Recovery PVCs
- Port Diversity
- Interworking Services to transparently access Agency locations that use (1) Contractor's FRS, and (2) Contractor's IP networks.
- IMA connectivity
- IP-enabled ATM
- Point-to-Multipoint PVCs
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for ATMS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for ATMS.
For more information on the general ATMS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.3.2 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.3.2 for pricing.
3. Price Description
ATMS Price Basics
ATMS provides connection-oriented data transmission, between user locations, with scalable port speeds of DS-1, DS-3, OC-3, and OC-12. PVCs are distinguished by simplex versus duplex and by bit rate type:
- Variable Bit Rate/real time (VBRrt): A class of ATM service, used primarily for voice, lower quality video, and media, in which bandwidth is made available only as needed but with a enough control of latency and jitter to deliver acceptable application quality.
- Variable Bit Rate/non-real time (VBRnrt): A class of ATM service used mainly for time-critical transaction processing, data transfer, and frame relay-to-ATM internetworking (FRASI) in which bandwidth is made available only as needed but with somewhat less control of latency and jitter than with VBRrt.
- Available Bite Rate (ABR): A class of ATM service, normally used for applications that do not require real-time delivery of data, e.g., local area network (LAN) interconnection, distributed file services, and Frame Relay to ATM Service Interworking (FRASI).
- Constant Bit Rate (CBR): Native Mode or Emulated: A class of ATM service that supports the transport and delivery of services that require a constant, unvarying rate of information delivery, e.g., high quality video, high quality voice, and emulated circuit switching. The cell rate is constant with time
- Unspecified Bit Rate (UBR): A class of ATM service, used for connections that transport variable bit rate traffic for which there is no reliance on time synchronization between the traffic source and destination. There are no flow-control mechanisms to dynamically adjust the amount of bandwidth available to the user.
ATMS is similar to the ATM Service offered on FTS2001 contracts.
Price components required for full end-to-end service for CONUS, OCONUS, and Non-Domestic ATMS:
-
- ATMS Port monthly recurring charge per port
- ATMS PVC monthly recurring charge per PVC
- DAA Originating and Terminating Wireline Access (MRC) and (NRC)
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- *Disaster Recovery PVCs
- Port Diversity
- Interworking Services
- Inverse Multiplexing for ATM (IMA)
- IP-enabled ATM
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement ATMS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
* Some or all price components are priced on an Individual Case Basis (ICB). CLINs with ICB prices are not available in the unit pricer.
Example 1: ATMS CONUS Dedicated T1
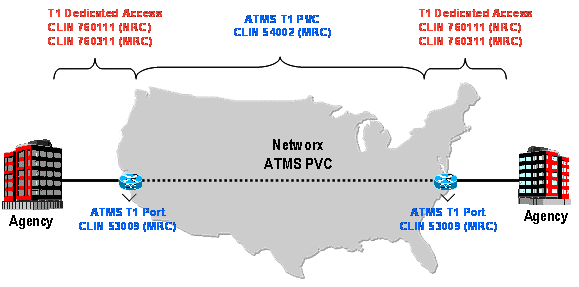
- ATMS Port: Choose CLIN 53009 (Routine Port T1 MRC)
- ATMS PVC: For a T1 (1.536 Mbps) PVC, choose a quantity 24 of CLIN 54002 (PVC VBRnrt Duplex NxDS0 MRC)
- Access NRC: Choose CLIN 760111 Routine DAA T1 NRC for each T1 port
- Access MRC: Choose CLIN 760311 Routine DAA T1 MRC for each T1 port
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs may differ between contractors
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for ATMS. The specific details can be found within each Contractors Networx contract files and pricing notes for ATMS.
For more information on the general ATMS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.3.2 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.3.2 for pricing.
Audio Conference Service (ACS)
1. Technical Description
ACS Technical Summary
ACS is a service that facilitates a call between three or more people in two or more locations that allows participants to converse with each other. The service allows participants to engage in either operator assisted or non-assisted multi-point audio conference calls. Audio conferencing can be initiated from Government sites using single-line telephones, multiline key telephone systems, conference-room audio equipment, PBX, Centrex, and Workstation/PC based soft-phone; and, from non-government sites while on travel or working from home.
ACS is a Networx Management and Applications level service that requires an underlying transport to connect to contractor's audio conference bridge. The audio connection from the conference participants to the ACS conference-bridge from on-net locations (i.e., government sites world-wide) is provided by Networx services, such as Voice Services (VS), Toll Free Service (TFS), Cellular/PCS Service (CPCS), Frame Relay Service (FRS) for VoFR, Asynchronous Transfer Mode Service (ATMS) for VoATM, and Voice over IP Transport Service (VOIPTS); and, from off-net locations world-wide over the Public Switched Telephony Network (PSTN).
ACS can support an audio conference call from a few participants to a few thousand participants, such as an Agency-wide video broadcast with audio feed back for questions and answers from viewers.
The diagram below shows the connectivity from multiple participants to an ACS audio conferencing bridge which supports the audio conference.
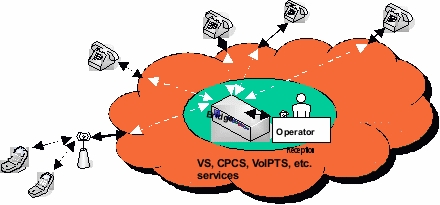
ACS allows selective conversations between conferees as well as a host of additional features. For example, a subset of conferees may engage in a two-way conference while the remaining conferees are listeners only. During a conference, the addition of a party to, or the deletion of a party from, the conference is indicated by a tone or by a verbal announcement from the operator. Additional capabilities are shown below.
- ACS allows participants to be added, without operator assistance, provided that the necessary facilities are available.
- An audio conference can be set up and controlled by users as well by an operator/attendant. ACS supports Meet-me conference and Preset conference for a user-initiated conference.
- Meet-Me conference allows each user to be connected in a conference by dialing a designated number and authorization or pass code at a predetermined time.
- Preset conference allows a user to activate a previously defined conference with associated conferees by dialing an access number followed by an authorization or pass code. Once activated, the system will attempt to connect the pre-designated participants using the predefined lists.
- ACS also supports, operator assisted conference, and advanced reservation system for scheduling audio conference for up to one year in advance by phone, Email, fax, or via online through the Internet.
- An Attendant-Assisted conference allows an operator to establish a conference. Conferees can recall an operator during a conference for immediate attention, such as general assistance or adding or dropping participants.
ACS is similar to Audio Conferencing features of FTS2001 Circuit Switched Service and FTS2001 Switched Voice Service.
2. Technical Detail
ACS will support the full range of technical capabilities that are available in commercial offerings. These include:
- Service availability 24 hours a day, seven days a week, including attendant assistance
- Capability to schedule one or more conferences by time and day of the week either as a single event or recurring event on a daily, weekly, monthly, or other periodic basis
- Capabilities during an operator assisted conference
- Announce late conference participant
- Enable and disable conferee tones
- Enable and disable music on hold
- Enable and disable self mute
- Guaranteed duration of dial-in call
- Listen-only broadcast mode and mixed mode
- Participant count
- Roll call.
These and other service capabilities are detailed in Section C.2.8.2.1.4 Technical Capabilities of the Networx contracts.
ACS also offers features that complement the basic service. These features are described in Section C.2.8.2.2 Features of the Networx contracts. These include:
- Audio recording of call
- Access Controlled Call
- Language translation
- Moderator led questions and answers
- Participant list report
- Password screening
- Replay of pre-recorded audio conference
- Transcription of pre-recorded audio call
- Temporary blocking of ports
- Secured Audio Conference
ACS is required to support audio connection to the conference bridge from the following Networx services:
- C.2.2.1 Voice Services (VS)
- C.2.2.3 Toll Free Services (TFS)
- C.2.7.10 Internet Protocol Telephony Service (IPTelS)
- C.2.3.1 Frame Relay Service (FRS) for VoFR
- C.2.3.2 Asynchronous Transfer Mode Service (ATMS) for VoATM
- C.2.14.1 Cellular/ Personal Communications Service (CPCS)
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for ACS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract and pricing notes for ACS.
For more information on the general ACS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.8.2 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.8.2 for pricing.
3. Price Description
ACS Price Basics
ACS allows users to participate in audio conference calls among multiple locations. Voice connectivity is required for ACS. ACS is similar to Audio Conferencing features of FTS2001 Circuit Switched Service or FTS2001 Switched Voice Service.
Price components required for full end-to-end service for ACS:
- Underlying transport services, such as VS, CPCS, FRS, ATMS, or VoIPTS, to provide connectivity
- Basic service (usage charges per bridge port per minute)
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- Audio recording of call
- Access Controlled Call
- Language translation
- Moderator led questions and answers
- Participant list report
- Password screening
- Replay of pre-recorded audio conference
- Transcription of pre-recorded audio call
- Temporary blocking of ports
- Secured Audio Conference
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement ACS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
Example 1: Basic ACS
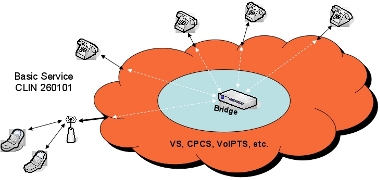
4. Price Additional Detail
Reservation service: Reservation charges apply only for conferences when advance reservations are made. Reservation charges are non-refundable in the event of cancellation of a scheduled conference less than 30 minutes before a conference is scheduled to occur.
Price components required for full end-to-end service for Reservation service:
- Underlying transport services, such as VS, CPCS, FRS, ATMS, or VoIPTS, to provide connectivity
- Basic service (usage charges per bridge port per minute)
- Reservation service (per conference)
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement ACS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
Example 2: Reservation Service for ACS
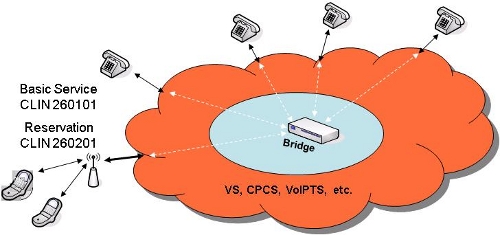
- Transport: Choose Networx telecommunications services such as VS
- ACS Basic Service: Choose CLIN 260101 (Audio Conferencing Service per bridge port per minute)
- Reservation Service: Choose CLIN 260201 (ACS Reservation Service per conference)
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs may differ between contractors.
Attendant-assisted ACS (aka Operator-assisted ACS): Attendant-assisted charges apply only for conferences when attendant-assistance is needed.
Price components required for full end-to-end service for Attendant-assisted ACS:
- Underlying transport services, such as VS, CPCS, FRS, ATMS, or VoIPTS, to provide connectivity
- Basic service (usage charges per bridge port per minute)
- Attendant Assisted service (usage charge per quarter hour)
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement ACS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
Example 3: Attendant-assisted ACS
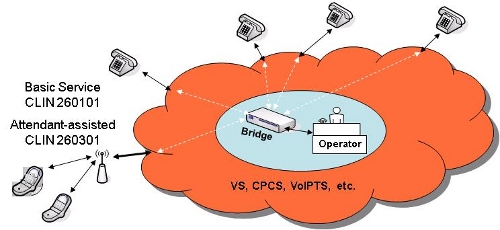
- Transport: Choose Networx telecommunications services such as VS
- ACS Basic Service: Choose CLIN 260101 (Audio Conferencing Service per bridge port per minute)
- Attendant-assisted Service: Choose CLIN 260301 (Attendant-Assisted ACS per quarter hour)
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs may differ between contractors.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for ACS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for ACS.
For more information on the general ACS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.8.2 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.8.2 for pricing.
Call Center / Customer Contact Center Services (CCS)
2. Technical Description
CCS Technical Summary
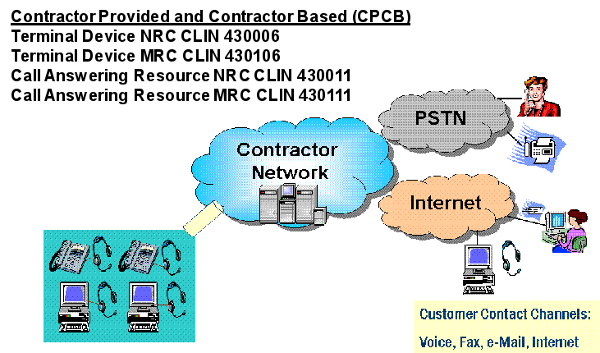
Call Center/Customer Contact Center Services (CCS) provides a cost effective multi-media contact center solution to enable Agencies to efficiently and effectively deliver customer service to their clientele across multiple contact channels (voice, fax, email, and Internet website, etc) by providing a single network call queue or multiple call queues (where applicable). The Call Queue Management Service of the CSS provides real-time management of routing and distribution of multi-media calls from multiple channels to the call center. CCS is available for single site, multiple site, and enterprise wide Agency contact centers.
CCS may be used in conjunction with Toll Free and other network services to facilitate Agency communications with the general public, businesses, and other Agencies. Along with the Call Queue Management Service, CCS provides a Call Answering Service that enables Agencies to utilize contractor provided resources to respond to caller inquiries. The call answering resources can be situated at either an Agency location(s) or a contractor location(s).
CCS is an application layer service that will interoperate with Internet and Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) using underlying network service(s) and their interfaces to deliver customer service capabilities. CCS may be ordered as a domestic (CONUS and OCONUS) or non-domestic service. The majority of contractor's support platforms are located in CONUS and the geographical scope for the local, national, and international coverage will vary with the contractor's network.
The diagram below shows a typical CCS configuration.
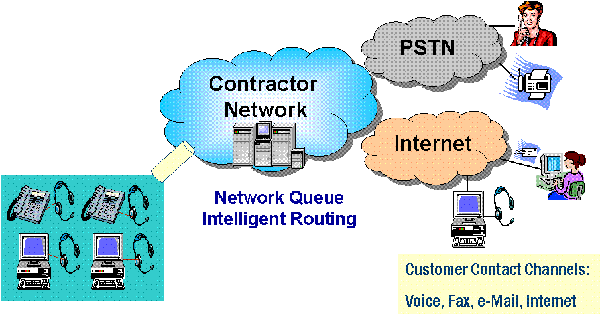
CCS Configuration
3. Technical Detail
CCS provides a wide range of mandatory and optional Technical Capabilities and Service Functionalities which are described in detail in Section C.2.11.2.1.4 of the Networx Contracts. The following is a brief summary of these capabilities.
4. Technical Capabilities
1. Delivery Methods. CCS provides five independent service delivery methods listed below. Three are service delivery methods for Call Management service and two for Call Answering service:
- Contractor Provided and Contractor Based (CPCB) Call Management Service.
- Contractor Provided and Agency Based (CPAB) Call Management Service.
- Contractor Based and Agency Provided (CBAP) Call Management Service*.
- CCS Provided at an Agency Location (CPAL) Call Answering Service.
- CCS Provided at a contractor Location (CPCL) Call Answering Service.
2. Call Management Service (Network Call Queue). This service provides many service management capabilities as briefly listed below:
- Management of call queue(s) for routing and distribution of contacts (calls) from multi-media channels and Prioritizing queue and contacts (calls) within the queue as required.
- Interoperating with the subscribing Agencies CCS communications channels.
- Traversing and successfully interoperating with Agency firewalls and security layers.
- Monitoring of the CCS trunks, agents, and agent groups for call quality by the authorized Agency personnel.
- Management of specific network queue, call-routing algorithms, contact center agent profiles, and reports. At a minimum, capabilities will include Authentication with password protection, performing scheduled and real time changes, and viewing the CCS configuration, Audit trail and change log history.
- Providing a wide variety of required real time, periodic, historic logs and reports.
- Transmitting and delivering music on hold (or recordings) to the originating caller.
- Performing a "Discovery Session" with key stakeholders to gather information required to meet the Agencies CCS needs.
- Supplying terminal devices (e.g. phones, IP phones, softphones, etc.) required for delivery of CCS if requested by the subscribing Agency.
- Accommodating Agency contact center closings by providing announcements, messages, or re-routing of contacts.
3. Call Answering Service - Capabilities include complete turnkey call center operation, including the appropriate network services, technology, personnel, business processes and workflows, training, and reporting to respond to caller inquiries and meet pre-determined performance.
4. Call Answering Resources - Capabilities included are briefly listed below:
- Call answering resources, as needed.
- The required deliverables such as Project Plan, Migration Plan, Staffing Plan, Training Plan, Call Center Management Plan, Continuity of Operations Plan (COOP), Security Plan, Quality Assurance (QA) Plan, and Monthly Status Report.
CCS also provides a wide range of service features that are listed below and described in the Networx Contracts Section C.2.11.2.2.1 of the Networx Contracts.
- Call Recording and Monitoring.
- Collaborative Browsing.
- Computer Telephony Integration (CTI).
- Customer Contact Application.
- E Mail Response Management.
- Interactive Voice Response (IVR).
- IVR - Agency Based Database (Host Connect).
- IVR - Office Locator database.
- IVR - Speech Recognition.
- Language Interpretation Service.
- Outbound Dialer.
- Text Chat (Web Chat).
- Web Call Back.
- Web Call Through.
- Workforce Management.
* The optional CBAP requirement may not be provided by all Networx contractors.
CCS was not offered on the original FTS2001 contracts. Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for CCS. The specific details can be found within each contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for CCS.
For more information on the general CCS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.11.2 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.11.2 for pricing.
5. Price Description
CCS Price Basics
(CCS) provides a network-based call queue that enables the intelligent routing of calls, from multiple channels, to a call center as part of the basic service. CCS also offers an outsourced call answering service. Operations for the Call Answering service may be performed either at the Agency location or the contractor location.
There are three (3) CCS Call Management Service configurations for the basic service:
- Contractor Provided and Contractor Based (CPCB): The contractor provides the necessary components required for CCS Call Management Service. This includes, but is not limited to, hardware, software, inside wiring, and power. The components are located within the contractor's network and maintained by the contractor. Agency supplied personnel will answer calls distributed by CCS Call Management service.
- Contractor Provided and Agency Based (CPAB): The contractor provides the necessary components required for CCS Call Management Service to be located at an Agency provided location. This includes, but is not limited to, CCS hardware and software. The contractor will install, configure, and maintain the CCS equipment. The Agency will provide the power, inside wiring, and a physical location for the contractor's CCS equipment. Agency supplied personnel will answer calls distributed by CCS Call Management service.
- Contractor Based and Agency Provided (CBAP): The Agency will provide the necessary components required for CCS Call Management Service including hardware and software. The contractor provides power, inside wiring, and a physical location for the Agency provided CCS equipment. The contractor will install, configure, and maintain the Agency CCS equipment. Agency supplied personnel will answer calls distributed by CCS Call Management service.
There are two (2) CCS Call Answering Service configurations available with the basic service (if required by an Agency):
- CCS Provided at an Agency Location (CPAL): The contractor provided personnel perform operations at an Agency provided location. The Agency is responsible for providing the work space, furniture, workstation hardware, software, and all necessary building utilities required for the call center. CPCB Call Management service is included as part of CPAL.
- CCS Provided at a Contractor Location (CPCL): The contractor personnel are located and perform operations at a contractor provided location. The contractor is responsible for providing the work space, furniture, workstation hardware, software, and all necessary building utilities for the call center. CPCB Call Management service is included as part of CPCL
For all of the CCS delivery methods, a service initiation charge applies for systems design and integration and software development. CCS was not offered on the original FTS2001 contracts.
6. CCS Price Details (CPCB)
For CPCB, there is a NRC and MRC for each terminal device and a NRC and MRC for each concurrent user. A terminal device is a phone/IP phone or soft phone that is installed and configured in the contact center. A concurrent user is a call answering resource that is logged into the call routing system at the same time as other call answering resources.
The CPCB NRCs will be used by Agencies for both the initial and incremental (or subsequent) provisioning of terminal devices and concurrent users for their call center / customer contact center. The CPCB NRCs are determined from the corresponding volume bands containing the number of terminal devices or concurrent users needed. For each call center / customer contact center, the contractor determines the MRCs for each month from the corresponding volume bands that contain the maximum number of terminal devices in use or maximum number of concurrent users for that month.
Price components required for CCS CPCB:
- Underlying access and transport services, such as TFS, to provide connectivity.
- Service Initiation Charge (ICB NRC).
- Terminal Device (NRC and/or MRC per terminal device).
- Call Answering Resource (NRC and/or MRC per concurrent user).
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- Call Recording and Monitoring**.
- Collaborative Browsing - Unstaffed.
- Computer Telephony Integration (CTI)**.
- Customer Contact Application - Unstaffed**.
- E-mail Response Management - Unstaffed.
- Interactive Voice Response (IVR) - Dedicated**.
- Interactive Voice Response (IVR) - Shared**.
- IVR - Agency Based Database (Host Connect)**.
- IVR - Office Locator Database**.
- IVR - Speech Recognition - Dedicated**.
- IVR - Speech Recognition - Shared**.
- Language Interpretation Service.
- Outbound Dialer - Unstaffed.
- Text Chat (Web Chat) - Unstaffed.
- Web Call Back - Unstaffed.
- Web Call Through - Unstaffed.
- Workforce Management.
- There are no SEDs for CCS. Applicable equipment costs are included in CLIN prices. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
** Some or all price components are priced on an Individual Case Basis (ICB). CLINs with ICB prices are not available in the unit pricer.
Example 1: CPCB with 100 IP Phones and 70 Concurrent Users
- Transport: Choose Networx telecommunications service such as TFS.
- Service Initiation Charge: CLIN 430340 (NRC) is ICB and not available in the unit pricer.
- Terminal Device NRC: Choose CLIN 430006 (CPCB 1 - 115 Phone/IP Phone Device NRC per terminal device).
- Terminal Device MRC: Choose CLIN 430106 (CPCB 1 - 115 Phone/IP Phone Device MRC per terminal device).
- Call Answering Resource NRC: Choose CLIN 430011 (CPCB 1 - 75 Concurrent Users NRC per concurrent user).
- Call Answering Resource MRC: Choose CLIN 430111 (CPCB 1 - 75 Concurrent Users MRC per concurrent user).
7. CCS Price Details (CPAB)
For CPAB, there is a NRC and MRC for each terminal device and a NRC and MRC for each concurrent user. The CPAB NRCs for initial provisioning are determined from the corresponding volume bands containing the number of terminal devices or concurrent users needed. For each call center / customer contact center, the contractor determines the MRCs for each month from the corresponding volume bands that contain the maximum number of terminal devices in use or maximum number of concurrent users for that month.
In addition, there is a separate NRC for the incremental provisioning of terminal devices or concurrent users. CPAB NRCs for incremental provisioning have no volume bands.
Price components required for CCS CPAB:
- Underlying access and transport services, such as TFS, to provide connectivity.
- Service Initiation Charge (ICB NRC).
- Terminal Device - Initial (NRC and/or MRC per terminal device).
- Terminal Device - Incremental (NRC per terminal device).
- Call Answering Resource - Initial (NRC and/or MRC per concurrent user).
- Call Answering Resource - Incremental (NRC per concurrent user).
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- Call Recording and Monitoring**.
- Collaborative Browsing - Unstaffed.
- Computer Telephony Integration (CTI)**.
- Customer Contact Application - Unstaffed**.
- E-mail Response Management - Unstaffed.
- Interactive Voice Response (IVR) - Dedicated**.
- IVR - Agency Based Database (Host Connect)**.
- IVR - Office Locator Database**.
- IVR - Speech Recognition - Dedicated**.
- Language Interpretation Service.
- Outbound Dialer - Unstaffed.
- Text Chat (Web Chat) - Unstaffed.
- Web Call Back - Unstaffed.
- Web Call Through - Unstaffed.
- Workforce Management.
- There are no SEDs for CCS. Applicable equipment costs are included in CLIN prices. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
** Some or all price components are priced on an Individual Case Basis (ICB). CLINs with ICB prices are not available in the unit pricer.
Example 2: CPAB with 100 IP Phones and 70 Concurrent Users

- Transport: Choose Networx telecommunications service such as TFS.
- Service Initiation Charge: CLIN 430335 (NRC) is ICB and not available in the unit pricer.
- Terminal Device NRC - Initial: Choose CLIN 430023 (CPAB 30 - 115 Phone/IP Phone Device NRC per terminal device).
- Terminal Device MRC: Choose CLIN 430123 (CPAB 30 - 115 Phone/IP Phone Device MRC per terminal device).
- Terminal Device NRC - Incremental: Choose CLIN 430422 (Incremental NRC per terminal device).
- Call Answering Resource NRC - Initial: Choose CLIN 430029 (CPAB 20 - 75 Concurrent Users NRC per concurrent user).
- Call Answering Resource MRC: Choose CLIN 430129 (CPAB 20 - 75 Concurrent Users MRC per concurrent user).
- Call Answering Resource NRC - Incremental: Choose CLIN 430428 (Incremental NRC per concurrent user).
8. CCS Price Details (CBAP)
For CBAP the initial ICB NRC additionally includes the initial installation of any routing and distribution equipment. CBAP is priced on an ICB.
Price components required for CCS CBAP:
- Underlying access and transport services, such as TFS, to provide connectivity.
- Basic Service (ICB NRC and/or ICB MRC).
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- Call Recording and Monitoring**.
- Collaborative Browsing - Unstaffed.
- Computer Telephony Integration (CTI)**.
- Customer Contact Application - Unstaffed**.
- E-mail Response Management - Unstaffed.
- Interactive Voice Response (IVR) - Dedicated**.
- IVR - Agency Based Database (Host Connect)**.
- IVR - Office Locator Database**.
- IVR - Speech Recognition - Dedicated**.
- Language Interpretation Service.
- Outbound Dialer - Unstaffed.
- Text Chat (Web Chat) - Unstaffed.
- Web Call Back - Unstaffed.
- Web Call Through - Unstaffed.
- Workforce Management.
- There are no SEDs for CCS. Applicable equipment costs are included in CLIN prices. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
** Some or all price components are priced on an Individual Case Basis (ICB). CLINs with ICB prices are not available in the unit pricer.
9. CCS Price Details (CPAL and CPCL)
CPAL and CPCL are priced on an ICB.
Price components required for CCS CPAL and CPCL:
- Underlying access and transport services, such as TFS, to provide connectivity.
- Basic Service (ICB NRC and/or ICB MRC).
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- Call Recording and Monitoring**.
- Collaborative Browsing - Staffed**.
- Computer Telephony Integration (CTI)**.
- Customer Contact Application - Staffed**.
- E-mail Response Management - Staffed**.
- Interactive Voice Response (IVR) - Dedicated**.
- Interactive Voice Response (IVR) - Shared**.
- IVR - Agency Based Database (Host Connect)**.
- IVR - Office Locator Database**.
- IVR - Speech Recognition - Dedicated**.
- IVR - Speech Recognition - Shared**.
- Language Interpretation Service.
- Outbound Dialer - Staffed**.
- Text Chat (Web Chat) - Staffed**.
- Web Call Back - Staffed**.
- Web Call Through - Staffed**.
- There are no SEDs for CCS. Applicable equipment costs are included in CLIN prices. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
** Some or all price components are priced on an Individual Case Basis (ICB). CLINs with ICB prices are not available in the unit pricer.
This document only addresses the CCS service at contract award. Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for CCS. The specific details can be found within each contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for CCS.
For more information on the general CCS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.11.2 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.11.2 for pricing.
Cellular /Personal Communications Service (CPCS)
1. Technical Description
Cellular/ Personal Communications Service (CPCS) Technical Summary
CPCS provides Agency users with wireless services for their mobile terminals such as cellular phones, wireless-enabled notebook computers, and other personal devices. This service can be used for applications such as voice, data, Short Messaging Services (SMS), Multimedia Messaging Services (MMS) and Internet Services. The CPCS contractor provides the wireless network.
The CPCS contractor's wireless network interoperates with:
- The Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) and the world wide dialing plan.
- Satellite-based services.
- The Internet.
- The contractor's IP-network providing Network and Premises-Based IP-VPN services.
The services and bandwidth provided depends on the characteristics of the mobile terminals and the technology used in the contractor's wireless network and service platforms, ranging from 2nd generation (2G) to 2.5G/3G wireless and beyond. The 2.5G/3G networks (and beyond) support IP packet-mode transmission.
The figure below shows a span of wireless technologies, including Personal Area Network (PAN), Local Area Network (LAN), Metropolitan Area Network (MAN), and Wide Area Network (WAN). CPCS operates primarily at the right side of the chart.
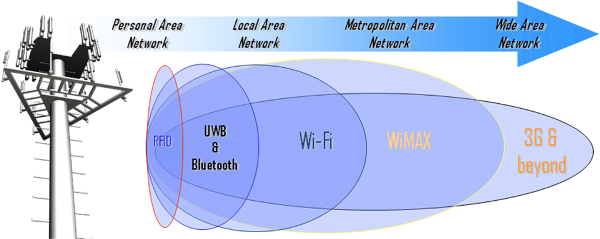
Span of Wireless Technologies
2. Technical Detail
Applications
Short Messaging Services (SMS), a feature of CPCS, provides the capability to send and receive text messages. The text can comprise of any alphanumeric characters; each short message may be up to 160 characters in length. Additionally, SMS supports interconnection with different message sources and public destinations including Email, paging, and instant messaging (IM).
Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS), a feature of CPCS, provides the capability to send and receive multimedia, such as pictures, streaming video, sound, and graphics.
Technical Capabilities
CPCS supports technical capabilities that are available in commercial offerings. These capabilities include:
- The capability to originate and receive voice calls from mobile phones, fixed wireline networks, and satellite-based networks.
- Roaming between compatible wireless networks.
- Packet-mode data transfer that supports a data rate in the range of 128 Kbps to 384 Kbps and above while indoors or traveling at up to 65 miles per hour. This category of service provides "always on" connections.
- Contractor compliance with Wireless Enhanced 911 (E911) Rules including Phases I and II as stipulated by the Federal Communications Commission. (Refer to http://www.fcc.gov/911/enhanced/).
- Wireless Priority Service (WPS) that allows authorized National Security and Emergency Preparedness (NS/EP) personnel to gain access to the next available wireless radio channel in order to initiate calls during an emergency when channels are congested. WPS is invoked by dialing *272 prior to the destination number on wireless terminals that have subscribed to WPS.
- Wireless modem cards for mobile terminals if required by an Agency. The cards provided will support the mobile terminals needed by the Agency, and will include but not be limited to Type II PCMCIA and those required for personal devices.
- If required by an Agency, the CPCS contractor will provide and support commercially available mobile terminals with the characteristics and features needed.
- If required by an Agency, the CPCS contractor will provide commercially available mobile terminals that support device access control and data protection, including but not limited to:
- Integrated authentication.
- Authorization.
- Virus scanning.
- Encryption capabilities (resident on terminal device).
These and other service capabilities are detailed in Section C.2.14.1.1.4 Technical Capabilities of the Networx contracts.
Features
CPCS also offer features that complement the basic service. These features are described in Section C.2.14.1.2.1 Features of the Networx contracts.
- Caller ID.
- Caller ID Blocking.
- Call Forwarding. Busy or No Answer Condition.
- Call Forwarding. Unconditional.
- Call Waiting.
- In-building Repeaters.
- Information Services.
- International Wireless Voice Service Roaming.
- International Wireless Data Service Roaming.
- Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS)*.
- Short Messaging Services (SMS). Basic Functionality.
- SMS - Interworking with Instant Messaging (IM).
- Three-way Calling.
- Voice-Activated Dialing (Network-hosted)*.
- Voice Mail.
- Walkie-talkie functionality*.
* These optional features may not be provided by all Networx contractors.
CPCS is similar to the FTS2001 cellular service. Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for CPCS. The specific details can be found within each contractor's Networx contract and pricing notes for CPCS.
For more information on the general CPCS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.14.1 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.14.1 for pricing.
3. Price Description
CPCS Price Basics
CPCS provides Agency users with wireless services for their mobile terminals including cellular phones, laptops, and PDAs. CPCS supports applications such as voice, data, Short Messaging Services (SMS), and Multimedia Messaging Services (MMS).
CPCS is ordered by selecting the type of plan: voice or data (or voice/data combination such as voice with tethering). The Home service area (national plan coverage) includes the contractor's CONUS coverage and may include additional country/jurisdiction IDs. Home service area is determined by the user's primary business address and/or zip code. Roaming charges apply to originating or receiving calls outside the Home service area. International roaming charges apply. Night/weekend and in-network mobile-to-mobile calling are included in the plans. An additional charge per six-second usage may apply for calls that terminate to a non-domestic wireless handset or terminal.
CPCS is similar to FTS2001 Cellular Communications. For Wireless Access Priority service, a subscription is required. There is a one time charge and a monthly recurring charge for subscription; there are additional usage charges per minute. These charges are not part of this contract; additional details are available at http:/wps.ncs.gov/.
Price components required for CPCS are:
- Basic service (MRC per voice or data plan).
- Overage for voice plans (usage per minute) automatically billed for usage exceeding the maximum allowed per month.
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- Basic Features:
- Caller ID**.
- Caller ID Blocking**.
- Call Waiting**.
- In-building Repeaters***.
- Information Services.
- Three-way Calling**.
- Voice Mail.
- Call Forwarding/Roaming Features:
- Call Forwarding. Busy or No Answer Condition.
- Call Forwarding. Unconditional.
- Voice Service Roaming.
- Calls to Outside Home Area.
- Data Roaming Features:
- International Wireless Data Service Roaming.
- SMS/MMS Features:
- Short Messaging Service (SMS).
- Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS).
- Basic Features:
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement CPCS. Wireless devices and accessories such as cell phones and batteries are considered SEDs. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
** These features are Not Separately Priced and are included in the basic service. These features do not have CLINs and are not in the unit pricer.
*** Some or all price components are priced on an Individual Case Basis (ICB). CLINs with ICB prices are not available in the unit pricer.
Example 1: Voice Plan up to 1,000 minutes
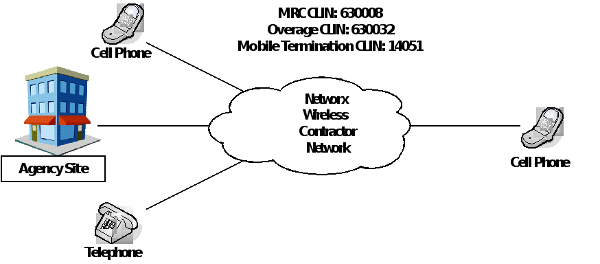
- Basic Service MRC: Choose CLIN 630008 (MRC per 1,000 minutes).
- Overage: Choose CLIN 630032 (Overage per minute) will be automatically billed for usage exceeding the maximum allowed per month.
- Non-Domestic Mobile Termination Add-On: CLIN 14051 will be automatically billed for calls that terminate to a Non-Domestic wireless handset or terminal.
- SEDs may be required to implement CPCS.
Example 2: Data Plan up to and including 384 kbps for a Laptop
- Basic Service MRC: Choose CLIN 630051 (MRC for unlimited usage up to and including 384 kbps for a Laptop/Other Internet device).
- SEDs may be required to implement CPCS.
This document primarily addresses the CPCS service at contract award. Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for CPCS. The specific details can be found within each contractor's Networx contract and pricing notes for CPCS.
For more information on the general CPCS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.14.1 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.14.1 for pricing.
Circuit Switched Data Service (CSDS)
1. Technical Description
Circuit Switched Data Service (CSDS) Technical Summary
CSDS is a mature switched data service provided by GSA in previous local and long distance telecommunications contracts. Some Agencies continue to use CSDS, particularly in the area of on-demand video conferencing applications.
CSDS provides a synchronous, full duplex, totally digital, circuit switched data connection at data rates from DS0 to DS1, including integral multiples of DS0 data rates (i.e., NxDS0, where N = 1 to 24) to on-net and off-net locations for compressed video conferencing and as a backup circuit for a dedicated circuit.
CSDS calls can be initiated from Government-specified terminals, such as digital PBX, Intelligent MUX, Group 4 FAX, Video codec, and Workstation/PC.
CSDS is interoperable with the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) and all Networx CSDS contractors' networks. The figure below illustrates CSDS connectivity from on-net locations, such as Agencies served by Digital-PBXs and Centrex Central Offices.
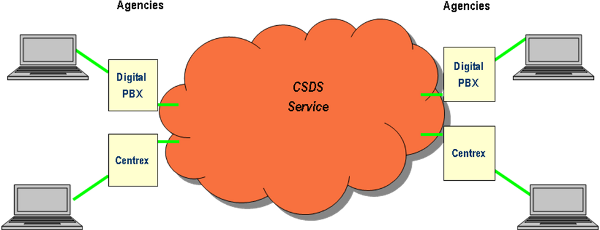
Example of CSDS Connectivity
2. Technical Detail
Technical Capabilities
CSDS supports the full range of technical capabilities that are available in commercial offerings. These capabilities include:
- Calling capability will not require scheduling (i.e., available on-demand, without a reservation).
- Following call establishment, all bit sequences transmitted by the DTE are transported as data/bit transparent and maintain data/bit sequence integrity.
- For calls terminating to off-net locations, the bandwidth requested by the originating on-net location will be limited to the bandwidth limitations in the PSTN between the contractor's network and the called location.
- CSDS uses the same uniform numbering plan as for Voice Services (VS) and is integrated with the Voice Services (VS) plan.
- CSDS uses the same Authorization Codes as specified for Voice Service (VS).
- CSDS provides network-derived clocking to the Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) or PBX/Multiplexer (MUX) at the Service Delivery Point (SDP).
- CSDS supports the following dialable information-payload bandwidths:
- DS0 (56 kbps and 64 Kbps) data rate.
- DS1 (1.536 Mbps) data rate.
- Multirate DS0 (NxDS0, where N= 1 to 24) data rates.
- For the Multirate DS0 category, the contractor will provide the following:
- Appropriate dialing sequence for initiating calls with different bandwidths.
- Transport of all bit sequences transmitted by the DTE as data/bit transparent after establishment of the dialing sequence.
These and other service capabilities are detailed in Section C.2.2.2.1.4 Technical Capabilities of the Networx contracts.
Features
CSDS also offer features that complement the basic service. These features are described in Section C.2.2.2.2 Features of the Networx contracts:
- Dial-In - Toll-free numbers where available commercially.
- User-to-User Signaling Via Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) D-Channel*.
* The optional User-to-User Signaling Via ISDN D-Channel feature may not be provided by all Networx contractors.
CSDS is similar to the Circuit Switched Data Service offering on the FTS2001 contracts.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for CSDS. The specific details can be found within each contractor's Networx contract and pricing notes for CSDS.
For more information on the general CSDS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.2.2 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.2.2 for pricing.
3. Price Description
CSDS Price Basics
CSDS provides a synchronous, full duplex, totally digital, circuit switched data connection to on-net and off-net locations for compressed video conferencing and as a backup circuit for a dedicated circuit. CSDS provides circuit switched service at data rates up to DS1, including integral multiples of DS0 data rates (i.e., NxDS0, where N = 1 to 24) to on-net and off-net locations. Calls can be either:
- CONUS to CONUS.
- CONUS to OCONUS/Non-Domestic.
- OCONUS/Non-Domestic to CONUS.
- OCONUS/Non-Domestic to OCONUS/Non-Domestic.
AT&T, MCI, and Sprint can integrate VS and CSDS traffic on the same dedicated access arrangement CLIN--a capability that was available on the FTS2001 contracts. Qwest also provides this capability but for only the CSDS CLINs with "Single PRI" in the CLIN descriptions (see CLINs 20150 - 20173). Integrating VS and CSDS traffic may reduce costs by reducing the number of required access arrangements. There is no contract requirement to integrate VS and CSDS traffic on the same dedicated access arrangement.
CSDS provides a similar capability to FTS2001 Circuit Switched Data Service.
Price components required for full end-to-end service for CSDS:
- For switched access origination:
- CSDS Transport per-six second increment charge.
- Access: Originating and terminating access costs are included in transport price.
- For dedicated access origination:
- CSDS Transport per-six second increment charge.
- Access: DAA Originating and Terminating Wireline Access (MRC) and (NRC).
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- Dial-In.
- User-to-User Signaling Via ISDN D-Channel.
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement CSDS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
Example 1: T1 CSDS with Switched Access Origination
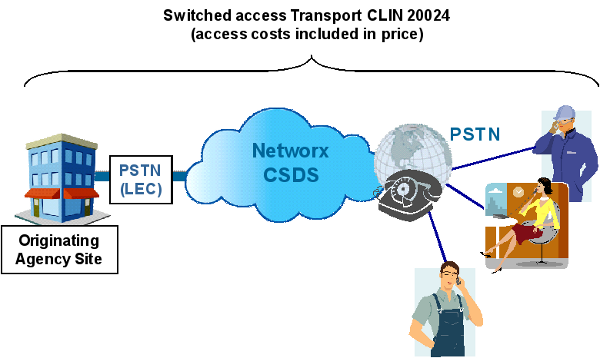
- CSDS Transport: Choose CLIN 20024 (Switched Access DS1 origination per six-second increment).
- Access: For calls originated over a switched access arrangement, the originating and terminating access costs are included in the transport pricing.
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs differ between vendors.
Example 2: T1 CSDS with Dedicated Access Origination
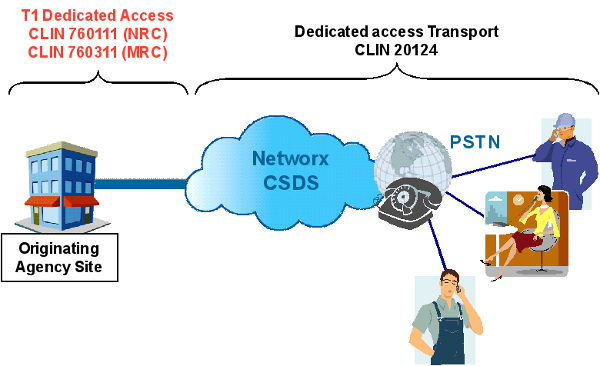
- CSDS Transport: Choose CLIN 20124 (Dedicated Access DS1 origination per six-second increment).
- Access NRC: Choose CLIN 760111 Routine DAA T1 NRC for the originating end of the T1 dedicated access circuit.
- Access MRC: Choose CLIN 760311 Routine DAA T1 MRC for the originating end of the T1 dedicated access circuit.
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs differ between vendors.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for CSDS. The specific details can be found within each contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for CSDS.
For more information on the general CSDS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.2.2 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.2.2 for pricing.
Co-located Hosting Service (CHS)
1. Technical Description
Co-located Hosting Services (CHS) Technical Summary
Agencies that own and operate their own Web hosting environments but require direct high-speed Internet connections or more secure facilities may opt for Co-located Hosting Services (CHS). With CHS, Agencies are provided a secure space located in a contractor's Internet Data Center (IDC) which includes power supply, climate control, smoke detection, fire suppression, and site surveillance (i.e., motion detection, closed circuit television, etc.).
CHS caters to Agencies electing to control their Web hosting platforms while also seeking the benefits of locating such platforms in highly secure IDC sites. CHS also addresses the "last mile" problem - the potential bandwidth limitations between Agency buildings and the Internet Service Providers (ISPs). By opting for collocation, Agencies obviate the need for substantial investment in high-speed access solutions. In the example configuration shown below, two Agencies locate their Government Furnished Property (GFP) in the hosting contractor's IDC.
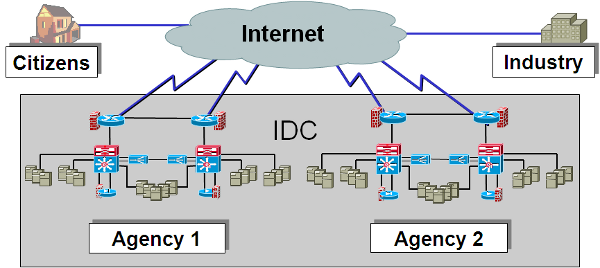
Example CHS Configuration
2. Technical Detail
CHS entails the leasing of rack space in a contractor's IDC. GFP, (principally servers) located within IDCs are connected to the Internet as described in Section C.2.4.1 of the Networx contracts, Internet Protocol Services (IPS).
Technical Capabilities
CHS technical capabilities are described in detail in Section C.2.4.3.1.4 of the Networx contracts and are summarized below.
- Basic Storage Space - configured and leased on a per-rack basis.
- Building and Facility Security - 24X7 security measures including guards, closed-circuit monitors, etc.
- Network Connectivity and Bandwidth - direct Internet connectivity offering high availability and scalability.
- Power Systems - including redundant and high-availability systems.
- Fire Detection and Suppression - including VESDA (Very Early Smoke Detection Apparatus).
- Cooling Systems - redundant IDC cooling systems.
Features
CHS features are described in detail in Section C.2.4.3.2.1 of the Networx contracts and are summarized below.
- Analog Line - for PSTN dialup access, allowing Agencies to remotely configure and manage equipment.
- Cabinets, Cages - equipped with locks for additional security.
- Host Administrative Tasks - on behalf of the Agency, intervene and perform minor unscheduled tasks (e.g. rebooting of GFE).
- Periodic Hardware Check - Ping devices every five minutes.
- Reporting - "virtual console" allowing Agencies to view, monitor, and update trouble tickets and power availability statistics.
- Seismic Bracing - mitigates the risk to servers and computer equipment in the event of seismic activity.
- Storage Media Change - change media in the Agency's storage drive on a mutually agreed schedule.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for CHS. The specific details can be found within each contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for CHS.
For more information on the general CHS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.4.3 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.4.3 for pricing.
3. Price Description
CHS Price Basics
CHS entails the leasing of rack space within a contractor-provided Internet Data Center (IDC). The price for CHS is based on Monthly Recurring Charges (MRCs) and Non-Recurring Charges (NRCs). An MRC based on server rackspace includes such elements as building/facilities security, power systems, fire and suppression, and cooling systems as described in Section C.2.4.3.1.4. An NRC for installation and/or initiation of service may also apply.
A separate MRC may apply for dedicated burstable Ethernet bandwidth between 1 Mbps - 1 Gbps for connectivity to the Internet. The monthly Internet usage is determined by the 95th percentile method. The usage is measured daily every five minutes. The top 5% of monthly usage is discarded and the usage representing the 95th percentile is designated as the Internet usage amount for the month. The monthly Internet usage charge is based on the following usage bands:
- 1 Mbps - 10 Mbps (minimum usage charge of 1 Mbps, then charged in 1 Mbps increments up to, but not including 10 Mbps).
- 10 Mbps - 100 Mbps (minimum usage charge of 10 Mbps, then charged in 10 Mbps increments up to, but not including 100 Mbps).
- 100 Mbps - 1 Gbps (minimum usage charge of 100 Mbps, then charged in 100 Mbps increments up to and including 1 Gbps).
CHS is similar to FTS2001 Web Hosting Service.
Price components required for CHS:
- Server Rackspace (NRC and/or MRC per rack).
- Initial Dedicated Burstable Internet Bandwidth (NRC and/or MRC per unit bandwidth).
- Additional Bandwidth above Initial Dedicated Internet Bandwidth (usage per unit bandwidth).
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- Analog Line.
- Cabinets/Cages.*
- Host Administrative Tasks.
- Periodic Hardware Check (Ping).
- Reporting.
- Seismic Bracing.
- Storage Media Change.
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement CHS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
* Some or all price components are priced on an Individual Case Basis (ICB). CLINs with ICB prices are not available in the unit pricer.
Example 1: Full Rackspace with Burstable Internet Bandwidth up to 10 Mbps with standard power:
- Server Rackspace NRC: Choose CLIN 94008 (Full Rackspace NRC per full rack).
- Server Rackspace MRC: Choose CLIN 94003 (Full Rackspace MRC per full rack).
- Initial Dedicated Burstable Internet Bandwidth NRC: Choose CLIN 94014 (Dedicated burstable Internet bandwidth - maximum 10 Mbps NRC per initial 1 Mbps Ethernet Bandwidth).
- Initial Dedicated Burstable Internet Bandwidth MRC: Choose CLIN 94013 (Dedicated burstable Internet bandwidth - maximum 10 Mbps MRC per initial 1 Mbps Ethernet Bandwidth).
- Additional Bandwidth above Initial Dedicated Internet Bandwidth: Choose CLIN 94015 (Dedicated burstable Internet bandwidth above 1 Mbps up to and including 10 Mbps Usage per additional 1 Mbps Ethernet bandwidth per month (Nx1 Mbps)).
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs may differ between contractors.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for CHS. The specific details can be found within each contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for CHS.
For more information on the general CHS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.4.3 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.4.3 for pricing.
Combined Services (CS)
2. Technical Summary
GSA provides Combined Services (CS) as a collection of separate Networx telecommunications services, packaged into a single service at a flat rate price. An Agency can utilize CS to procure core voice telecommunication services for its needs from a single source, at a predictable monthly cost. Additional features are available to provide flexible service plans that support Agency business needs.
The core CS service is a packaged voice service providing unlimited use of local, regional, and domestic long distance (CONUS and OCONUS) service. The core service supports analog, ISDN BRI and PRI, analog trunk, and T1 local loop types.
CS complies with the connectivity requirements for the individual services being combined. The connectivity requirements of the core CS are listed in Section C.2.2.1.1 Voice Service (VS) of the Networx Contract, and those of the optional services are listed in Sections C.2.4.1 Internet Protocol Service (IPS), C.2.2.3 Toll Free Service (TFS), and C.2.14.1 Cellular/Personal Communications Service (CPCS).
The Networx Request for Proposal (RFP) also included optional packages to bundle the basic core package with other services, such as Calling Card Service (Authorization Codes), Internet Protocol Service (IPS), Toll Free Service (TFS), and Cellular/Personal Communications Service (CPCS) as described in Sections C.2.2.1.2.1, C.2.4.1, C.2.2.3 and C.2.14.1 respectively. However, none of the Networx contractors offer these CS options at this time.
3. Technical Detail
CS will support the full range of technical capabilities that are available in comparable commercial offerings.
Mandatory CS Technical Capabilities
The following CS Technical Capabilities are mandatory:
- Local, regional toll and domestic long distance (CONUS and OCONUS) calling capabilities with unlimited usage in a single combined service package.
- A portfolio of standard features with unlimited usage as defined in the list of features in the section below.
- Contractor flexibility to supplement the core CS service with additional optional offerings such as non-domestic calling, wireless, toll free service, and Internet services.
- A single invoice for all services included in the CS offering.
- Compliance with all applicable local and FCC regulatory requirements including Local Number Portability (LNP), directory assistance, and emergency services (911 or E911) requirements.
- Non-domestic dialing (a CS feature. See below). Non-domestic calling can be restricted if requested by a subscribing Agency.
CS Features
CS provides the service features listed below and described in detail in Networx Contract Section C.2.6.1.2.1:
- Call Forwarding (All, Busy, No Answer).
- Call Transfer.
- Call Waiting.
- Caller ID.
- Caller ID Block.
- Remote Access to Call Forwarding.
- Speed Dial.
- Three Way Calling.
- Voice Mail.
- Calling Card Service*.
- Internet Service*.
- Non-Domestic Calling Service.
- Toll Free Calling Service*.
- Wireless Service*.
* The optional Calling Card Service, Internet Service, Toll Free Calling Service, and Wireless Service features were included in the Networx RFP, but are not currently provided by the Networx contractors.
Also, please note that the list of the features available for the Networx Enterprise Contracts is same as that from the Networx Universal Contracts with the exception that all Enterprise features were optional for contractors to bid.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for CS. The specific details can be found within each contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for CS.
For more information on the general CS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.6.1 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.6.1 for pricing.
4. Price Description
CS Price Basics
CS provides Government users with unlimited local, regional toll, and domestic long distance voice services bundled into a single, core package from a single service provider. CS provides local "dial-tone" as well as long distance voice as part of the core service. The CS Core Package offers unlimited usage of local, regional toll and domestic long distance services and five (5) local loop types:
- Analog.
- ISDN BRI.
- ISDN PRI.
- Analog Trunk.
- T1.
CS is priced in CONUS and OCONUS. Within the CONUS region, prices are differentiated by state. For the OCONUS region, prices are based on the Country/Jurisdiction ID where the service is provided. The specific locations where service is available can be found within each contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for CS. Agencies may also want to confirm specific coverage requirements with the contractor to ensure availability at a specific location.
An NRC is required for the installation of a new local loop. However, if the Agency already has an existing local loop from the contractor, the NRC does not apply. The following features are included in the basic service MRC:
- Call Forwarding (All, Busy, No Answer).
- Call Transfer.
- Call Waiting.
- Caller ID.
- Caller ID Block.
- Remote Access to Call Forwarding.
- Speed Dial.
- Three Way Calling.
- Voice Mail.
- Non-Domestic Calling Service.
Non-Domestic Calling Service (NDCS) is offered at a percent discount off of the per six-second increment charges for the Voice Service (VS) as defined in Section B.2.2.1. CS is a service that was not offered on the FTS2001 contracts, but is similar to MAA capabilities.
The Networx RFP included optional packages to bundle the basic core package with other services (e.g. Internet Service, Toll Free Service, etc.). At this time none of the Networx contractors offer these options.
Price components required for CS Core Package:
- Basic service consisting of either:
- Including local loop (NRC and MRC per line).
- Without local loop (MRC per line).
- Non-Domestic Calling Service (% discount off usage per six-second increment).
- Features are included in the basic service MRC.
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement CS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
Example 1: Core Package with Local Loop and Non-Domestic Calling Service:
- Basic Service NRC: Choose CLIN 184011 (Core Package including local loop - CONUS NRC per analog line).
- Basic Service MRC: Choose CLIN 184001 (Core Package including local loop - CONUS MRC per analog line).
- NDCS: Choose CLIN 184260 (NDCS Percent Discount off of the CONUS/ OCONUS/ Non-domestic to CONUS/ OCONUS/ Non-domestic VS usage charges).
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs differ between vendors.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for CS. The specific details can be found within each contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for CS.
For more information on the general CS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.6.1 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.6.1 for pricing.
Content Delivery Network Service (CDNS)
1. Technical Description
Technical Summary
A content delivery network is a system of computers containing copies of data placed at various points in a network so as to maximize bandwidth for access to the data from clients throughout the network. The Networx contractor provides CDNS which efficiently and rapidly delivers an Agency's content to Web browsers worldwide by reducing the infrastructure required to provide a domestic or global Web presence. CDNS providers guarantee that Agency content and applications will be available to constituents at all times, even in the event of periods of unexpected high usage, network outages, security incidents, and large-scale natural disasters.
The CDNS provider will incorporate equipment and algorithms to cache content on geographically dispersed servers on the Internet. When a request is made from a particular location for specific content, the server that can most rapidly and efficiently provide the content is dynamically identified.
CDNS consists of a collection of surrogate servers that attempt to offload work from origin servers (where content originates) by delivering content on their behalf. The servers belonging to a CDNS may be located at the same site as the origin server, or at different locations around the network, with some or all of the origin server's content cached or replicated amongst the CDNS servers. For each request, the CDNS attempts to locate a CDNS server close to the client Agency to serve the request, where the notion of "close" could include geographical, topological, or latency considerations.
The picture below shows a typical CDNS server site connected to the Internet.

Typical CDNS Server Site
2. Technical Detail
CDNS addresses the following technical and operational issues:
- Latency - the delay in delivering Web content to the end-user.
- Scalability - Web services automatically scale-up while the end-user requests increase.
- Reliability - content is always available and its integrity is assured (i.e. not been altered by third parties including "hackers").
- Flash crowd control - i.e., effectively meeting demand during periods of unexpected high usage.
CDNS is an application-layer service and therefore requires a connectionless data service, such as the Networx Internet Protocol Service (IPS), for the data transfer from the origin server to the CDNS servers.
CDNS supports the full range of technical capabilities that are available in commercial offerings. It is similar to Content Delivery Network Service on the FTS2001 contracts. These capabilities include:
Content Distribution
- Static Content Download Service
- This capability provides fast, secure, and reliable download of content including text, video, music, etc. Such content will likely be stored on CDNS servers deployed globally at the edge of the Internet for faster access.
- Real-time Streaming (Webcasting).
- The CDNS provider will deliver streams in real-time. Real-time streaming content will include (but not be limited to) RealNetworks Real Media, Microsoft Windows Media, and Apple QuickTime.
- On-demand Streaming
- The CDNS provider will host (i.e., provide storage) and deliver streams on demand when requested by end-users. On-demand streaming content will include (but not be limited to) RealNetworks Real Media, Microsoft Windows Media, and Apple QuickTime.
Site Monitoring/ Server Performance Measurements
CDNS will provide a continuous monitoring to ensure performance and quality of service. Measurements will include:
- Availability.
- Latency.
- File Transfer Protocol (FTP) Load.
- Central Processing Unit (CPU) Load.
- Memory Usage.
- Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) Service Load.
- HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Port Service Load.
- HTTP Connections Queue Statistics.
The contractor will provide statistics via a performance dashboard - a secure, Web-based portal accessible by Agency clients on a 24x7 basis. The performance dashboard will be consistent with commercial best practices.
These and other service capabilities are detailed in Section C.2.4.6.1.4 Technical Capabilities of the Networx contracts.
CDNS also offers features that complement the basic service. These features are described in Section C.2.4.6.2 Features of the Networx contracts.
- Failover Service.
- Redirection and Distribution Service (Global Load Balancing - Optional to Offer).
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for CDNS. The specific details can be found within each contractor's Networx contract and pricing notes for CDNS.
For more information on the general CDNS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.4.6 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.4.6 for pricing.
3. Price Description
CDNS Price Basics
CDNS efficiently and rapidly delivers Agency's content to Web browsers worldwide. CDNS basic service consists of two main service types:
- Domestic CDNS where CDNS servers are located only in domestic regions.
- Global CDNS where CDNS servers located in either domestic or non-domestic regions.
CDNS is ordered by specifying a monthly bandwidth commitment level and storage commitment level.
- Committed Bandwidth: Users specify a monthly bandwidth commitment level. Contractor unit prices per Mbps vary by bandwidth commitment level. In general, the larger the bandwidth commitment level, the lower the unit price per Mbps. The MRC is calculated by multiplying the bandwidth commitment level by the unit price per Mbps. This calculation is done automatically in the unit pricer. This MRC is the minimum level charged.
- Bandwidth Overage: If the actual bandwidth used exceeds the bandwidth commitment level, then a separate overage MRC may be applied. The actual bandwidth used is measured at the 95th percentile per month and rounded up to the next highest Mbps bandwidth. The overage MRC applies only to the excess bandwidth (defined as the actual bandwidth used minus the bandwidth commitment level). The overage MRC is calculated by multiplying the excess bandwidth by the unit price per Mbps corresponding to the original committed bandwidth level.
- Committed Storage: Users specify a monthly storage commitment level. Contractor unit prices per GB vary by storage commitment level. In general, the higher the storage commitment level, the lower the unit price per GB. The MRC is calculated by multiplying the storage commitment level by the unit price per GB. This calculation is done automatically in the unit pricer. This MRC is the minimum level charged.
- Storage Overage: If the actual storage used exceeds the storage commitment level, then a separate overage MRC may be applied. The overage MRC applies only to the excess storage (defined as the actual storage used minus the storage commitment level). The overage MRC is calculated by multiplying the excess storage by the unit price per GB corresponding to the original committed storage level.
The CDNS NRC CLINs apply only to the initial service order. Therefore, when only upgrading or changing committed bandwidth levels, the NRC does not apply. Charges for underlying transport services from the origin server to CDNS servers are in addition to the CDNS charges. CDNS is similar to Content Delivery Network Service on the FTS2001 contracts.
Price components required for Domestic and Global CDNS:
- Underlying transport services, such as IPS, to provide connectivity
- Basic service (NRC per service)
- Committed Bandwidth (MRC per Mbps)
- Bandwidth Overage (Overage charges (MRC per Mbps) are incurred when the actual bandwidth used exceeds the monthly committed level)
- Committed Storage (MRC per GB)
- Storage Overage (Overage charges (MRC per GB) are incurred when the actual storage used exceeds the monthly committed level)
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- Failover Service
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement CDNS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
Example 1: Domestic CDNS
- Underlying Transport: Choose Networx telecommunications service such as IPS
- CDNS Basic Service: Choose CLIN 120001 (NRC per service)
- Committed Bandwidth: Choose CLIN 120101 (Committed Bandwidth Domestic MRC per Mbps)
- Bandwidth Overage: Choose CLIN 120103 (MRC Bandwidth Overage Domestic MRC per Mbps)
- Committed Storage: Choose CLIN 120201 (Committed Storage MRC per GB)
- Storage Overage: Choose CLIN 120202 (Storage Overage MRC per GB)
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs may differ between contractors.
Example 2: Global CDNS
- Underlying Transport: Choose Networx telecommunications service such as IPS
- CDNS Basic Service: Choose CLIN 120001 (NRC per service)
- Committed Bandwidth: Choose CLIN 120102 (Committed Bandwidth Global MRC per Mbps)
- Bandwidth Overage: Choose CLIN 120104 (MRC Bandwidth Overage Global MRC per Mbps)
- Committed Storage: Choose CLIN 120201 (Committed Storage MRC per GB)
- Storage Overage: Choose CLIN 120202 (Storage Overage MRC per GB)
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs may differ between contractors.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for CDNS. The specific details can be found within each contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for CDNS.
For more information on the general CDNS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.4.6 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.4.6 for pricing.
Converged IP Service (CIPS)
2. Technical Description
Technical Summary
CIPS is an IP application that provides real-time, two-way voice, video, and data capability over a single broadband connection. As a hosted solution, CIPS delivers a service that provides automatic, remote technology refresh software updates and is highly scalable to accommodate Agency growth. CIPS is an emerging service and has no FTS2001 equivalent.
CIPS offers potential cost savings by allowing customers to combine data, voice, and video applications onto a single network instead of managing such legacy networks separately. The service has gateways to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) and includes embedded security. Additionally, the service includes Service Level Agreements (SLAs) to guarantee reliable service.
Domestic service coverage for CIPS provides coverage CONUS wide, with OCONUS locations optional to offer. The Agency can order CIPS to connect to and interoperate with the:
- PSTN.
- Agency's Local Area Network (LAN).
- Internet.
The diagram below illustrates an example implementation of CIPS. Call processing and other telephony functions are transported over the Contractor's IP network. CIPS requires a connection to the Contractor's IP network as shown below by a broadband access from the user's location. Gateways will provide interoperability with non-IP networks and devices, such as a PSTN gateway. Additional Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) such as telephones, video teleconferencing terminals, or protocol converters may be required to implement and use CIPS.
.Example CIPS Implementation
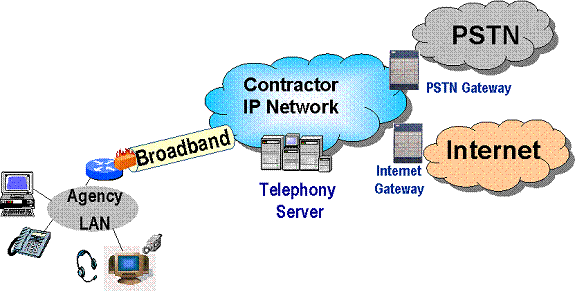
Converged Internet Protocol Service (CIPS) Technical Detail
CIPS provides the integration of IP-based data, voice, and video across a common, converged network infrastructure. Basic CIPS includes traffic prioritization and a secure communications path to ensure delivery of time sensitive services.
For voice services, the following calling features are included at a minimum at no additional cost:
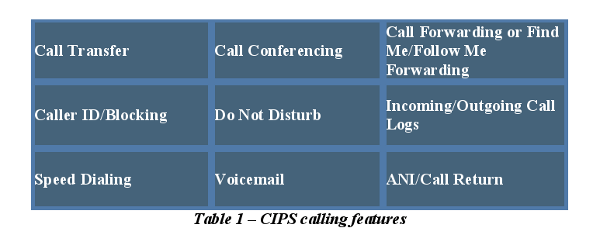
Additionally, the service is fully compliant with local number portability and emergency service requirements including 911 and E911, and offers directory assistance and operator services. Contractors also provide a routing prioritization scheme or class of service to prioritize applications that require real-time accessibility. CIPS is compatible with customer provided Active Directory services.
CIPS minimizes security issues and unauthorized access through constant updating of security practices and policies as well as regular Contractor conducted audits. General areas of security addressed include safeguards against denial of service, intrusion, invasion of privacy, as well as providing encryption at the Sensitive but Unclassified (SBU) level.
When ordering the CIPS service, an underlying transport service must be in place to support the service.
Each Networx Contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for CIPS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for CIPS.
For more information on the general CIPS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.7.11 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.7.11 for pricing.
3. Price Description
CIPS Price Basics
CIPS is a converged voice, data, and video communications service delivered over a common IP network connection. CIPS is provided over a common, contractor-provided, IP network. Access to these services can be through agency locations, or through gateways connected to the Internet or to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN). PSTN gateways provide access to/from off-net locations.
CIPS basic service includes domestic off-net termination and non-domestic off-net termination to any non-domestic country/jurisdiction where the contractor provides CIPs telephony service, up to 7,500 minutes per month per telephone number. Off-net termination usage in excess of 7,500 minutes per month per telephone number in countries where the contractor provides CIPs telephony service is charged at the off-net usage rate for VOIPTS off-net usage.
CIPS was not offered on the original FTS2001 contracts.
Price components required for full end-to-end service for Domestic and Non-Domestic CIPS:
- Underlying transport services, such as NBIP-VPNS, in conjunction with CIPS
- DAA Originating and Terminating Wireline Access (MRC) and (NRC)
- CIPS Basic Service MRC per port (by port type)
- CIPS Telephony Service NRC and MRC per telephone number for voice
- CIPS Usage charges for off-net usage per month per six-second increment when off-net minutes are in excess of 7,500 monthly minutes per telephone number (the first 7,500 minutes are included with the basic service)
- No features available currently
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement CIPS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
Example 1: CIPS
- Underlying Transport: Choose Networx telecommunications services such as NBIP-VPNS (e.g., NBIP-VPNS CLIN 213145 T1 MRC per port)
- Access NRC: Choose CLIN 760111 Routine DAA T1 NRC
- Access MRC: Choose CLIN 760311 Routine DAA T1 MRC
- CIPS Basic Service: Choose CLIN 813209 (T1 per port)
- CIPS Telephony Service NRC: Choose CLIN 812101 (Telephony Service NRC per telephone number)
- CIPS Telephony Service MRC: Choose CLIN 812201 (Telephony Service MRC per telephone number)
- CIPS Usage: Choose CLIN 813101 (Outbound to off-net Location per six-second increment [charged only when monthly off-net minutes exceed 7,500 per telephone number])
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs may differ between contractors.
This document only addresses the CIPS service provided at contract award. Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for CIPS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for CIPS.
For more information on the general CIPS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.7.11 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.7.11 for pricing.
Dark Fiber Service (DFS)
2. DFS Technical Description
DFS Technical Summary
A fiber cable typically contains many optical fibers, which are either "lit" to carry a signal or "unlit" to be used at a future date. A Dark Fiber is an optical fiber through which no light is transmitted. The simplest Dark Fiber Service is a point-to-point connection between two locations. More elaborate configurations (e.g. Diverse Ring, Star, etc.) enable Agencies to interconnect any number of selected locations. DFS is a new service that was not offered on FTS2001 contracts.
DFS is acquired as a facility which will allow the Agency the indefeasible right of use of the fiber route. The term fiber route could mean a fiber pair in a fiber-optic cable, or the entire fiber-optic cable.
DFS may be ordered for inter-city, intra-city interconnections in the CONUS and OCONUS with Non-Domestic locations being optionally offered. The Agencies have the option either to provide their own optoelectronics equipment or to obtain optoelectronics equipment from the contractor. DFS is delivered to the customer-specified Service Delivery Point (SDP). The Agency can order DFS that will connect to and interoperate with:
- Contractor's metro and long haul networks
- Internet
- Agency's network
- Other Agency networks in the same vicinity
The diagram below illustrates a CONUS wide contractor's DFS transport network delivering available optical paths to the Agency between two cities. Collocation capabilities are available from the contractor to host Agencies' optoelectronics if required. Collocation capabilities include the capability to add/drop traffic (gateways) and to regenerate and amplify traffic where needed.
3. DFS Technical Detail
The SDP for DFS is where the Agency has installed its optoelectronics. The Agency determines the specific location of the Service Delivery Point (SDP) for the contracted DFS route(s). The SDP can be either a fiber patch panel at a Government location or a collocation facility.
The contractor will provide optical fiber strands as specified by the Agency that complies with the optical performance characteristics (KPIs) as in Section C.2.5.3.1.4. of the Networx contracts. Fiber types include NZDS (Non-Zero Dispersion Shifted), LEAF, True-Wave, and SMF-28 for distances less than 60 km). The fiber installed will have to work with the specified amplifier types as required by the Agency (i.e., Erbium- doped Fiber Amplifiers (EDFA), Raman Amplifiers, EDFA/Raman hybrid Amplifiers, Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers (SOA)). The Agency also determines the number of fiber strands to be supported and the number of ducts required between the connecting locations.
The Agency can specify its expected growth to allow the contractor to plan infrastructure build-up based on such forecast. The Agency is also able to specify if gateways (add/drop points in the network) will be needed and their locations.
DFS features that may be ordered include:
- Collocation Services for hosting Agency optronics
- Diverse Routes Single and Multi Drops to prevent service interruptions
- Multiple Ducts for fiber installation
- Off-Net Laterals (fiber cables from the Agency's premises to the nearest splice point on the DFS cable trunk)
A complete description of DFS features can be found in Section C.2.5.3.2.1 (Dark Fiber Features) of the Networx contract.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for DFS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for DFS.
For more information on the general DFS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.5.3 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.5.3 for pricing.
4. DFS Price Description
DFS Price Basics
Dark Fiber is an optical fiber through which no light is transmitted and can be later "lit" and used to carry an optical signal. DFS capacity may be purchased in single fiber strand(s) or pair(s) within a fiber-optic cable. Charges for the actual fiber or to light the fiber are not included in DFS. DFS is a service that was not offered on the FTS2001 contracts.
The MRC for transport consists of a fixed component plus a distance-dependent (per mile) component. CONUS-to-CONUS distance is calculated using the distance formula:
- Distance (miles) = ROUNDUP(SQRT(((V1-V2)^2+(H1-H2)^2)/10),0) Where (V1, H1) and (V2, H2) are the V and H coordinates of the locations, respectively
Distance involving OCONUS or non-domestic locations is calculated using airline miles. Note: The Networx Pricer automatically calculates the distance when given the originating and terminating locations.
Price components required for full end-to-end service for Domestic and Non-Domestic DFS:
- DFS Transport monthly recurring charge with a fixed component and charge per mile for the Indefeasible Rights of Use (IRU) per pair of fibers or per fiber, for on-net connections or along routes where fiber is installed. The management, ongoing monitoring support, maintenance, and repair of DFS due to normal wear and tear and repairing of DFS in case of breaks are included in the MRC.
- DAA Originating and Terminating Wireline Access (MRC) and (NRC)
- The following features may be ordered as needed by the Agency:
- Collocation Service
- Duct
- Dark Fiber Local Loop
- Diverse Route Single Drop
- Diverse Route Dual Drop
- Inter-city Connectivity
- Multiple Duct
- Off-net Laterals
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement DFS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
Example: One DFS Fiber Pair
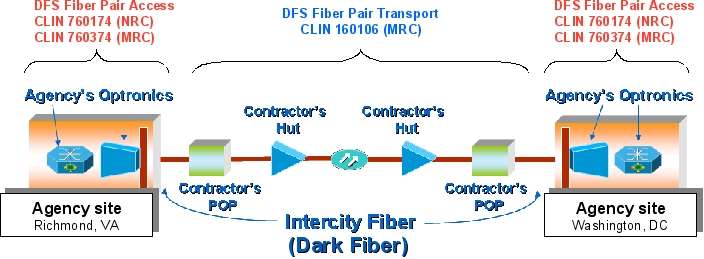
- DFS Transport: Choose CLIN 160106 (DFS - Fiber Pair - Less than 12 Fiber Pairs)
- Access NRC: Choose CLIN 760174 Routine DAA DFS Fiber Pair NRC (ICB) for both ends of the transport. Prices for this CLIN are not available in the unit pricer. Prices are available on an Individual Case Basis (ICB).
- Access MRC: Choose CLIN 760374 Routine DAA DFS Fiber Pair MRC (ICB) for both ends of the fiber. Prices for this CLIN are not available in the unit pricer. Prices are provided by the contractor after a street address has been provided and a case number has been assigned.
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs may differ between contractors.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for DFS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for DFS.
For more information on the general DFS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.5.3 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.5.3 for pricing.
Dedicated Access (DAA all services)
2. Technical Description
Access Arrangements (AA) Technical Summary
AAs provide the convention to specify the originating and/or terminating access component required to connect the Service Delivery Point (SDP) to the contractor's Point of Presence (POP) when that access component is required to deliver a telecommunications service. AAs are a component of an ordered telecommunications service to facilitate proper service delivery and cannot be ordered as a standalone access service. Since AAs are a component of an ordered telecommunications service which already contains service delivery metrics, there are no separate Performance metrics specified for AAs.
There are two types of AAs:
- Circuit-Switched Access Arrangements (CSAA), where the SDPs are located at the serving local Central Office (CO) for circuit-switched services (Voice Service (VS), Circuit Switched Data Service (CSDS), Toll-Free Service (TFS), and Combined Services (CS)) for sites with Presubscription to Interexchange Carriers (PICs).
- Dedicated Access Arrangements (DAA), where the SDPs are located at customer sites. DAA offers the following access types:
- Wireline Access Arrangement (WLNAA)
- Broadband Access Arrangement (BBAA)
- Wireless Access Arrangement (WLSAA)
- Satellite Access Arrangement (SatAA)
A user will be able to select, at a minimum, a DAA for a particular telecommunications service type (e.g., VS, Asynchronous Transfer Mode Service (ATMS), Layer 2 Virtual Private Network Services (L2VPNS)) for the above access arrangement types from the table below.
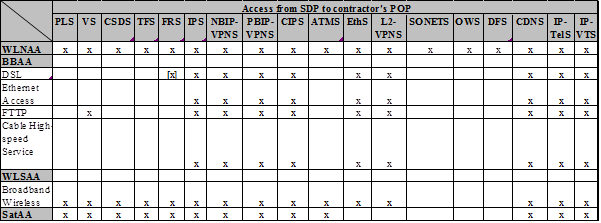
The diagram below shows various DAA configurations for connecting SDPs to POPs.
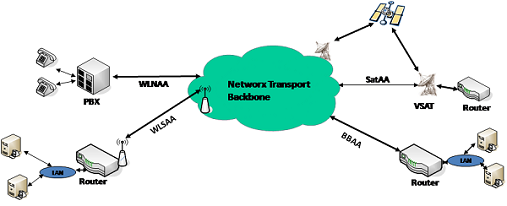
3. Technical Detail
Wireline Access Arrangement (WLNAA)
A Wireline Access Arrangement connects an Agency location with dedicated, reliable bandwidth to the contractor's network. The range of line speeds and reliability options provided within this access arrangement category allows Agency users to satisfy their diverse needs for accessing the contractor's networks. The WLNAA can be used for any application, such as voice, data, video, and multimedia.
WLNAA supports the full range of technical capabilities that are available in commercial offerings. Data rates supported by WLNAA include: Subrate-DS0 and DS0; Channelized or Unchannelized T1, Frac-T1, T3, Frac-T3, E1, and E3; SONET OC-1 and OC1 Virtual Tributary; Channelized or Concatenated SONET OC-3, OC-12, OC-48, and OC-192; and Analog circuits.
WLNAA provides transparency to any protocol used by Government Furnished Equipment (GFE) and to all bit sequences transmitted by GFP through the SDP. In addition, WLNAA supports integrated access of different services (e.g., VS, Internet Protocol Service (IPS), and CS).
The mandatory WLNAA features are detailed in Section C.2.16.2.1 of the Networx contract. The features are "Access Route or Path Diversity" and "Access Route or Path Avoidance."
Broadband Access Arrangement (BBAA)
Broadband Access Arrangement connects an Agency location with dedicated, reliable broadband bandwidth to the contractor's data network over communication facilities, such as Digital Subscriber Line (DSL), Ethernet Access, Cable High-Speed Service, and Fiber-To-The-Premises (FTTP) service. The range of broadband line speeds (e.g., 256 kbps up to 1Gbps) and reliability options provided within this access arrangement category allows Government users to satisfy their diverse needs for accessing the contractor's data networks. With this access arrangement, applications such as desktop video conferencing, distance learning, transferring of large files can be realized.
DSL supports Asymmetric DSL (ADSL), Symmetric DSL (SDSL), and Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) DSL (IDSL). ADSL supports 16 kbps to 768 kbps upstream and 1.5 Mbps to 9 Mbps downstream. SDSL supports up to 2.3 Mbps symmetric data rates upstream and downstream. IDSL supports 144 kbps symmetric data rates upstream and downstream.
Ethernet Access supports 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, 1 Gbps, and optional 10 Gbps Ethernet access.
Cable High-Speed Service (optional) supports data rates of 256 Kbps to 30 Mbps according to DOCSIS (Cable Labs) standards.
FTTP (optional) supports 5 Mbps (downstream) and 2 Mbps (upstream), 15 Mbps (downstream) and 2 Mbps (upstream), and 30 Mbps (downstream) and 5 Mbps (upstream). Please note that FTTP was on "optional to bid" service on the original Networx Request for Proposals (RFPs). At this time, there are no CLINs to provide this service.
There are no mandatory BBAA features.
Wireless Access Arrangement (WLSAA)
Wireless Access Arrangement connects Agency locations to the contractor's network through broadband wireless communication facilities/networks operating with licensed frequencies (e.g., Multichannel Multipoint Distribution Service (MMDS), Local Multipoint Distribution Service (LMDS), and Ultra High at 2 to 66 GHz and an optional upper limit of 90 GHz spectrum; and, National Guard Frequency at 1.755 to 1.850 GHz spectrum through a roof-top antenna). This access arrangement can be used for Networx services (e.g., VS, Network-based IP VPN Services (NBIP-VPNS), and Video Teleconferencing Services (VTS)).
WLSAA supports data rates of DS1, NxDS1 (where N=2 through 27), DS3, E1 for Non-domestic, NxE1 (where N=2 through 15) for Non-domestic, E3 for Non-domestic, and optional higher data rates (e.g., SONET).
There are no mandatory WLSAA features.
Satellite Access Arrangement (SatAA)
Satellite Access Arrangement connects Agency locations with dedicated and reliable satellite based transmission to the contractor's network. The connection from the satellite earth station to the SDP is also included in this access arrangement. This access arrangement could be used for voice, data, and video traffic. The access arrangement provides full-duplex and half-duplex transmissions using C-band, Ku-band, and Ka-band satellites.
SatAA supports the full range of technical capabilities that are available in commercial offerings. Data rates supported by SatAA include: Channelized or Unchannelized T1, Frac-T1, T3, Frac-T3, E1; and optional SONET data rates (e.g., SONET OC-3). SATAA provides transparency to any protocol used by GFP and to all bit sequences transmitted by GFP through the SDP.
In addition, SatAA supports full-duplex, half-duplex, and simplex (i.e., one way) for point-to-point transmission (i.e., SDP to POP) for voice, data, and video traffic and for simplex egress connection (i.e., POP to SDP).
There are no mandatory SatAA features.For more information on the general AA specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.16 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.3 for pricing.
4. Price Description
Access Arrangements (AA) Price Basics
The Networx contracts include the following access arrangements:
- 1. Wireline Access Arrangement: A Wireline Access Arrangement connects an Agency location with dedicated, reliable bandwidth to the contractor's network.
- 2. Broadband Access Arrangement: Broadband Access Arrangement connects an Agency location with dedicated, reliable broadband bandwidth to the contractor's data network over communication facilities, such as:
- Digital Subscriber Line (DSL).
- Ethernet Access (BBEthAA).
- Cable High-Speed Service.
- Fiber-To-The-Premises (FTTP). Please note that FTTP was on "optional to bid" service on the original Networx Request for Proposals (RFPs). At this time, there are no CLINs to provide this service.
- 3. Wireless Access Arrangement: Wireless Access Arrangement connects Agency locations to the contractor's network through broadband wireless communication facilities/networks.
- 4. Satellite Access Arrangement: Satellite Access Arrangement connects Agency locations with dedicated and reliable satellite based transmission to the contractor's network.
Dedicated Access Arrangements can only be used in conjunction with other services provided under the Networx contracts. In order to price a circuit both a physical address and speed are required. Prices for Critical Service Level are Individual Case Basis (ICB). SEDs are not part of the dedicated access arrangements, but SEDs are often used to meet the service requirements at the Service Delivery Point (SDP) when implemented between a dedicated access arrangement and the SDP(s).
Wireline Access Arrangement (WLNAA)
For pricing purposes, the physical address of the SDP location determines the wire center used for the provision of WLNAA. All optical WLNAA CLINs (OC-3 speed and above) are ICB.
Price components required for Domestic WLNAA:
- Non-recurring charge (NRC) per circuit by Domestic Region ID.
- Monthly recurring charge (MRC) per circuit:
- By Serving Wire Center (SWC) or,
- In selected cases, at the contractor's option, by Network Site Code (NSC). The WLNAA price determined by the NSC is less than or the same as the WLNAA price determined by the SWC.
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- *Access Route or Path Diversity.
- *Access Route or Path Avoidance.
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement WLNAA. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
* Some or all price components are priced on an Individual Case Basis (ICB). CLINs with ICB prices are not available in the Networx Unit Pricer.
Example 1: WLNAA T3 circuit at 10304 Eaton Place, Fairfax, VA 22030:
- NRC:
- Choose CLIN 760117 (DAA T3 (43.008 Mb/s) NRC).
- Choose CONUS Domestic Region.
- MRC:
- Choose CLIN 760317 (DAA T3 (43.008 Mb/s) MRC).
- Enter Address, NSC, or SWC.
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs differ between vendors.
Price components required for Non-Domestic WLNAA:
- Non-recurring charge (NRC) per circuit by NSC (physical address and speed required).
- Monthly recurring charge (MRC) per circuit by NSC (physical address and speed required).
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- *Access Route or Path Diversity.
- *Access Route or Path Avoidance.
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement WLNAA. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
-
* Some or all price components are priced on an Individual Case Basis (ICB). CLINs with ICB prices are not available in the Networx Unit Pricer.
Broadband Access Arrangement (BBAA)
BBAA provides permanent broadband connection (always on) from SDP to Networx-POP or Internet for data services (e.g., EthS, NBIP-VPNS). Broadband Access Arrangements include:
- Broadband DSL:
- Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL).
- Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line (SDSL).
- ISDN Digital Subscriber Line (IDSL).
- Ethernet.
- Cable High Speed.
Broadband DSL Access
For pricing purposes, the physical address of the SDP location determines the wire center used for the provision of Broadband DSL Access. Broadband DSL Access includes:
- Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL).
- Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line (SDSL).
- ISDN Digital Subscriber Line (IDSL).
- Non-recurring charge (NRC) per line by Domestic Region ID.
- Monthly recurring charge (MRC) per line:
- By Serving Wire Center (SWC) or,
- In selected cases, at the contractor's option, by Network Site Code (NSC). The Broadband DSL Access price determined by the NSC is less than or the same as the Broadband DSL Access price determined by the SWC.
- No features available currently.
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement Broadband DSL Access. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
- NRC:
- Choose CLIN 760130 (ADSL (1.536 Mbps / 384 kbps) NRC per line).
- Choose CONUS Domestic Region.
- MRC:
- Choose CLIN 760330 (ADSL (1.536 Mbps / 384 kbps) MRC per line).
- Enter Address, NSC, or SWC.
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs differ between vendors.
- Non-recurring charge (NRC) per line by NSC.
- Monthly recurring charge (MRC) per line by NSC.
- No features available currently.
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement Broadband DSL Access. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
Price components required for Domestic Broadband DSL Access:
Example 1: Domestic Broadband DSL ADSL (1.536 Mbps / 384 kbps) at 10304 Eaton Place, Fairfax, VA 22030:
Price components required for Non-Domestic Broadband DSL Access:
Broadband Ethernet Access (BBEthAA)
Prices for Domestic Broadband Ethernet Access are based on distance from the SWC serving the SDP to the designated connecting POP. BBEthAA is the only access arrangement that includes distance-sensitive pricing. This is sometimes referred to as legacy pricing and is the original BBEthAA contract pricing. Non-domestic BBEthAA prices are ICB.
At the option of the Contractor, prices may also be based on the location of the SDP as identified by NSC in addition to the distance based prices. BBEthAA prices based on NSCs, where available, apply in place of the distance based prices. This is referred to as SWC or NSC based pricing and was added to the Networx contract post-award. NSC prices are less than or the same as the distance based prices.
Price components required for Domestic BBEthAA:
- Non-recurring charge (NRC) per access line or circuit by Domestic Region ID.
- Monthly recurring charge (MRC):
- Legacy Pricing: Distance-based per access line + per mile per access line or,
- SWC or NSC Based Pricing: In selected cases, at the contractor's option, by Network Site Code (NSC). The BBEthAA price determined by the NSC is less than or the same as the BBEthAA distance based price.
- No features available currently.
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement BBEthAA. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
Example 1: BBEthAA SWC or NSC Based Pricing for 10Mbps at 10304 Eaton Place, Fairfax, VA 22030:
- NRC: Choose CLIN 760146 (Ethernet Access - 10 Mbps NRC per circuit). Choose CONUS Domestic Region.
- MRC: Choose CLIN 760346 (Ethernet Access - 10 Mbps MRC per circuit). Enter Address, NSC, or SWC.
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs differ between vendors.
Price components required for Non-Domestic BBEthAA:
- *Non-recurring charge (NRC) per access line by Country/Jurisdiction ID.
- *Monthly recurring charge (MRC) per access line by Country/Jurisdiction ID.
- No features available currently.
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement BBEthAA. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
* Some or all price components are priced on an Individual Case Basis (ICB). CLINs with ICB prices are not available in the Networx Unit Pricer.
Broadband Cable High Speed Access
Non-domestic Broadband Cable High Speed Access fixed prices are ICB.
Price components required for Domestic and Non-Domestic Broadband Cable High Speed Access:
- Non-recurring charge (NRC) per connection to cable network by Country/Jurisdiction ID.
- Monthly recurring charge (MRC) per connection to cable network by Country/Jurisdiction ID.
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- Specific to Cable TV Service.
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement Broadband Cable High Speed Access. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
Example 1:
Domestic Cable High Speed Access CONUS Cable Modem (1.536 Mbps/384 kbps):- NRC:
- Choose CLIN 760552 (Cable Modem (1.536 Mbps/384 kbps) NRC per connection to cable network).
- Choose CONUS Country/Jurisdiction.
- MRC:
- Choose CLIN 760752 (Cable Modem (1.536 Mbps/384 kbps) MRC per connection to cable network).
- Choose CONUS Country/Jurisdiction.
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs differ between vendors.
Wireless Access Arrangement (WLSAA)
WLSAA is priced per link. A link is defined as a line of sight connection, or one hop, using licensed frequencies. Prices for domestic Wireless Access do not vary by location within each domestic region. Non-domestic Broadband Wireless Access fixed prices are ICB.
Price components required for Domestic WLSAA:
- *Non-recurring charge (NRC) per link by Domestic Region ID priced ICB.
- Monthly recurring charge (MRC) per link by Domestic Region ID.
- No features available currently.
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement WLSAA. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
* Some or all price components are priced on an Individual Case Basis (ICB). CLINs with ICB prices are not available in the Networx Unit Pricer.
Example 1: WLSAA CONUS Routine Broadband Wireless DS3:
- NRC: Choose CLIN 760599 (Broadband Wireless - DS3 NRC per link). Prices for this CLIN are ICB and are not available in the Networx Unit Pricer.
- MRC: Choose CLIN 760799 (Broadband Wireless - DS3 MRC per link).
- Choose CONUS Domestic Region.
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs differ between vendors.
Price components required for Non-Domestic WLSAA:
- *Non-recurring charge (NRC) per link by Country/Jurisdiction ID priced ICB.
- *Monthly recurring charge (MRC) per link by Country/Jurisdiction ID priced ICB.
- No features available currently.
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement WLSAA. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
* Some or all price components are priced on an Individual Case Basis (ICB). CLINs with ICB prices are not available in the Networx Unit Pricer.
Satellite Access Arrangement (SatAA)
SatAA is priced per circuit and provides full-duplex and half-duplex transmissions using C-band, Ku-band, and Ka-band satellites. Non-domestic SatAA prices are ICB.
Price components required for Domestic SatAA:
- Non-recurring charge (NRC) per circuit by Domestic Region ID.
- Monthly recurring charge (MRC) per circuit by Domestic Region ID.
- No features available currently.
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement SatAA. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
- NRC:
- Choose CLIN 762015 (C-Band Channelized T3 NRC per circuit).
- Choose CONUS Domestic Region.
- MRC:
- Choose CLIN 762115 (C-Band Channelized T3 MRC per circuit).
- Choose CONUS Domestic Region.
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs differ between vendors.
- *Non-recurring charge (NRC) by Country/Jurisdiction ID priced ICB.
- *Monthly recurring charge (MRC) by Country/Jurisdiction ID priced ICB.
- No features available currently.
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement SatAA. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
* Some or all price components are priced on an Individual Case Basis (ICB). CLINs with ICB prices are not available in the Networx Unit Pricer.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for AA. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for AA.
For more information on the general AA specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.16 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.3 for pricing.
Dedicated Hosting Service (DHS)
1. Technical Description
Dedicated Hosting Services (DHS) Technical Summary
GSA provides Networx Dedicated Hosting Services (DHS) to allow an Agency to focus on its mission rather than managing its own Web-related infrastructure. DHS is fully managed by the Networx contractor. Facilities and equipment comprising the Web hosting environment are operated and administered by the Networx contractor.
Web hosting refers to the process of publishing a Web site and making it available for Worldwide Web access. This is accomplished by the Networx contractor. DHS includes the provision of high-speed Internet connectivity with Internet Data Centers (IDCs) that are administered and operated by the contractor. DHS allows Agencies to procure hardware and software platforms, monitoring and management, platform security, and other capabilities to meet the Agency's hosting needs.
In the example configuration shown below, Agencies hire a Networx contractor to store its content (Web pages) on a dedicated server located in the contractor's IDC. A dedicated server is leased strictly to a single Agency. In addition, other infrastructure, including Internet connectivity, is also dedicated or leased for the exclusive use of the Agency. As shown below, the IDC may independently provide hosting services to multiple Agencies.
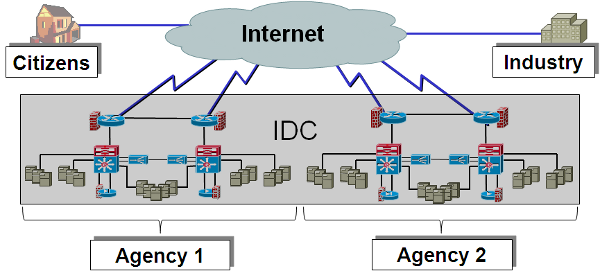
Example DHS Configuration
2. Technical Detail
DHS arranges for an Agency to hire a contractor for its Web site operations. This includes providing server configurations to include processor and storage capacity, software, and data center and network connectivity to meet the Agency's needs.
Technical Capabilities
DHS technical capabilities are described in detail in Section C.2.4.2.1.4 of the Networx contracts and are summarized below:
- Servers - hardware and software platforms including Linux/Apache, Microsoft Windows, and UNIX/Apache Web servers.
- Standard Operating Environment - including system availability monitoring and management and Web monitoring and management.
- Software Platform Security - including firewalls, security patch updates, vulnerability scanning, etc.
- Building and Facility Security - 24X7 security measures including guards, closed-circuit monitors, etc.
- Network Connectivity and Bandwidth - Internet bandwidth as needed by the Agency.
- Power Systems - including redundant and high-availability systems.
- Fire Detection and Suppression - including VESDA (Very Early Smoke Detection Apparatus).
- Cooling Systems - redundant IDC cooling systems.
Features
DHS features are described in detail in Section C.2.4.2.2.1 of the Networx contracts and are summarized below:
- Load Balancing - applicable with multiple servers according to Agency load balancing criteria.
- Restoration - restoration of Agency Web site data using the most recent back-up on request.
- Web Server Traffic Analyses - including but not limited to User Profile by region, most downloaded files, etc.
- Application Hosting* - applications that can be hosted by the Networx contractor instead of on-Agency premises.
* The optional Application Hosting feature may not be provided by all Networx contractors.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for DHS. The specific details can be found within each contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for DHS.
For more information on the general DHS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.4.2 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.4.2 for pricing.
3. Price Description
DHS Price Basics
DHS entails the leasing of dedicated Web and applications servers in a Networx contractor' Internet Data Center (IDC). Two (2) web server types are offered:
- Single Web Server.
- Web Server Cluster.
An MRC charge is based on the following software platforms of the managed server required by the Agency.
- UNIX operating system.
- LINUX operating system.
- Microsoft operating system.
This charge includes any charges for standard operating environment monitoring and management, building and facilities security, software platform security, shared 10 Mbps of Ethernet bandwidth for Internet connectivity, daily incremental and weekly full backup, power systems, fire and suppression, and cooling systems as described in Section C.2.4.2.1.4.
A separate MRC may apply for dedicated burstable Ethernet bandwidth between 10 Mbps and 1 Gbps for connectivity to the Internet. The monthly Internet usage is determined by the 95th percentile method. The usage is measured daily every five minutes. The top 5% of monthly usage is discarded and the usage representing the 95th percentile is designated as the Internet usage amount for the month.
A separate MRC may apply for additional storage capacity and a separate NRC may apply for installation and/or service initiation. The monthly Internet usage charge is based on the following usage bands:
- 1 Mbps - 10 Mbps (minimum usage charge of 1 Mbps, then charged in 1 Mbps increments up to, but not including 10 Mbps).
- 10 Mbps - 100 Mbps (minimum usage charge of 10 Mbps, then charged in 10 Mbps increments up to, but not including 100 Mbps).
- 100 Mbps - 1 Gbps (minimum usage charge of 100 Mbps, then charged in 100 Mbps increments up to and including 1 Gbps).
DHS is similar to the FTS2001 Web Hosting Service.
Price components required for Single Web Server DHS:
- Initial Storage Capacity (NRC and/or MRC per server).
- Additional Storage Capacity (NRC per server).
- Initial Dedicated Burstable Internet Bandwidth (NRC and/or MRC per unit bandwidth).
- Additional Bandwidth above Initial Dedicated Internet Bandwidth (usage per unit bandwidth).
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- Load Balancing (intra-Internet Data Center solution).
- Restoration.
- Web Server Traffic Analyses.
- Application Hosting*
- There are no SEDs for DHS. Applicable equipment costs are included in CLIN prices. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
* Some or all price components are priced on an Individual Case Basis (ICB). CLINs with ICB prices are not available in the unit pricer.
Example 1: Managed LINUX/Apache Single Web Server with Burstable Internet Bandwidth between 10 Mbps and 100 Mbps:
- Initial Storage Capacity NRC: Choose CLIN 84013 (Managed LINUX/Apache Single Web server NRC per 100 GB storage capacity server).
- Initial Storage Capacity MRC: Choose CLIN 84001 (Managed LINUX/Apache Single Web server MRC per 100 GB storage capacity server).
- Additional Storage Capacity: Choose CLIN 84015 (Managed LINUX/Apache Web server - additional storage NRC per additional 10 GB storage capacity per server).
- Initial Dedicated Burstable Internet Bandwidth NRC: Choose CLIN 84022 (Dedicated burstable Internet bandwidth - maximum 100 Mbps NRC per initial 10 Mbps Ethernet bandwidth).
- Initial Dedicated Burstable Internet Bandwidth MRC: Choose CLIN 84010 (Dedicated burstable Internet bandwidth - maximum 100 Mbps MRC per initial 10 Mbps Ethernet bandwidth).
- Additional Bandwidth above Initial Dedicated Internet Bandwidth: Choose CLIN 84024 (Dedicated burstable Internet bandwidth above 10 Mbps up to and including 100 Mbps Usage per additional 10 Mbps Ethernet bandwidth per month (Nx10 Mbps)).
4. Price Additional Detail
Price components required for Web Server Cluster DHS:
- Initial Storage Capacity (NRC and/or MRC per server).
- Additional Server with Initial Storage Capacity (NRC and/or MRC per server).
- Additional Storage Capacity (NRC per server).
- Initial Dedicated Burstable Internet Bandwidth (NRC and/or MRC per unit bandwidth).
- Additional Bandwidth above Initial Dedicated Internet Bandwidth (usage per unit bandwidth).
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- Load Balancing (intra-Internet Data Center solution).
- Restoration.
- Web Server Traffic Analyses.
- There are no SEDs for DHS. Applicable equipment costs are included in CLIN prices. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
Example 2: Managed LINUX/Apache Web Server Cluster with Burstable Internet Bandwidth between 10 Mbps and 100 Mbps:
- Initial Storage Capacity NRC: Choose CLIN 84013 (Managed LINUX/Apache Single Web server NRC per 100 GB storage capacity server).
- Initial Storage Capacity MRC: Choose CLIN 84001 (Managed LINUX/Apache Single Web server MRC per 100 GB storage capacity server).
- Additional Server with Initial Storage Capacity NRC: Choose CLIN 84014 (Managed LINUX/Apache Web Server Cluster NRC per additional server with 100 GB storage capacity).
- Additional Server with Initial Storage Capacity MRC: Choose CLIN 84002 (Managed LINUX/Apache Web Server Cluster MRC per additional server with 100 GB storage capacity).
- Additional Storage Capacity: Choose CLIN 84015 (Managed LINUX/Apache Web server - additional storage NRC per additional 10 GB storage capacity per server).
- Initial Dedicated Burstable Internet Bandwidth NRC: Choose CLIN 84022 (Dedicated burstable Internet bandwidth - maximum 100 Mbps NRC per initial 10 Mbps Ethernet bandwidth).
- Initial Dedicated Burstable Internet Bandwidth MRC: Choose CLIN 84010 (Dedicated burstable Internet bandwidth - maximum 100 Mbps MRC per initial 10 Mbps Ethernet bandwidth).
- Additional Bandwidth above Initial Dedicated Internet Bandwidth: Choose CLIN 84024 (Dedicated burstable Internet bandwidth above 10 Mbps up to and including 100 Mbps Usage per additional 10 Mbps Ethernet bandwidth per month (Nx10 Mbps)).
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for DHS. The specific details can be found within each contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for DHS.
For more information on the general DHS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.4.2 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.4.2 for pricing.
Ethernet Service (EthS)
2. Technical Description
EthS Technical Summary
EthS allow Agencies to interconnect their Local Area Networks (LANs) seamlessly over Metro Area Networks (MANs) or Wide Area Networks (WANs) regardless of the geographical location of their sites. Ethernet provides Intra and Extranet services as well as Intra and Inter-Agency communications. EthS is offered over point-to-point connections as well as multi-point to multi-point connections. Ethernet Private Line (E-LINE) service provides reserved bandwidth for point -to-point mission critical traffic and Ethernet Private LAN (E-LAN) service provides multi-point to multi-point interconnections of disparate LAN segments into a single virtual LAN.
EthS exploits Ethernet's flexibility, cost effectiveness, and capabilities while providing end-to-end transport to data traffic. EthS provides scalability to agencies to meet growth demand as Agencies can throttle bandwidth by using the Bandwidth on Demand feature while paying only for the bandwidth being used.
EthS may be ordered as a domestic (CONUS and OCONUS) or non-domestic service. The geographical scope for the local, national and international coverage will vary with the contractor's network.
A wide variety of User-to-Network Interfaces (UNIs) with different Signaling Interface Types, Protocols, and Data Bandwidths are available to provide Intra and Inter internet connectivity for Agency LANs. These UNIs are described in Section C.2.7.1.3 of the Networx Contracts. The diagram below shows a typical EthS configuration.
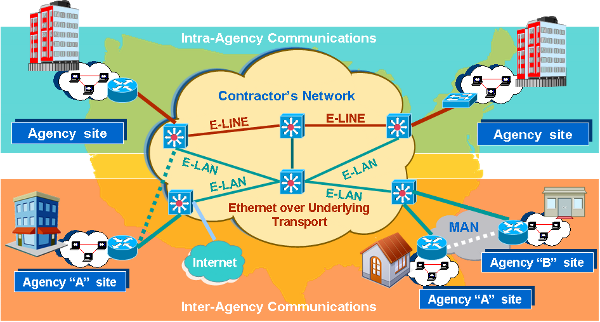
EthS Configuration
3. Technical Detail
EthS was not offered on the original FTS2001 contracts but its capabilities for originating and terminating domestic wireline access were available in FTS2001. EthS provides a wide range of mandatory and optional Technical Capabilities and Service Functionalities which are described in detail in Section C.2.7.1.1.4 of the Networx Contracts. The following is a brief summary of these capabilities.
Technical Capabilities
- Delivery of the EthS at the Agency's Service Delivery Point (SDP) via a UNI to support Layer 2 and Layer 3 clients with Layer 3 protocol packets such as IPv4, IPv6.
- Point-to-point, multi-point-to-multi-point, and point-to-multi-point Ethernet Virtual Connections (EVCs). EVC defines the association of two or more UNIs.
- EVC multiplexing to build more sophisticated services while minimizing the required hardware UNIs.
- Ingress/Egress bandwidth profiles for the UNIs and EVCs at the SDPs and virtual LANS (VLANs).
- Support for Privacy and security similar to a Frame Relay (FR) or Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) Permanent Virtual Circuit (PVC).
- Optional support of circuit emulation services for FR, ATM and Time Division Multiplexed (TDM) services.
Service Functionalities
- Service attributes covering support for: UNIs, various Traffic Profiles, conformance to Performance Parameters, various Service Frame Delivery options, VLAN tag support, bundling VLAN IDs to be mapped into a single EVC at a UNI, and Security Filters as options.
- Proactive Performance Monitoring.
- Maintenance Functions.
- Delivery over Copper, Fiber, Passive Optical Networks (E-PON), and Coaxial Cable.
- Wide range of Access methods and Network Topologies as required by the Agencies.
- Geographical Diverse Routes for providing added reliability.
- Bridging Compliance with IEEE 802.1X.
- Transport Methods and Protocols to provide Ethernet over specified transport networks.
Features
EthS provides service features listed below and described in the Networx Contracts Section C.2.7.1.2.1 Ethernet Services Features.
- Bandwidth-on-Demand (BoD) - supports bandwidth increments and decrements on demand.
- Reserved Protection Bandwidth - allows reservation of bandwidth with desired constraints.
- Shared Protection Bandwidth - specifying the amount of bandwidth required for protection with no constraints on how the protection channels shall be routed.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for EthS. The specific details can be found within each Contractors Networx contract files and pricing notes for EthS.
For more information on the general EthS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.7.1 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.7.1 for pricing.
4. Price Description
EthS Price Basics
EthS provides a service that allows Agencies to connect their Local Area Networks (LANs) at sites in different locations into a single virtual network. EthS supports Ethernet Private Line (E-LINE) to provide reserved bandwidth for point-to-point mission critical traffic, and Ethernet Private LAN (E-LAN) to provide multi-point to multi-point interconnections of disparate LAN segments into a single virtual LAN.
EthS was not offered on the original FTS2001 contracts but its capabilities for originating and terminating domestic wireline access were available in FTS2001.
Price components required for full end-to-end service for Domestic EthS:
- EthS Transport monthly recurring charge per port
- DAA Originating and Terminating Access (MRC) and (NRC). Wireline or Broadband Access may be used for EthS.
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- Bandwidth-on-Demand (BoD)
- Reserved Protection Bandwidth*
- Shared Protection Bandwidth
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement EthS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
* Some or all price components are priced on an Individual Case Basis (ICB). CLINs with ICB prices are not available in the unit pricer.
Example 1: EthS E-Line 10 Mbps
- EthS Transport: Choose CLIN 193001 (E-Line CONUS - 10 Mbps MRC per port)
- Access NRC: Choose CLIN 760116* Routine DAA DS1x7 NRC
- Access MRC: Choose CLIN 760316* Routine DAA DS1x7 MRC
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs may differ between contractors.
* CLINs are for illustrative purposes only. Other speeds and types of access may be chosen according to Agency requirements.
Example 2: EthS E-LAN 10 Mbps
- EthS Transport: Choose CLIN 193081 (E-LAN CONUS - 10 Mbps MRC per port)
- Access NRC: Choose CLIN 760116* Routine DAA DS1x7 NRC
- Access MRC: Choose CLIN 760316* Routine DAA DS1x7 MRC
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs may differ between contractors.
* CLINs are for illustrative purposes only. Other speeds and types of access may be chosen according to Agency requirements.
EthS Price Additional Detail
Domestic to Non-Domestic service: Fixed prices are provided for the domestic half channel elements, domestic port(s), and non-domestic port(s) in other countries where offered. Charges for the half-channel in the non-domestic country are a pass-through of actual cost from the foreign carrier with no additional markup.
Price components required for full end-to-end service for Domestic to Non-Domestic EthS:
- EthS Transport monthly recurring charge per half channel for the Domestic location
- EthS Transport monthly recurring charge per port for the Non-Domestic location
- EthS Transport half channel (charges are pass-through of actual cost)
- DAA Originating and Terminating Access (MRC) and (NRC). Wireline or Broadband Access may be used for EthS.
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency*
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement EthS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
* Some or all price components are priced on an Individual Case Basis (ICB). CLINs with ICB prices are not available in the unit pricer.
Example 3: EthS E-Line 40 Mbps Domestic to Non-Domestic
- EthS Transport (Domestic Half-Channel): Choose CLIN 193164 (E-Line Domestic Half Channel - 40 Mbps MRC per half channel)
- EthS Transport (Non-Domestic Port): Choose CLIN 193244 (E-Line - Non-domestic - 40 Mbps per port)
- EthS Transport (Non-Domestic Half Channel): No CLIN (Charges are a pass-through of actual cost from the foreign carrier with no additional markup)
- Domestic Access NRC: Choose CLIN 760117* Routine DAA T3 NRC
- Domestic Access MRC: Choose CLIN 760317* Routine DAA T3 MRC
- Non-Domestic Access NRC: Choose CLIN 760128* Routine DAA E3 NRC
- Non-Domestic Access MRC: Choose CLIN 760328* Routine DAA E3 MRC
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs may differ between contractors.
* CLINs are for illustrative purposes only. Other speeds and types of access may be chosen according to Agency requirements.
Non-Domestic to Non-Domestic service: Prices are provided between two SDPs on a pass-through of actual cost from the foreign carrier with no additional markup.
Price components required for full end-to-end service for Non-Domestic to Non-Domestic EthS:
- EthS Transport half-channel (charges are pass-through of actual cost)
- DAA Originating and Terminating Access (MRC) and (NRC). Wireline or Broadband Access may be used for EthS.
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency*
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement EthS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
* Some or all price components are priced on an Individual Case Basis (ICB). CLINs with ICB prices are not available in the unit pricer.
Example 4: EthS E-Line 40 Mbps Non-Domestic to Non-Domestic
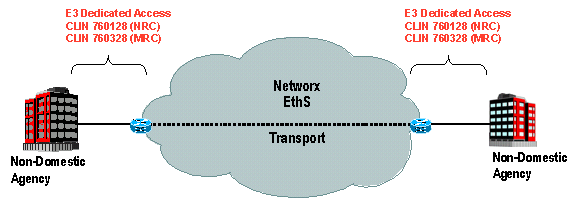
- EthS Transport (Non-Domestic Half Channel): No CLIN (Charges are a pass-through of actual cost from the foreign carrier with no additional markup)
- Access NRC: Choose CLIN 760128* Routine DAA E3 NRC
- Access MRC: Choose CLIN 760328* Routine DAA E3 MRC
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs may differ between contractors.
* CLINs are for illustrative purposes only. Other speeds and types of access may be chosen according to Agency requirements.
This document only addresses the EthS service at contract award. Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for EthS. The specific details can be found within each Contractors Networx contract files and pricing notes for EthS.
For more information on the general EthS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.7.1 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.7.1 for pricing.
Frame Relay Service (FRS)
2. Technical Description
FRS Technical Summary
Frame Relay Service (FRS) provides reliable, connection-oriented data transmission between user locations at service levels that are determined by the customer. Networx FRS provides service continuity to FTS2001 contracts, covering CONUS, OCONUS, and some Non-Domestic locations. The service's flexibility and built-in secure reliability make it an attractive alternative to private line networks.
The example shown below illustrates some of the key technical requirements provided by FRS. Agencies with both Routine and Critical Service Level Agreements (SLAs) are connected to the contractor's backbone network through contractor-provided access services that include dial-up Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN), Digital Subscriber Line (DSL), Ethernet, high speed cable, Asynchronous Transfer Mode Service (ATMS), Private Line Service (PLS), other Agency FRS, and dial-backup. FRS will connect customer locations via customer's routers, layer 2/3 switches, multiplexing/switching devices, computers, and other Frame Relay Access Devices (FRADs).
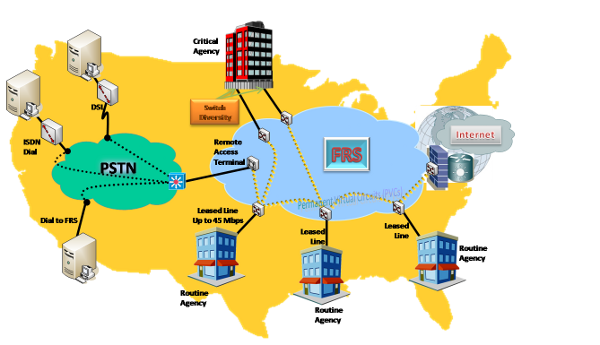
Example FRS Implementation
3. Technical Detail
The Networx FRS solution provides connection-oriented, data transmission at data rates up to DS3. An Agency purchases bandwidth by specifying the Committed Information Rate (CIR), which is the Agency's guaranteed minimum transmission rate for a Permanent Virtual Circuit (PVC). FRS enables bursting above the CIR up to the capacity of the access circuits. In addition, FRS provides E-1 and E-3 port speeds for terminations outside the United States.
FRS supports the following technical capabilities as described in Section C.2.3.1.1.4 of the Networx contracts:- Provisioning as single or multiple point-to-point virtual connection.
- Variable frame sizes up to 4096 bytes.
- CIR options in 64 Kbps from 0-DS3.
FRS allows Agencies to interconnect sites served by ATMS, FRS, PLS, and Ethernet services. The Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) backbone creates virtual circuits between MPLS-enabled endpoints on the network and Agencies will receive customized FRS solutions that meet the Agency's specific requirements.
FRS features are available that include:
- Three Class of Service (CoS) levels:
- Variable Frame Rate/real time (VFRrt) - highest queuing, lowest latency.
- Variable Frame Rate/non-real time (VFRnrt) - standard delivery, minimal loss and delay.
- Unspecified Frame Rate (UFR) - basic service, lowest queuing.
- Disaster Recovery PVCs.
- IP-enabled Frame Relay.
- Port Diversity.
- Interworking Services to transparently access Agency locations that use contractor's ATMS, or contractor's IP networks.
These features are described in more detail in Section C.2.3.1.2.1 of the Networx contracts.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for FRS. The specific details can be found within each contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for FRS.
For more information on the general FRS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.3.1 of the Networx contracts for technical specifications and Section B.2.3.1 for pricing.
4. Price Description
FRS Price Basics
FRS provides connection-oriented data transmission, between user locations, at contracted service levels up to DS3. Permanent Virtual Circuits (PVCs) are distinguished by simplex versus duplex and by frame rate type:
- Variable Frame Rate/real time (VFRrt): A class of FR service, this is a premium service that offers the highest queuing, the most liberal discard and the highest bumping priorities with the lowest latency network paths.
- Variable Frame Rate/non-real time (VFRnrt): A class of FR service, this is a standard service that offers network delivery of services by minimizing traffic loss and delay.
- Unspecified Frame Rate (UFR): A class of FR service, this is a basic service that has the lowest priority and is used for primarily email, file transfers, and Internet access.
FRS is similar to the FR Service offered on FTS2001 contracts.
Price components required for full end-to-end service for CONUS, OCONUS, and Non-Domestic FRS:
- FRS Port monthly recurring charge per port
- FRS PVC monthly recurring charge per PVC
- DAA Originating and Terminating Wireline Access (MRC) and (NRC)
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- Class of Service (CoS)
- *Disaster Recovery PVCs
- Frame Relay-to-Internet Gateway
- Interworking services
- IP-enabled FR
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement FRS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
* Some or all price components are priced on an Individual Case Basis (ICB). CLINs with ICB prices are not available in the unit pricer.
Example 1: FRS CONUS T1
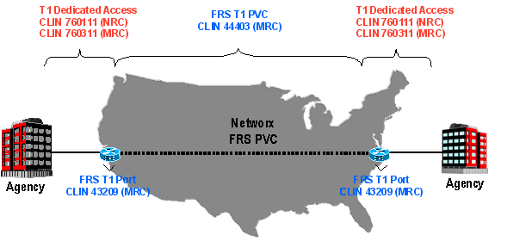
Example 1: FRS CONUS T1
- FRS Port: Choose CLIN 43209 (Routine Port T1 MRC)
- FRS PVC: For a T1 (1.536 Mbps) PVC, choose a quantity 24 of CLIN 44403 (PVC VFRnrt Duplex Routine NxDS0 MRC)
- Access NRC: Choose CLIN 760111 Routine DAA T1 NRC for each T1 port
- Access MRC: Choose CLIN 760311 Routine DAA T1 MRC for each T1 port
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs may differ between contractors.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for FRS. The specific details can be found within each of the Networx contract files and pricing notes for FRS.
For more information on the general FRS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.3.1 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.3.1 for pricing.
Incident Response Service (INRS)
1. Overview
The Networx contracts require a basic level of security management for its contractors that ensures compliance with Federal Government generally accepted security principles and practices, or better. The contracts employ adequate and reasonable means to ensure and protect the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of Networx services, Operational Support Systems (OSS), and Government information transported or stored in the contractor's Networx services infrastructure. These requirements are detailed in Section C.3.3.2 Security Management of the Networx contracts.
In addition to this mandatory level of security, the Networx contracts provide additional security services that may be ordered on a fee-for-service basis. These are:
- Managed Tiered Security Services (MTSS)
- Managed Firewall Service (MFS)
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Service (IDPS)
- Vulnerability Scanning Service (VSS)
- Anti-Virus Management Service (AVMS)
- Incident Response Service (INRS)
- Managed E-Authentication Service (MEAS)
- Secure Managed E-Mail Service (SMEMS)
The Incident Response Service (INRS) offering is described below.
2. Technical Description
Technical Summary
INRS is one of the security services that allow Agencies to combat cyber attacks and crime. The service helps Agencies respond to potential malicious attacks that can lead to service disruptions. INRS enables Agencies to complement in-house security expertise, or obtain outside assistance with a greater depth and breadth of experience. The service provides proactive services that are designed to prevent incidents, and reactive services that provide support for responding to malicious events. In addition, INRS provides forensics services that can assist in apprehending and prosecuting offenders. The diagram below highlights the functionalities and capabilities of INRS.
INRS Functionality
3. Technical Detail
INRS does not currently offer any features. The service does provide Agencies with secure Web access to contractor incident analyses and recommendations. INRS was not offered as a service on the FTS2001 contracts.
INRS is comprised of both proactive and reactive activities. Proactive services are designed to prevent incidents. They include onsite consulting, strategic planning, security audits, policy reviews, vulnerability assessments, security advisories, and training. Reactive services involve telephone and on-site support for responding to malicious events such as Denial of Services (DoS) attacks; virus, worm, and trojan horse infections; illegal inside activities, espionage, and compromise of sensitive internal Agency databases. INRS provides an effective method of addressing these security intrusions, thereby ensuring operational continuity in case of attacks.
Under INRS, the contractor reviews the Agency's security infrastructure and develops the appropriate strategic plans in collaboration with the customer. These plans detail the incident response process, identify internal resources, assign duties to team members, describe policies, define severity levels, list escalation chains, and specify emergency/recovery procedures.
The contractor also provides the Agency with effective incident response support around the clock. The contractor provides incident analysis and assessment in order to determine the scope and impact of incidents. In addition, the contractor coordinates with the Agency to handle potential security incidents according to the appropriate response procedures; and provides countermeasures to contain the security incident, limit its spread, and protect internal systems. The contractor assists the Agency in containing the damage, recommends the fixes necessary to eliminate identified vulnerabilities, and helps to restore the affected systems to their normal operational state. The contractor also proposes the appropriate procedures to guard against future attacks.
Furthermore, the contractor provides post-incident investigative and forensics services. This includes isolating the impacted area, capturing and collecting data, categorizing malicious or illegal events, and performing reconstruction analyses. The contractor handles and preserves the data collected according to sound scientific and evidence rules, as the information may serve as evidence in administrative actions and legal proceedings. The contractor traces the offenders and assists in prosecuting attackers, as required. These and other INRS service capabilities are detailed in Section C.2.10.5.1.4 Technical Capabilities of the Networx contracts.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for INRS. The specific details can be found within each contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for INRS.
For more information on the general INRS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.10.5 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.10.5 for pricing.
Please note these service guides are for informational purposes only.
4. Price Description
INRS Price Basics
INRS is one of the security services that allow Agencies to combat cyber attacks and crime. The service helps Agencies respond to potential malicious attacks that can lead to service disruptions. INRS can be ordered the following ways:
- Proactive: Proactive services are intended to prevent security incidents. Proactive INRS consists of NRC and MRC pricing elements and is priced on an Individual Case Basis (ICB). The NRC covers the design, implementation and configuration of INRS. The MRC covers ongoing monitoring and management support provided by the contractor.
- Reactive: Reactive services are intended to respond to malicious security incidents and are priced the following two ways:
- Per incident basis priced ICB
- ICB MRC which allows for unlimited incidents
INRS was not offered as a service on the FTS2001 contracts.
Price components required for service are:
- Basic service (NRC and/or MRC) consisting of either:
- Proactive INRS intended to prevent security incidents (ICB NRC + ICB MRC)
- Reactive INRS intended to respond to malicious security incidents comprising either:
- ICB NRC per incident
- ICB MRC for unlimited incidents
- No features available currently
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement INRS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
Example 1: Proactive INRS
- Proactive INRS NRC: Choose CLIN 370001. Prices for this CLIN are ICB and are not available in the unit pricer.
- Proactive INRS MRC: Choose CLIN 370101. Prices for this CLIN are ICB and are not available in the unit pricer.
- SEDs may be required to implement INRS.
Example 2: Reactive INRS per incident
- Reactive INRS NRC: Choose CLIN 370201 per incident. Prices for this CLIN are ICB and are not available in the unit pricer.
- SEDs may be required to implement INRS.
Example 3: Reactive INRS unlimited incidents
- Reactive INRS MRC: Choose CLIN 370301 MRC for unlimited incidents. Prices for this CLIN are ICB and are not available in the unit pricer.
- SEDs may be required to implement INRS.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for INRS. The specific details can be found within each contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for INRS.
For more information on the general INRS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.10.5 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.10.5 for pricing.
Internet Protocol Service (IPS)
2. Technical Description
Internet Protocol Service (IPS) Technical Summary
IPS provides transport of Internet Protocol (IP) packets. IP is the primary protocol in the suite which is used for communicating data across a packet-switched internetwork. IP has the task of delivering packets to destination hosts based solely on their addresses. IPS supports a wide range of connectivity requirements that enable Government users to access the Internet as well as Government-wide intranets, and extranets.
IPS provides dedicated Internet access service on a Networx IP/MPLS (Multi-Protocol Label Switching) backbone. This IP/MPLS backbone delivers a broad range of IP transit and network interconnections tailored to meet the specific needs of Government Agencies. IPS employs the industry standard Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) with registered Autonomous System (AS) numbers as the routing protocol used to exchange routing information across the Internet.
The example shown below illustrates some of the key technical capabilities required for IPS. Agencies with both Routine and Critical Service Level Agreements (SLAs) are connected to the contractor's backbone network through contractor-provided access services that include dial-up ISDN ( Integrated Services Digital Network), DSL (Digital Subscriber Line), Ethernet, high speed cable, FRS (Frame Relay Service), PLS (Private Line Service), satellite, ATMS (Asynchronous Transfer Mode), and dial-backup. IPS will connect Agency SDP (Service Delivery Point) devices (e.g., customer routers, switches, and firewalls) as well as a wide range of equipment (e.g., notebook PCs, PDAs) to the Internet. The contractor will provide peering arrangements from the contractor's network to the internet.
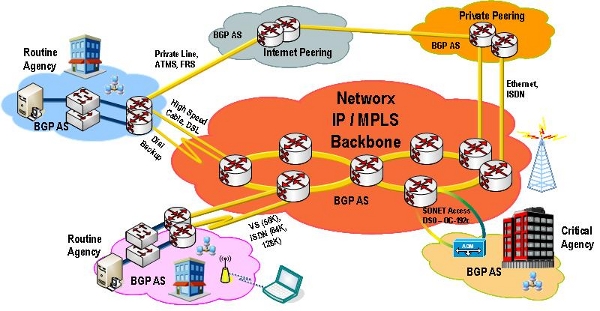
Example of IPS Implementation
3. Technical Detail
IPS is similar to the Internet Protocol Service offered on FTS2001 contracts. It supports the following technical capabilities:
- Peak data rates at the IPS ports as specified by the customer.
- Appropriate access to the contractors IP/MPLS backbone network including dial-up ISDN, DSL, Ethernet, high speed cable, FRS, PLS, satellite, ATMS, and dial-backup.
- Border Gateway Protocol for Networx customers with registered Autonomous System (AS) numbers.
- The contractor's network will provide:
- Established public peering arrangements from the contractor's network to the Internet (Peering is an interconnection of administratively separate networks for the purpose of exchanging traffic between the customers of each network).
- Established private peering arrangements from the contractor's network with redundant links to connect to private peering partners.
- Support for Government assigned and InterNIC registered IP addresses and domain names (InterNIC is a registered service mark of the U.S. Department of Commerce. It is licensed to the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers).
- Primary and Secondary Domain Service (DNS) to provide an authoritative name server for the customer.
The IPS feature set is described in Section C.2.4.1.2.1 of the Networx contracts (IPS Feature Set). It consists of:
- Dialup backup of dedicated ports.
- Web Based Directory Services (Optional for contractor to offer).
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for IPS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for IPS.
For more information on the general IPS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.4.1 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.4.1 for pricing.
4. Price Description
Internet Protocol Service (IPS) Price Basics
IPS provides Agencies with Internet connectivity. CLINs are distinguished by access type:
- Embedded: One CLIN is ordered to obtain both access and transport with one rate.
- Independent (aka Access Services): A separate CLIN for the access is ordered from one contractor to connect an agency's site to another contractor's network.
- Dedicated (i.e. Dedicated Access Arrangements (DAA)): A separate CLIN for the access is ordered along with transport service from the same contractor. This is the most commonly ordered option as shown in Example 1 below.
IPS is similar to the Internet Protocol Service offered on FTS2001 contracts.
- IPS Transport monthly recurring charge per port.
- DAA Originating and Terminating Wireline Access (MRC) and (NRC).
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- Dialup backup of dedicated ports
- Web Based Directory Services
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement IPS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
Price components required for full end-to-end service for Domestic and Non-Domestic IPS:
- IPS Transport: Choose CLIN 744349 (Routine Dedicated Port T1 MRC)
- Access NRC: Choose CLIN 760111 Routine DAA T1 NRC
- Access MRC: Choose CLIN 760311 Routine DAA T1 MRC
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs may differ between contractors
Example 1: IPS CONUS Dedicated T1
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for IPS. The specific details can be found within each Contractors Networx contract files and pricing notes for IPS.
For more information on the general IPS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.4.1 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.4.1 for pricing.
Internet Protocol Telephony Service (IPTelS)
2. Technical Description
Internet Protocol Telephony Service (IPTelS) Technical Summary
IPTelS provides a network based voice communications service with a set of telephony features including voice mail using the Voice over the Internet Protocol (VoIP). Basic IPTelS is a full featured, hosted dialtone service that can be used to replace legacy Centrex or PBX service. The service has gateways to the PSTN and includes embedded security, a robust set of calling features, and supports user mobility. Additionally, the service includes Service Level Agreements (SLAs) to guarantee reliable service.
Domestic service coverage for IPTelS is extensive and provides coverage CONUS wide, with OCONUS locations optional to offer. The Agency may opt to manage its own network or obtain network management (for a voice only Local Area Network (LAN)) from its contractor. The Agency can order IPTelS to connect to and interoperate with the:
- Contractor's IP network
- Agency's LAN
- PSTN
The diagram below illustrates an example implementation of IPTelS. Call processing and other telephony functions are transported over the contractor's IP network. IPTelS requires a connection to the contractor's IP network as shown below by a broadband access from the user's location. Gateways will provide interoperability with non-IP networks and devices, such as a PSTN gateway. Additional Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) such as telephones or soft switches may be required to implement and use IPTelS.
Example IPTelS Implementation
3. Technical Detail
IPTelS is an IP application that provides real-time, two-way voice capability over a broadband connection. As a hosted and managed solution, IPTelS delivers a voice technology that provides automatic, remote technology refresh software updates and is highly scalable to accommodate Agency growth. This service is specifically designed to be a network based VoIP replacement for traditional switched voice local service. IPTelS is an emerging service and has no FTS2001 equivalent.
Basic IPTelS provides a suite of 21 calling features included at no additional cost:
| Caller ID (i.e., ANI) | Call Forward - All | Call Forward - Busy |
| Call Forward - Don't Answer | Call Hold | Calling Number Suppression |
| Call Transfer | Conference Calling | Call Park |
| Call Pickup | Do Not Disturb | Distinctive Ringing |
| Speed Dial | Call Waiting | Class of Service |
| Last Number Dialed | Hunt Groups | Multi-Line Appearance |
| Directory | Hotline | Specific Call Rejection |
Table 1 - IPTelS calling features
IPTelS also offers several additional optional features that can be ordered on an a la carte basis, including:
- Voicemail - voicemail boxes are available on a per station basis allowing Agencies the flexibility to provide voicemail only to subscribers who need the feature
- Find me Follow me Routing - provides the capability to route incoming calls to a minimum of five alternate numbers sequentially or simultaneously before routing to voice mail
- IP Telephony Manager - secure browser based online portal provides Agencies with easy access to instant profile and feature management at two different access levels (subscriber and administrator)
- LAN management - provides contractor management of all LAN components required to deliver IPTelS (this feature is a contract modification that is available only on Networx Enterprise contracts)
The LAN management feature adds the capability to provide complete VoIP service to the desktop and includes contractor management of the LAN needed to deliver the service.
When ordering the IPTelS service, an underlying transport service, access, and Quality of Service (QoS) must be in place to support the service.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for IPTelS. The specific details can be found within each Contractors Networx contract files and pricing notes for IPTelS
For more information on the general IPTelS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.7.10 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.7.10 for pricing.
4. Price Description
Internet Protocol Telephony Service (IPTelS) Price Basics
IPTelS provides a network based telephone service over a contractor provided IP network with a set of telephony features using the Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP).
IPTelS basic service includes domestic off-net termination and non-domestic off-net termination to any non-domestic country/jurisdiction where the contractor provides IPTelS basic service, up to 7,500 minutes per month per telephone number. Off-net termination usage in excess of 7,500 minutes per month per telephone number in countries where the contractor provides IPTeLS basic service is charged at the off-net usage rate provided for VOIPTS off-net usage.
IPTelS is a service that was not offered on the original FTS2001 contracts.
- Basic service (NRC and/or MRC) per telephone number
- Included with the basic service is a bank of 7,500 off-net minutes; an off-net usage charge per six-second increment is charged when off-net minutes are in excess of 7,500 monthly minutes per telephone number
- Underlying transport services, such as NBIP-VPNS, to provide connectivity and NBIP-VPNS Premium Class of Service (CoS) feature charges
- DAA Originating and Terminating Wireline Access (MRC) and (NRC)
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- Find Me Follow Me Routing
- IP Telephony Manager (Subscriber)
- IP Telephony Manager (Administrator)
- Voice Mail Box
- IPTelS LAN Management (Enterprise Contract only)
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) such as telephones may be required to implement IPTelS [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
Price components required for full end-to-end service for Domestic and Non-Domestic IPTelS:
Example 1: IPTelS
- IPTelS Basic Service NRC: Choose CLIN 802101 (Basic Service NRC per telephone number
- IPTelS Basic Service MRC: Choose CLIN 802201 (Basic Service MRC per telephone number
- IPTelS Overage: Choose CLIN 803101 (Outbound to Off-net Location per six-second increment [charged only when off-net minutes exceed 7,500 per telephone number])
- NBIP-VPNS Transport: Choose CLIN 213145 (Port T1 MRC)
- Premium Class of Service (CoS): Choose CLIN 219001 (Class of Service (CoS) - Premium)
- Access NRC: Choose CLIN 760111 Routine DAA T1 NRC
- Access MRC: Choose CLIN 760311 Routine DAA T1 MRC
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement IPTelS; illustrative hardware such as routers and Agency servers are not provided as part of the IPTelS
This document only addresses the IPTelS service at contract award. Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for IPTelS. The specific details can be found within each Contractors Networx contract files and pricing notes for IPTelS.
For more information on the general IPTelS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.7.10 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.7.10 for pricing.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Service (IDPS)
1. Overview
Networx Security Services - Overview
The Networx contracts require a basic level of security management for its contractors that ensures compliance with Federal Government generally accepted security principles and practices, or better. The contracts employ adequate and reasonable means to ensure and protect the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of Networx services, Operational Support Systems
In addition to this mandatory level of security, the Networx contracts provide additional security services that may be ordered on a fee-for-service basis. These are:
- 1. Managed Tiered Security Service (MTSS)
- 2. Managed Firewall Service (MFS)
- 3. Intrusion Detection and Prevention Service (IDPS)
- 4. Vulnerability Scanning Service (VSS)
- 5. Anti-Virus Management Service (AVMS)
- 6. Incident Response Service (INRS)
- 7. Managed E-Authentication Service (MEAS)
- 8. Secure Managed E-Mail Service (SMEMS)
The IDPS offering is described below.
2. Technical Description
IDPS Technical Summary
Agency networks, like their commercial counterparts, continue to be challenged with increasing security risks. IDPS serves as a component of the Agency's security infrastructure by providing an extra layer of protection for its internal networks. The service enables the monitoring and identification of potential security threats, and helps reduce network service disruptions caused by malicious attacks. IDPS analyzes packet activity for indications of network attack, misuse, and anomalies. The service then generates alerts and records suspicious events.
The contractor provides the IDPS software and hardware components, as required. The Agency may order one or more of the following:
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Service (IDPS) to secure the Agencies internal networks.
- Host Intrusion Detection and Prevention Service (Host IDPS) which monitors critical Agency servers for security breaches and misuse while enforcing best industry practices, and Agency security policies.
The diagram below illustrates a sample IDPS implementation. Illustrative hardware such as edge routers and Agency servers are not provided as part of the IDPS.
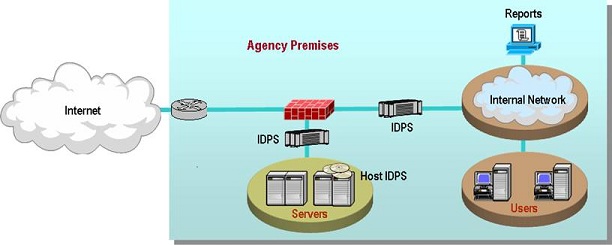
Currently IDPS does not provide any features.
3. Technical Detail
IDPS is an intrusion recognition and mitigation service that protects Agency networks against cyber attacks. The service detects signs of intrusion that may jeopardize the confidentiality, integrity, availability, and control of Agency networks. IDPS supports corrective responses to stop or alleviate malicious attacks. IDPS helps to maintain the availability of Agency mission-critical resources.
IDPS supports a range of technical capabilities that are available in commercial offerings. These include design and implementation services to allow the Agency and the contractor to discuss matters such as system recommendations, a baseline assessment, rules, signature sets, configurations, and escalation procedures. In addition, the service proactively monitors the Agency network on a 24X7 basis for indications of compromise such as intrusions, anomalies, malicious activities, and network misuse. IDPS also performs anomaly detection to identify atypical traffic trends and unusual behaviors that may indicate a potential attack. The service detects precursor activities such as unauthorized network probes, sweeps, and scans. In addition, IDPS performs signature-based detection and analyze system activity for known attacks such as, but not limited to, buffer overflows, brute force, Denial of Service (DOS), and reconnaissance efforts. The service responds dynamically to threats and takes proactive and corrective actions to secure the network. These measures include, for example, automatically terminating affected connections, blocking traffic from the originating host, and disconnecting ports. These and other service capabilities are detailed in Section C.2.10.2.1.4 Technical Capabilities of the Networx contracts.
IDPS is required to support the User-to-Network Interfaces (UNIs) defined in applicable Networx services, for example:
- C.2.4.1Internet Protocol Service (IPS)
- C.2.7.2Premises-based IP VPN Services (PBIP-VPNS)
- C.2.7.3Network-based IP VPN Services (NBIP-VPNS)
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for IDPS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for IDPS.
For more information on the general IDPS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.10.2 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.10.2 for pricing.
4. Price Description
IDPS Price Basics
IDPS is an intrusion recognition and mitigation service that detects signs of intrusion that may jeopardize the confidentiality, integrity, availability, and control of Agency networks. IDPS builds on the FTS2001 contracts offerings. Basic services include software, installation, maintenance and ongoing service support and are available as:
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Service (IDPS) to secure the Agencies internal networks available in the following two Tiers:
- Tier I. providing IDPS support for up to and including 100 Mbps
- Tier II. providing IDPS support for over 100 Mbps and up to and including 1 Gbps
- Host Intrusion Detection and Prevention Service (Host IDPS) per server which monitors critical Agency servers for security breaches and misuse while enforcing best industry practices, and Agency security policies.
Price components required for service are:
- Underlying transport services, such as IPS, NBIP-VPNS or PBIP-VPNS, to provide connectivity
- Basic service (NRC and/or MRC) consisting of either:
- IDPS (NRC + MRC per IDPS device). Two (2) tiers of service are available based on required bandwidth.
- Host IDPS (NRC + MRC per server)
- No features available currently
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement IDPS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
Example 1: IDPS support for over 100 Mbps and up to and including 1 Gbps
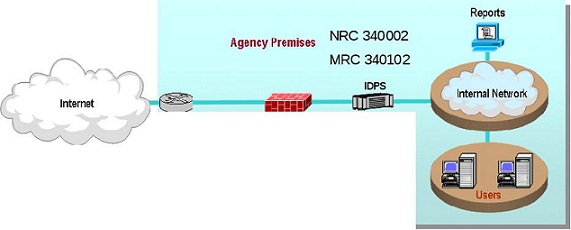
- Choose Networx telecommunications services such as NBIP-VPNS
- Choose CLIN 340002 (Intrusion Detection and Prevention Service: Tier II NRC per IDPS device)
- Choose CLIN 340102 (Intrusion Detection and Prevention Service: Tier II MRC per IDPS device)
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement IDPS. Illustrative hardware is not provided as part of the IDPS.
Example 2: Host IDPS
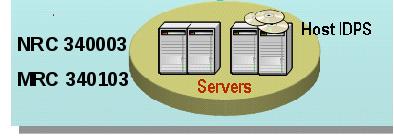
- Choose Networx telecommunications services such as IPS
- Choose CLIN 340003 (Host Intrusion Detection and Prevention Service NRC per service)
- Choose CLIN 340103 (Host Intrusion Detection and Prevention Service MRC per service)
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement Host IDPS. Illustrative hardware is not provided as part of the IDPS.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for IDPS. The specific details can be found within each Contractors Networx contract files and pricing notes for IDPS.
For more information on the general IDPS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.10.2 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.10.2 for pricing.
Managed E-Authentication Service (MEAS)
1. Overview
The Networx contracts require a basic level of security management for its contractors that ensures compliance with Federal Government generally accepted security principles and practices, or better. The contracts employ adequate and reasonable means to ensure and protect the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of Networx services, Operational Support Systems (OSS), and Government information transported or stored in the contractor's Networx services infrastructure. These requirements are detailed in Section C.3.3.2 Security Management of the Networx contracts.
In addition to this mandatory level of security, the Networx contracts provide additional security services that may be ordered on a fee-for-service basis. These are:
- 1.Managed Tiered Security Services (MTSS)
- 2.Managed Firewall Service (MFS)
- 3.Intrusion Detection and Prevention Service (IDPS)
- 4.Vulnerability Scanning Service (VSS)
- 5.Anti-Virus Management Service (AVMS)
- 6.Incident Response Service (INRS)
- 7.Managed E-Authentication Service (MEAS)
- 8.Secure Managed E-Mail Service (SMEMS)
The Managed E-Authentication Service (MEAS) offering is described below.
2. Technical Description
Managed E-Authentication Service (MEAS) Technical Summary
MEAS enables an individual to remotely authenticate his or her identity to an Agency Information Technology (IT) system. The service provides validation and verification of users via tokens and certificates. MEAS allows Agencies to securely conduct electronic transactions and implement E-Government initiatives via the Internet and other networks. The MEAS contractor provides and manages the authentication systems.
The diagram below illustrates a sample token-based MEAS implementation.
The following diagram illustrates a certificate-based MEAS implementation.
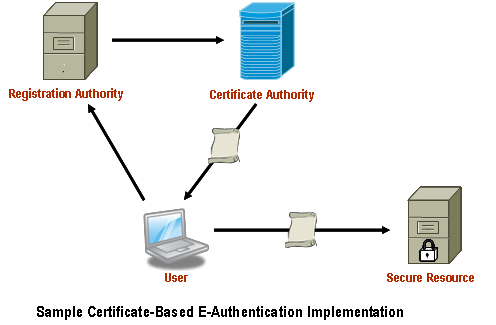
Note that illustrative hardware such as routers and firewalls depicted in the diagrams are not provided as part of the MEAS.
MEAS builds on the FTS2001 contracts offerings. The service connects to and interoperates with the Agency networking environment, including Demilitarized Zones (DMZs) and secure LANs as required by the Agency. The service also supports connectivity to extranets and public networks such as the Internet.
3. Technical Detail
MEAS enables the remote authentication of individual users over a network for the purpose of electronic government and commerce. MEAS technical capabilities are defined in three major categories that are further detailed in Sections C.2.10.6.1.4.1, C.2.10.6.1.4.2 and C.2.10.6.1.4.3 of the Networx contracts.
Design and Engineering Services
- Provide system architecture and equipment recommendations, a baseline assessment, a final design configuration, and operational procedures.
- Support the Agency in developing a detailed implementation plan.
- Provide installation and integration support.
Token-Based Implementation Management
- Setup the authentication service at the identity authentication assurance level specified by the Agency.
- Issue smart cards and/or other token devices.
- Follow the E-Authentication federated authentication model to allow agencies to validate multiple levels of authentication via a single interface, enabling inter-Agency acceptance of digital certificates, and a single sign-on capability.
- Provide authentication methods such as passwords and Personal Identification Numbers (PINs), mechanisms based on fingerprints, and network authentication systems and servers for embedded devices (e.g., routers, modem servers, switches, etc.).
- Support Agencies in developing, implementing, and maintaining the Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) system and servers for network access, including the related tokens, based on, but not limited to protocols such as RADIUS, TACACS/TACACS+ (Cisco), and DIAMETER.
Token-Based Implementation
- Manage and maintain the user authentication service including the related tokens, such as one-time password devices, smart cards, and hardware tokens.
- Provide change management functions such as adding/deleting a user, resetting a PIN, modifying the IP addresses of software agent, and user ID administration.
- Ensure uninterrupted operations using mechanisms such as redundant servers that are located in geographically separate locations with the content continuously synchronized between them.
Token-Based Management
Certificate-Based Implementation and Management
- Set-up a managed Public-Key Infrastructure (PKI) that comprises, but is not limited to Certification Authority (CA), Registration Authority (RA), directory, and associated servers.
- Host and administer PKI certificates for the Agency, including but not limited to certificate issuance, validation services, Agency application certificate registration, and management.
- Setup the authentication service at the identity authentication assurance level specified by the Agency.
- Follow the E-Authentication federated authentication model to allow agencies to validate multiple levels of authentication via a single interface, enabling inter-Agency acceptance of digital certificates, and a single sign-on capability.
Certificate-Based Implementation
- Maintain the database of user names, user IDs, and passwords.
- Provide digital certificates and digital signatures as well as CA services.
- Ensure uninterrupted operations using mechanisms such as redundant servers that are located in geographically separate locations with the content continuously synchronized between them.
- Provide change management functions such as adding/deleting a user, resetting a password, modifying the IP addresses of software agent, and user ID administration.
Certificate-Based Management
The MEAS feature set is described in Section C.2.10.6.2 of the Networx contracts. It consists of:
- Biometric Characteristics - Provide biometric authentication methods including iris scan, voice, and facial recognition, as required by the Agency.
- Encryption/Digital Signature Client Software - Provide and support the encryption/digital signature client software for the Agency.
- E-Authentication Training - Provide E-Authentication training to Agency personnel as required.
- Directory/Repository Function - Develop, implement, and maintain a Directory/Repository function that will support the PKI and/or other e-authentication mechanism chosen by the Agency.
MEAS is required to support the User-to-Network Interfaces (UNIs) defined in applicable Networx services, for example:
- C.2.3.1 Frame Relay Service (FRS)
- C.2.3.2 Asynchronous Transfer Mode Service (ATMS)
- C.2.4.1 Internet Protocol Service (IPS)
- C.2.7.2 Premises-based IP VPN Services (PBIP-VPNS)
- C.2.7.3 Network-based IP VPN Services (NBIP-VPNS)
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for MEAS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for MEAS.
For more information on the general MEAS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.10.6 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.10.6 for pricing.
4. Price Description
MEAS Price Basics
MEAS provides various methods (e.g., tokens, digital certificates, biometrics, e-signatures) for the authentication, validation, and verification of users over an Agency's systems and networks. Any required software components are included in the service prices. MEAS provides the following components:
- Token-based MEAS.
- Certificate-based MEAS.
MEAS builds on the FTS2001 contracts offerings.
Price components required for service are:
- Underlying transport services, such as IPS, to provide connectivity.
- Basic service (NRC ICB and/or MRC) consisting of either:
- Token-Based MEAS (NRC ICB + MRC per user)
- Certificate-Based MEAS (NRC ICB + MRC per user)
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- *Biometric Characteristics
- Encryption/Digital Signature Client Software
- E-Authentication Training
- *Directory/Repository Function
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement MEAS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
- Design and Engineering (NRC ICB), if necessary.
* Some or all price components are priced on an Individual Case Basis (ICB). CLINs with ICB prices are not available in the unit pricer.
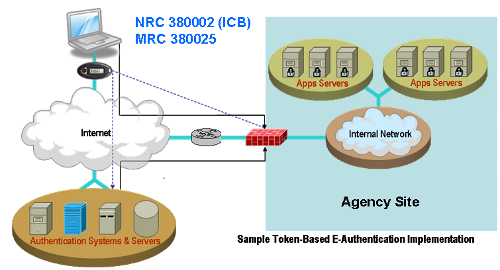
- Underlying transport: Choose Networx telecommunications services such as IPS.
- Basic Service NRC: Choose CLIN 380002 (Token-based MEAS NRC ICB).
- Basic Service MRC: Choose CLIN 380025 (Token-based MEAS between 251 and 500 users MRC per user).
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs may differ between contractors.
- A Design and Engineering NRC may be applicable.
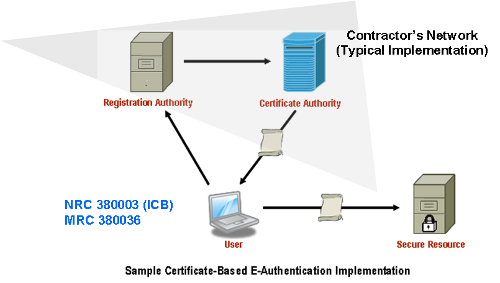
- Underlying transport: Choose Networx telecommunications services such as IPS.
- Basic Service NRC: Choose CLIN 380003 (Certificate-based MEAS NRC ICB).
- Basic Service MRC: Choose CLIN 380036 (Certificate-based MEAS between 501 and 1,000 users MRC per user).
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs may differ between contractors.
- A Design and Engineering NRC may be applicable.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for MEAS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for MEAS.
For more information on the general MEAS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.10.6 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.10.6 for pricing.
Managed Firewall Service (MFS)
1. Overview
The Networx contracts require a basic level of security management for its contractors that ensures compliance with Federal Government generally accepted security principles and practices, or better. The contracts employ adequate and reasonable means to ensure and protect the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of Networx services, Operational Support Systems (OSS), and Government information transported or stored in the contractor's Networx services infrastructure. These requirements are detailed in Section C.3.3.2 Security Management of the Networx contracts.
In addition to this mandatory level of security, the Networx contracts provide additional security services that may be ordered on a fee-for-service basis.
These are:
- 1.Managed Tiered Security Service (MTSS)
- 2.Managed Firewall Service (MFS)
- 3.Intrusion Detection and Prevention Service (IDPS)
- 4.Vulnerability Scanning Service (VSS)
- 5.Anti-Virus Management Service (AVMS)
- 6.Incident Response Service (INRS)
- 7.Managed E-Authentication Service (MEAS)
- 8.Secure Managed E-Mail Service (SMEMS)
- 2.Managed Firewall Service (MFS)
The MFS offering is described below.
2. Technical Description
MFS Technical Summary
MFS builds on the FTS2001 contracts offerings. The service is implemented to secure internal Agency networks. MFS allows Agencies to mitigate the increasing network security risks they face. The service is one of the security tools that will help reduce service disruptions caused by malicious access, and prevent unauthorized access to or from private networks, such as Local Area Networks (LANs).
MFS safeguards internal networks and systems from hostile activity, protecting critical data from compromise and tampering. As buffers between trusted internal networking environments and external networks, firewalls inspect traffic according to a set of defined security policies, blocking all traffic not meeting the Agency's criteria.
MFS connects to and interoperates with the Agency networking environment, including Demilitarized Zones (DMZs) and secure LANs as required by the Agency. The service also supports connectivity to extranets and public networks such as the Internet.
The contractor provides the firewall software and hardware components, as required. The Agency may order one or more of the following:
Premises-based firewalls deployed at the Agency location. Network-based firewalls located in the contractor's infrastructure. Application/proxy-based firewalls positioned and implemented as per agency needs, and monitor traffic at the application layer.
The diagram below illustrates a sample firewall implementation. Illustrative hardware such as edge routers and Agency servers are not provided as part of the MFS.
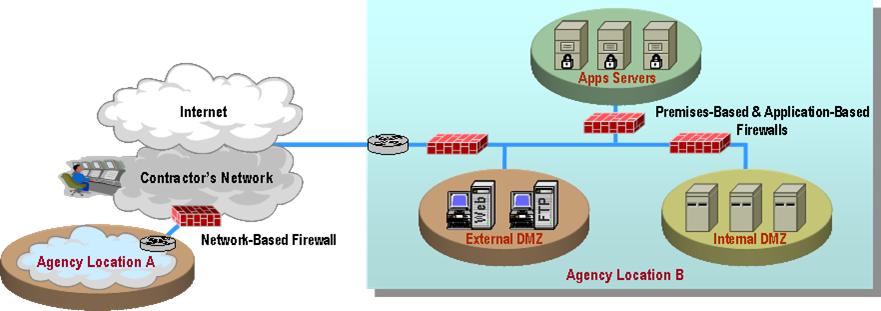
MFS also offers several features that complement the basic service. They are
- Demilitarized Zones (DMZs) Support
- Email Security
- Extranet Support
- Fast Ethernet Connection
- Firewall Load Balancing
- Firewall Redundancy
- Firewall-to-Firewall VPNs
- Personal Firewalls
- Remote Client VPNs
- Uniform Resource Locator (URL) Filtering
- User Authentication Integration
These features are described in Section C.2.10.1.2 Features of the Networx contracts.
3. Technical Detail
MFS provides Agency's internal networks with a layer of protection against cyber attacks. This includes providing Agencies with real-time monitoring that helps mitigate attacks and maintain the availability of Agency mission-critical resources; and a single point of accountability for designing, implementing, managing, monitoring, and maintaining the security solution.
MFS will support the full range of technical capabilities that are available in commercial offerings. These include implementing firewall security policies according to the Agency's needs, proactively monitoring the firewall components on a 24x7 basis, and detecting suspicious activity and policy violations. MFS employs various protection techniques, including but not limited to Stateful Packet Inspection, Network Address Translation (NAT) and Port Address Translation (PAT), to guard the Agency's networks from attacks. The service also uses best practices against Denial of Service (DOS), Ping of Death, IP Spoofing, SYN Flood, and Tear Drop attacks. These and other service capabilities are detailed in Section C.2.10.1.1.4 Technical Capabilities of the Networx contracts.
MFS is required to support the User-to-Network Interfaces (UNIs) defined in applicable Networx services, for example:
- C.2.3.1 Frame Relay Service (FRS)
- C.2.3.2 Asynchronous Transfer Mode Service (ATMS)
- C.2.4.1 Internet Protocol Service (IPS)
- C.2.7.2 Premises-based IP VPN Services (PBIP-VPNS)
- C.2.7.3 Network-based IP VPN Services (NBIP-VPNS)
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for MFS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for MFS.
For more information on the general MFS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.10.1 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.10.1 for pricing.
4. MFS Price Description
MFS Price Basics
MFS builds on the FTS2001 contracts offerings. MFS provides the following components:
- Premises-based firewalls deployed at the Agency location.
- Network-based firewalls serving the Agency from the contractor's infrastructure.
- Application/proxy-based firewalls, implemented as per agency requirement, monitor traffic at the application layer.
Premise-based and network-based MFS basic services are available in the following three Tiers:
- Tier I - providing firewall support up to 10 Mbps and up to 100 IP addresses
- Tier II - providing firewall support for up to 100 Mbps and up to 1,000 IP addresses
- Tier III - providing firewall support for up to 1 Gbps and unlimited IP addresses
Price components required for service are:
- Underlying transport services, such as FRS or IPS, to provide connectivity
- Basic service (NRC and/or MRC) consisting of either:
- Premise-Based MFS (NRC + MRC per firewall). Three (3) tiers of service are available based on required bandwidth and number of IP addresses.
- Network-Based MFS (NRC + MRC per firewall). Three (3) tiers of service are available based on required bandwidth and number of IP addresses.
- Application Proxy-Based MFS is priced ICB (NRC + MRC).
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- Demilitarized Zones (DMZs) Support
- Email Security
- Extranet Support
- Fast Ethernet Connection
- Firewall Load Balancing
- Firewall Redundancy
- Firewall-to-Firewall VPNs
- Personal Firewalls
- Remote Client VPNs
- Uniform Resource Locator (URL) Filtering
- User Authentication Integration
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement MFS.
[Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and
Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers.
The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment
or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a
MRC for maintenance.]
- SEDs are required to implement Premise-based MFS
- SEDs may be required to implement Network-based MFS
- SEDs are required to implement Application/proxy-based MFS
Example 1: Premise-based MFS providing firewall support up to 10 Mbps and up to 100 IP addresses:
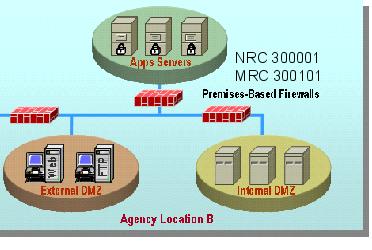
- Transport: Choose Networx telecommunications services such as FRS
- Premise-based NRC: Choose CLIN 300001 (Premise-Based MFS: Tier I NRC per firewall)
- Premise-based MRC: Choose CLIN 300101 (Premise-Based MFS: Tier I MRC per firewall)
- SEDs are required to implement Premise-based MFS. Illustrative hardware such as routers and Agency servers are not provided as part of the MFS.
Example 2: Network-based MFS providing firewall support up to 500 Mbps and up to 2,000 IP addresses:
- Transport: Choose Networx telecommunications services such as IPS
- Network-based NRC: Choose CLIN 300203 (Network-Based MFS: Tier III NRC per firewall)
- Network-based MRC: Choose CLIN 300303 (Network-Based MFS: Tier III MRC per firewall)
- SEDs may be required to implement Network-based MFS. Illustrative hardware such as routers and Agency servers are not provided as part of the MFS.
Example 3: Application/proxy-based firewall:
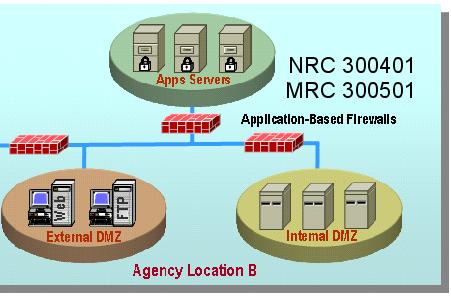
- Transport: Choose Networx telecommunications services such as IPS
- Application Proxy Firewall NRC: Choose CLIN 300401 (Application Proxy Firewall NRC - ICB)
- Application Proxy Firewall MRC: Choose CLIN 300501 (Application Proxy Firewall MRC - ICB)
- SEDs are required to implement Application/proxy-based MFS. Illustrative hardware such as routers and Agency servers are not provided as part of the MFS.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for MFS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for MFS.
For more information on the general MFS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.10.1 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.10.1 for pricing.
Managed Network Services (MNS)
2. Technical Description
Managed Network Services (MNS) Technical Summary
MNS offers comprehensive network management solutions that are designed to meet Agency requirements. Under the MNS offering, the contractor provides overall management of an Agency's infrastructure, including real-time proactive network monitoring, rapid troubleshooting and service restoration.
The basic MNS concept is illustrated in the Figure below. The MNS contractor provides the necessary design, engineering, project management, and other functional requirements to satisfy the particular requirements of an Agency. Agency networks vary in complexity in terms of size, bandwidth, and functionality. The MNS contractor is the Agency's single point of accountability for all networks managed under this service, including operations, maintenance, and administrative activities.
Basic MNS Concept
MNS works with underlying Networx offerings such as Frame Relay Service (FRS). Asynchronous Transfer Mode Service (ATMS), IP-enabled FRS/ATMS, IP Virtual Private Networks (VPN), Private Line Service (PLS), and other services as needed to ensure seamless connectivity to Agency networking environments. MNS is similar to managed network service offerings on FTS2001 contracts. However, there is not a direct correlation between specific FTS2001 and Networx solutions.
3. Technical Detail
MNS technical capabilities are defined in two following major categories that are identified in more detail in Sections C.2.9.1.1.4.1 and C.2.9.1.1.4.2 of the Networx contracts.
- Provide design and engineering services that fully satisfy Agency requirements.
- Incorporate the Agency security requirements into the design. This may include integration of a security package or individual Networx security services.
- Identify network components and protocol, redundancy, traffic filtering, and traffic prioritization requirements. Also specification of the appropriate Committed Information Rates (CIRS), Permanent Virtual Circuits (PVC) levels, and network access speeds as required.
- Provide complete project management including design, implementation, installation, access coordination, provisioning, equipment configuration, hardware testing, and service activation.
Managed Design and Engineering Services
- Conduct integrated management of services including, as required by the Agency, managing services provided by other contractors.
- Develop implement, and manage comprehensive solutions constructed from components of Networx services to meet Agency-specific requirements.
- Supply and manage the hardware, firmware, and related software required by the agency.
- Manage the network in real-time on a 24X7 basis.
- Support Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) data feeds that provide the Agency with managed equipment information as applicable.
- Support configuration changes, provide IP address management, monitor and control access to equipment, perform hardware and software upgrades, and additional functions described in Section C.2.9.1.1.4.2 (Implementation, Management, and Maintenance).
Implementation, Management, and Maintenance
- Government Furnished Property (GFP) and Maintenance (maintenance and repair of GFP unless maintained under an SED monthly maintenance charge).
- Agency-specific Network Operations Center (NOC).
- Network Testing (performed at the Agency's discretion and structured in collaboration with the contractor).
The MNS feature set is described in Section C.2.9.1.2 of the Networx contracts (MNS Feature Set). It consists of:
- C.2.3.1 Frame Relay Service (FRS).
- C.2.3.2 Asynchronous Transfer Mode Service (ATMS).
- C.2.5.1 Private Line Services (PLS).
- C.2.4.1 Internet Protocol Service (IPS).
- C.2.7.2 Premises-based IP VPN Services (PBIP-VPNS).
- C.2.7.3 Network-based IP VPN Services (NBIP-VPNS).
MNS is required to support the (UNIs) defined in applicable Networx services, for example:
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for MNS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for MNS.
For more information on the general MNS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.9.1 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.9.1 for pricing.
4. Price Description
MNS Price Basics
MNS provides comprehensive design, engineering, operation, management, monitoring, and maintenance of Agency networks. MNS does not include access and transport services. Prices exclude the cost of bandwidth and SED maintenance covered by the SED's MMRC.
- Connection-Oriented Networks: Networks using circuit switched services, FRS, and ATM.
- Connectionless Networks: Networks using IP-based services.
MNS Basic Service CLINS are charged per device. A device under MNS is typically a router, switch, or similar equipment at the user's location that acts as a point of connection between user location and the contractor's networking service(s). The Basic Service CLINs are distinguished by network type:
MNS is similar to MNS offerings on FTS2001 contracts. However, there is not necessarily a direct correlation between all specific FTS2001 and Networx solutions
- Managed Network Implementation, Management and Maintenance (NRC + MRC per device).
- Features* ordered as needed by the Agency:
- Government Furnished Property (GFP) Maintenance.
- Agency-Specific Network Operations Center (NOC).
- Network Testing.
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement MNS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.].
- Managed Network Design and Engineering (NRC + MRC ICB), if necessary, comprises design and engineering services including a review of the current network traffic, performance, transport, hardware and software components; and an overall evaluation of network topology, configuration, addressing, bandwidth, availability, scalability, reliability and disaster recovery requirements.
- Agency specific interfaces, software, and equipment to meet SOW requirements (NRC + MRC ICB), if necessary.
Price components required for MNS Basic Service:
* All original contract MNS features are priced on an Individual Case Basis (ICB). CLINs with ICB prices are not available in the unit pricer.
- MNS NRC: Choose CLIN 280258 (Managed Network Implementation, Maintenance and Management, device up to 45 Mbps peak, NRC per device).
- MNS MRC: Choose CLIN 280358 (Managed Network Implementation, Maintenance and Management, device up to 45 Mbps peak, MRC per device.
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs differ between vendors.
- Managed Network Design and Engineering NRC and/or MRC may be applicable.
- Agency specific interfaces, software, and equipment to meet SOW requirements NRC and/or MRC may be applicable.
Example 1: MNS for a connectionless device peaking up to 45 Mbps
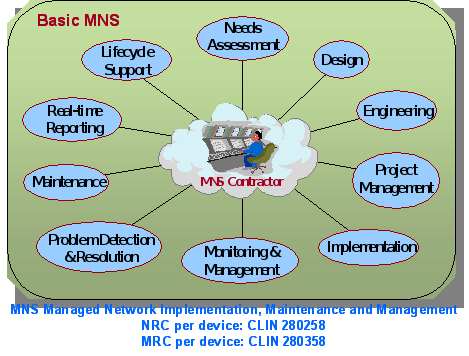
- MNS NRC: Choose CLIN 280051 (Managed Network Implementation, Maintenance and Management, device up to 1.544 Mbps peak, NRC per device).
- MNS MRC: Choose CLIN 280151 (Managed Network Implementation, Maintenance and Management, device up to 1.544 Mbps peak, MRC per device.
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs differ between vendors.
- Managed Network Design and Engineering NRC and/or MRC may be applicable.
- Agency specific interfaces, software, and equipment to meet SOW requirements NRC and/or MRC may be applicable.
Example 2: MNS for a connection-oriented device peaking up to 1.544 Mbps
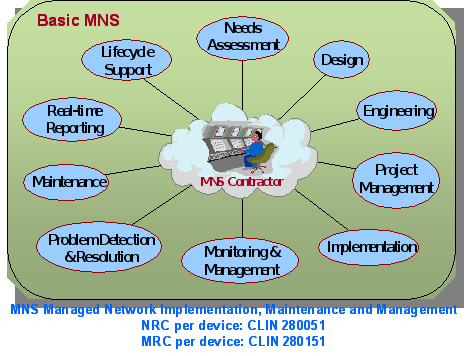
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for MNS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for MNS.
For more information on the general MNS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.9.1 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.9.1 for pricing.
Managed Tiered Security Services (MTSS)
1. Overview
The Networx contracts require a basic level of security management for its contractors that ensures compliance with Federal Government generally accepted security principles and practices, or better. The contracts employ adequate and reasonable means to ensure and protect the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of Networx services, Operational Support Systems (OSS), and Government information transported or stored in the contractor's Networx services infrastructure. These requirements are detailed in Section C.3.3.2 Security Management of the Networx contracts.
In addition to this mandatory level of security, the Networx contracts provide additional security services that may be ordered on a fee-for-service basis. These are:
- 1.Managed Tiered Security Service (MTSS)
- 2.Managed Firewall Service (MFS)
- 3.Intrusion Detection and Prevention Service (IDPS)
- 4.Vulnerability Scanning Service (VSS)
- 5.Anti-Virus Management Service (AVMS)
- 6.Incident Response Service (INRS)
- 7.Managed E-Authentication Service (MEAS)
- 8.Secure Managed E-Mail Service (SMEMS)
The MTSS offering is described below.
2. Technical Description
Technical Summary
With MTSS, GSA provides Government users with four levels of security solutions (tiers) which can be customized to individual users based on their needs for sensitive information protection. A specific tier includes all services for that tier as listed in Section C.2.7.4.1.4.1 of the Networx contracts. The tiers and services within the individual tiers are similar to the FTS2001 Multiple Tiered Security Profile (MSTP) service.
Tier 1 - Standard Service. This tier supports basic internet connectivity and is appropriate for non-mission critical functions or non-sensitive communications requirements. Help desk functions are provided in tier 1 and Agency installed security mechanisms are employed as needed. Additionally, Networx contracts have basic requirements for adequate and reasonable means to ensure and protect the integrity and confidentiality of information, and availability of Networx services. There are no requirements for protection of information content beyond these measures.
Tier 2 - Protected Services. This tier is tailored to Secure but Unclassified (SBU) mission functions and information. A secure path to the Internet and the service provider's network is required. Tier 2 includes all tier 1 capabilities with the addition of a set of tier 2 services as shown in the diagram below.
MTSS Tiered Architecture
Tier 3 - High Assurance Service. This tier includes all of the security enhancements of tier 2 and is tailored to protect sensitive information up to and including information that may be classified up to the DoD Secret level. This tier operates in an environment that does not employ a direct connection to the Internet except via a tier 2 enclave and its associated security enhancements. Connectivity to tier 2 enclaves is permitted only via NSA approved trusted gateways, secure mail guard technologies, or other NSA approved multilevel security solutions. Connectivity via the service provider's secure network is permitted among tier 3 enclaves.
Tier 4 - Network High Service. This tier provides protection of information that may be classified up to DoD Top Secret, Sensitive Compartmented Information (SCI), or Single Integrated Operational Plan - Extremely Sensitive Information (SIOP-ESI). This tier operates in a closed and isolated network environment. Connectivity is permitted among other tier 4 enclaves within a community of interest.
3. Technical Detail
The multi-tiered MTSS offering provides security enhancement services beyond the basic Networx infrastructure requirements as detailed in Section C.3.3.2 and the fee-for-services as detailed in Section C.2.10 (e.g., Managed Firewall Service) of the Networx contracts. The component services by tier are listed in the following table and are specified in detail in Section C.2.7.4.1.5 (Technical Capabilities) of the Networx contracts.
| Security Enhancement Services | Tier | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Agency Dedicated Help Desk | X | X | X | X |
| Anti-virus (AVMS) | X | X | X | |
| Firewall (MFS) | X | X | X | |
| Intrusion Detection/Prevention (IDPS) | X | X | X | |
| Incidence Response (INRS) | X | X | X | |
| Secure Managed E-Mail (SMEMS) | X | X | X | |
| Vulnerability Scanning (VSS) | X | X | X | |
| Packet Filtering | X | X | X | |
| Premise-based VPN (PBIP-VPNS) | X | X | X | |
| Security Certification Support | X | X | X | |
| Security Maintenance | X | X | X | |
| Proxy Server | X | X | ||
| Agency Sponsored Type 1 Encryption | X | X | ||
| NSA Approved Multilevel Security Solution | X | X | ||
| Network Isolation (AirGap) | X | |||
4. Security Enhancement Services
The MTSS Security Enhancement Services are summarized briefly below:
- Agency Dedicated Help Desk - A single point-of-contact help desk capability for all issues concerning service delivery 24X7. The help desk capability is a component of all four tiers.
- Networx fee-for-service offerings - A package of Networx security services consisting of AVMS, MFS, IDPS, SMEMS, and VSS. This package is included in tiers 2, 3, and 4.
- Packet Filtering - Contractor-provided routers that restrict packets to specific ports based on protocol specific criteria. This capability is included in tiers 2, 3, and 4.
- Premise-based VPN Service - Networx Premise-Based IP VPN Service (PBIP-VPNS) as detailed in Section C.2.7.2 of the Networx contracts. This capability is included in tiers 2, 3, and 4.
- Security Certification Support - Contractor assistance to the Agency in the development of all documents in the certification and accreditation (C&A) process for systems and services provided under the Networx contract. This capability is included in tiers 2, 3, and 4.
- Security Maintenance - Including but not limited to advising the Agency concerning control and elimination of vulnerabilities, maintenance of security systems and necessary hardware\software upgrades, updates, and replacements. This capability is included in tiers 2, 3, and 4.
- Proxy Server - Secure web servers to shield a sensitive network enclave from an enclave of lesser sensitivity. This capability is included in tiers 2 and 3.
- Agency sponsored Type I encryption - Contractor-provided and managed NSA Type 1 encryption devices through Agency sponsorship. This capability is included in tiers 3, and 4.
- NSA Approved Multilevel Security Solution - Solution that includes but is not limited to an NSA approved secure mail guard service and NSA trusted gateway service. This capability is included in tiers 3, and 4.
- Network Isolation (air gap) - Absolute physical isolation from lesser sensitive networks. This capability applies only to tier 4.
The following features are available only for tiers 2, 3, and 4 as detailed in Section C.2.7.4.2 (Features) of the Networx contracts:
- On-site management and monitoring 24X7
- On-site installation services as required by the Agency
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for MTSS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for MTSS.
For more information on the general MTS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.7.4 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.7.4 for pricing.
5. Price Description
MTSS Price Basics
Managed Tiered Security Service (MTSS) provides Government users with four combinations of security services, which can be customized to individual needs based on information sensitivity. MTSS consists of four (4) tiers of services. All services within a tier must be ordered.
- Tier 1 - Standard Service: This tier supports basic internet connectivity and is appropriate for non-mission critical functions or non-sensitive communications requirements. Help Desk functions are provided in Tier 1.
- Tier 2 - Protected Services: This tier is tailored to Secure but Unclassified (SBU) mission functions and information. Tier 2 includes all Tier 1 capabilities with the addition of a set of Tier 2 services. A discount is applicable to the total charge for the included security services.
- Tier 3 - High Assurance Service: This tier includes all of the security enhancements of Tier 2 and is tailored to protect extremely sensitive information up to and including information that may be classified up to the DoD Secret level. A discount is applicable to the total charge for the included security services.
- Tier 4 - Network High Service: This tier provides protection of information that may be classified up to DoD Top Secret, Sensitive Compartmented Information (SCI), or Single Integrated Operational Plan - Extremely Sensitive Information (SIOP-ESI). A discount is applicable to the total charge for the included security services.
The tiered structure and services within the individual tiers of MTSS are similar to the FTS2001 Multiple Tiered Security Profile (MTSP) service, which is priced on an Individual Case Basis (ICB).
Price components required for MTSS by Service Tier:
- NRC and/or MRC for each basic service listed in a given Tier
- DAA Originating and Terminating Wireline Access (MRC) and (NRC) for Tiers 1 and 2
- Features* ordered as needed by the Agency:
- On-site management and monitoring 24x7 (Tiers 2 - 4)
- On-site installation (Tiers 2 - 4)
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement MTSS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
* All original contract MTSS features are priced on an Individual Case Basis (ICB). CLINs with ICB prices are not available in the unit pricer.
MTSS Basic Service Components by Tier
Description Charging Unit Tier 1 Tier 2 Tier 3 Tier 4 Discount Help Desk Service NRC + MRC per user seat (ICB for Tiers 3 & 4) X X X X Packet Filtering Service ICB NRC + ICB MRC per filter X X X Proxy Server Service ICB NRC + ICB MRC per proxy server X X Security Maintenance Service ICB NRC + ICB MRC per network X X X Security Certification Support Service ICB NRC + ICB MRC per network certification X X X NSA Approved Multilevel Security Solution ICB NRC + ICB MRC per network X X Network Isolation (Air Gap) ICB NRC per isolation X Firewall Service See MFS Section B.2.10.1 for pricing X X X % off Intrusion Detection / Prevention Service See IDPS Section B.2.10.2 for pricing X X X % off Vulnerability Scanning Service See VSS Section B.2.10.3 for pricing X X X % off Anti-Virus Service See AVMS Section B.2.10.4 for pricing X X X % off Incident Response Service See INRS Section B.2.10.5 for pricing X X X % off Secured Managed Email Service See SMEMS Section B.2.10.8 for pricing X X X % off Premise-based Virtual Private Network See PBIP-VPNS Section B.2.7.2 for pricing X X X Agency Sponsored Type 1 Encryption See SEDS Section B.4 for pricing X X
Example 1: MTSS Routine Level for Tier 2
- MTSS Tier 2 Services defined only in MTSS
- Help Desk Service: Choose NRC CLIN 224010 and MRC CLIN 224005
- Packet Filtering Service: Choose NRC CLIN 224011 and MRC CLIN 224006 (prices for these CLINs are ICB and are not available in the unit pricer)
- Proxy Server Service: Choose NRC CLIN 224012 and MRC CLIN 224007 (prices for these CLINs are ICB and are not available in the unit pricer)
- Security Maintenance Service: Choose NRC CLIN 224013 and MRC CLIN 224008 (prices for these CLINs are ICB and are not available in the unit pricer)
- Security Certification Support Service: Choose NRC CLIN 224014 and MRC CLIN 224009 (prices for these CLINs are ICB and are not available in the unit pricer)
- MTSS Tier 2 Services defined elsewhere in the Networx Contract
- MFS: See MFS Section B.2.10.1 for pricing
- IDPS: See IDPS Section B.2.10.2 for pricing
- VSS: See VSS Section B.2.10.3 for pricing
- AVMS: See AVMS SectionB.2.10.4 for pricing
- INRS: See INRS SectionB.2.10.5 for pricing
- SMEMS: See SMEMS Section B.2.10.8 for pricing
- PBIP-VPNS: See PBIP-VPNS Section B.2.7.2 for pricing
- Access NRC: Choose CLIN 760117 Routine DAA T3 NRC
- Access MRC: Choose CLIN 760317 Routine DAA T3 MRC
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs differ between vendors.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for MTSS. The specific details can be found within each Contractors Networx contract files and pricing notes for MTSS.
For more information on the general MTSS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.7.4 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.7.4 for pricing.
- MTSS Tier 2 Services defined only in MTSS
Managed Trusted Internet Protocol Service (MTIPS)
2. Technical Description
Technical Summary
In November 2007, the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) announced its Trusted Internet Connections (TIC) initiative which will limit the number of internet connections (gateways) into Federal Departments and Agencies. In response, GSA developed MTIPS, a Networx service that enables Agencies to meet their TIC requirements. This is a new service that was not offered on previous GSA contracts.
MTIPS allows Agencies to transport Internet Protocol (IP) packets to/from external networks including the Public Internet, business partner's networks and Government-wide intranets and extranets. MTIPS enables Federal Agencies to achieve full compliance with the TIC mandate by facilitating the reduction of the number of Internet connections in Government networks while providing stipulated security functions and controls to all Government users.
The figure below shows a notional architecture for MTIPS. It is a realization of the TIC 1.0 Reference Architecture as required by the OMB TIC initiative.
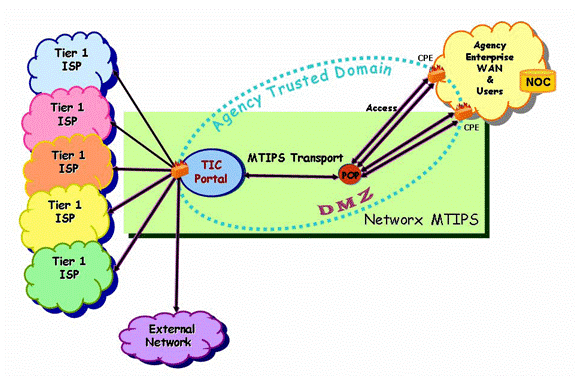
MTIPS Notional Architecture
As shown in the figure, MTIPS is comprised of (1) the network infrastructure to transport IP traffic originating in the Agency Enterprise Wide Area Network (WAN) and (2) the TIC portal (DHS Approved Access Point). Together they create an Agency TIC Trusted Domain (DMZ) for IP traffic. (The term DMZ was originally coined as an acronym for demilitarized zone). The DMZ is created by the contractor to ensure that Agency traffic is protected and physically isolated when transported to the TIC portal and the public internet. Contractor-provided access to the MTIPS Transport POP is included in the DMZ.
The MTIPS (TIC) Portals built by Networx contractors provide access to multiple Tier 1 Internet Service Providers (ISPs). An MTIPS portal functions as an OMB approved Multi-Service Trusted Internet Connection Access Provider (TICAP) capable of hosting multiple Agencies and able to manage and correlate multiple independent traffic streams for each subscribing Agency. The MTIPS Portal provides security services to multiple clients, but allows for specific controls based on Agency requirements.
Prior to subscribing to MTIPS, Agencies must do the following:
- Designate a Dedicated Approval Authority (DAA).
- Sign a "Banner" Memorandum of Agreement (MOA) with DHS. The MOA is signed by the DAA and is a legal requirement to monitor Agency traffic using EINSTEIN devices (see Technical Detail section below).
- Identify MTIPS Gateway Site(s). It is recommended that the Agency consolidate internet/external network bound traffic at a single or at a few Agency sites and conduct site assessments.
- Review MTIPS C&A certification package and issue Authorization to Operate (ATO) or accept a Global ATO from GSA.
3. Technical Detail
The MTIPS ensures 100% compliance with the OMB mandate upon subscription by the Agencies. MTIPS is an enhancement to the Networx Internet Protocol Service (IPS). It provides an additional layer of security which isolates Agencies internal traffic from un-trusted zones (i.e., the Public Internet and other external networks).
MTIPS Technical Capabilities
MTIPS supports the following technical capabilities described in detail in Section C.2.4.1.5.1.4 of the Networx contracts:
- Access to the Internet - This capability includes:
- Established public peering arrangements from the contractor's network to the Internet.
- Established private peering arrangements from the contractor's network with redundant links to connect to private peering partners.
- Hosting for the EINSTEIN Enclave - The MTIPS contractors provide cage, power and environmental conditions to host the EINSTEIN enclave; the Government provides the network elements as GFE.
- DCID 6/9 SCIF - Contractor-provided SCIF space.
- MTIPS Portal Security Operations Center (SOC) - The SOC provides the following functions:
- Event Generation of Security Sensors - The security sensors installed support the following functions
- E-mail scanning and Filtering.
- Network Based Firewall virtualized to support all hosted Agencies.
- Intrusion Detection and Protection in support of vendor and Agency supplied signatures.
- Anti Virus Protection.
- Event collection and normalization - The event collectors gather raw information from the security sensors. The messages are normalized and reflect the operating states of the security appliances at the Portal.
- Control Mechanisms - The MTIPS provides mechanisms for the exchange of information and enables action and reaction to attacks to mitigating and preventing them.
- Systems Logs.
- Event Generation of Security Sensors - The security sensors installed support the following functions
- MTIPS Transport Collection and Distribution Capabilities.
4. MTIPS Features
The MTIPS Feature set is described in Section C.2.4.1.5.2.1 of the Networx contracts (MTIPS Feature Set). It consists of:
- Encrypted traffic - Provides scanning and filtering of incoming and outgoing email, web traffic and known bad mail.
- Agency security policy enforcement.
- Forensic analysis.
- Custom reports for ad-hoc user defined reports.
- Agency NOC/SOC Console-customized to Agency requirements.
- Custom Certification and Accreditation Support to support more stringent security controls.
- External network connection.
- Encrypted DMZ.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for MTIPS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for MTIPS.
For more information on the general MTIPS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.4.1.5 of the Networx contracts for technical specifications and Section B.2.4.1.5 for pricing.
5. Price Description
MTIPS Price Basics
MTIPS facilitates the reduction of the number of Internet connections in Government networks and provides standard security services to all Government users. MTIPS is in full compliance with the Office of Management and Budget's (OMB) Trusted Internet Connection (TIC) initiative (M-08-05).
The MTIPS port price includes:
- TIC Security Operations Center (SOC) equipment
- TIC Portal Capabilities (Section C.2.4.1.5.1.4.1)
- Transport Collection and Distribution Capabilities (Section C.2.4.1.5.1.4.2)
- Network Operations and Management (Section C.2.4.1.5.5)
- TIC Portal SOC Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA) Certification and Accreditation (C&A) (Section C.2.4.1.5.8)
CLINs are distinguished by access type:
- Embedded Access: One CLIN is ordered to obtain both access and transport with one rate.
- Independent Access (aka Access Services): A separate CLIN for the access is ordered from one contractor to connect an agency's site to another contractor's network.
- Dedicated Access: A separate CLIN for the access is ordered along with transport service from the same contractor. This is the most commonly ordered option as shown in Example 1 below.
MTIPS is a service that was not offered on the FTS2001 contracts.
Price components required for full end-to-end service for Domestic and Non-Domestic MTIPS:
- MTIPS Transport monthly recurring charge per port
- Dedicated Access Arrangements (DAA) Originating and Terminating Wireline Access (MRC) and (NRC)
- Features* ordered as needed by the Agency:
- Encrypted Traffic
- Agency Security Policy Enforcement
- Forensic Analysis
- Custom Reports
- Agency NOC/SOC Console
- Custom Certification and Accreditation (C&A) Support
- External Network Connection
- Encrypted DMZ
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement MTIPS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
* All MTIPS features are priced on an Individual Case Basis (ICB). CLINs with ICB prices are not available in the unit pricer.
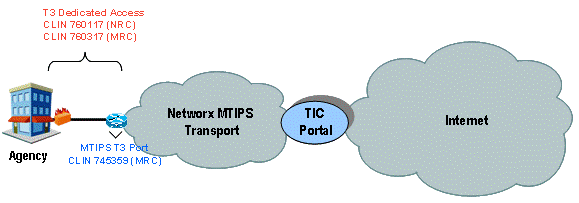
- MTIPS Transport: Choose CLIN 745359 (MTIPS - Dedicated T3 MRC per port)
- Access NRC: Choose CLIN 760117 Routine T3 Dedicated Access NRC
- Access MRC: Choose CLIN 760317 Routine T3 Dedicated Access MRC
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs may differ between contractors.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for MTIPS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for MTIPS.
For more information on the general MTIPS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.4.1.5 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.4.1.5 for pricing.
Multimode Wireless LANs (MWLANS)
2. Technical Description
MWLANS Technical Summary
Multimode/Wireless LAN Service provides Agency users with wireless access points, commonly called WiFi hotspots. MWLANS satisfies Agency requirements for global remote wireless connectivity to IP-based services from outside Government networks by offering 802.11 wireless connections in public hot spots around the world, or with custom-designed wireless networks deployed at Agency sites.
3. Technical Detail
MWLANS is a wireless transmission service for mobile terminals. Agency personnel, using WiFi-enabled notebook computers or personal digital assistants (PDAs), can access E-mail, government intranets, and the Internet when located within WiFi coverage areas or hotspots. MWLANS complies with the near-ubiquitous standard known as WiFi or wireless fidelity. Through partnerships with WiFi providers, the Networx contractors provide essentially global coverage.
Client software, which is loaded on the subscriber's mobile device, simplifies the process of accessing the network by providing MWLANS access tools to assist the Agency subscriber. Access to the network is secured through multiple security layers. An IP Security (IPSec) connection is established between the client software and the remote access server in the contractor's network. Traffic is encrypted between the mobile device and the MWLANS base station in private hotspot implementations.
The following Multimode/Wireless LAN Service capabilities are supported:
- The user is provided access only after authentication by user-id and password by the contractor. The user is able to change password as often as deemed necessary.
- The service supports dynamic IP address as well as single or multiple static IP address.
- The contractor provides commercially available Wireless Network Interface Cards (NICs) for mobile terminals.
Figure No. 1 depicts how MWLANS (i.e., a wireless LAN supporting IEEE 802.11 standard) obviates the needs for enterprise cabling.
Figure 1 - Wireline versus Wireless LANs
Figure No. 2 depicts the role of Wi-Fi in the IEEE family of wireless network specifications.
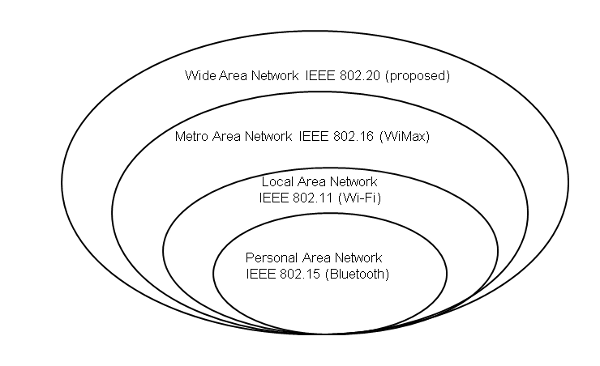
Figure 2 - IEEE Wireless Standards
Basic service level agreements (SLAs) supported include:
- Time to Restore.
For more information on the general MWLANS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.14.3 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B2.14.3 for pricing.
4. Price Description
MWLANS Price Basics
MWLANS is commonly known as WiFi or Wireless Fidelity. MWLANS consists of two service types:
- Subscription Service: A subscription-based service to public hot spots is available as a monthly or daily subscription.
- The monthly subscription offers unlimited usage.
- As part of the daily subscription, each subscription lasts 24 hours from the time of first logon to the service. Customers can logoff and logon to the service during the 24 hour period without incurring additional charges.
- Private Hotspot: Private WiFi hotspots are priced an Individual Case Basis (ICB). Private hotspots require an initial survey, design and network installation; a monthly recurring service charge applies after cutover.
MWLANS is a service that was not offered on the original FTS2001 contracts.
- Subscription Service
- Daily (per day) or Monthly (per month) Subscription
- Private Hotspot
- Survey, Design, and Setup (NRC ICB). CLINs with ICB prices are not available in the unit pricer
- Ongoing Operations and Maintenance (MRC ICB). CLINs with ICB prices are not available in the unit pricer
- No features available currently
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement MWLANS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
Price components required for MWLANS:
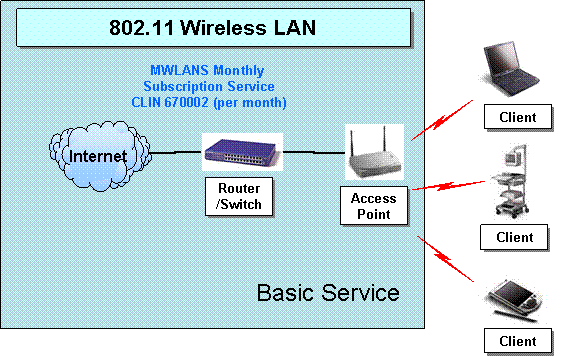
- Subscription Service: Choose CLIN 670002 (MWLANS Subscription Service Monthly, per month).
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs differ between vendors.
- Hotspot NRC: Choose NRC CLIN 670003 (price for this CLIN is ICB and is not available in the unit pricer)
- Hotspot MRC: Choose NRC CLIN 670004 (price for this CLIN is ICB and is not available in the unit pricer)
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs differ between vendors.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for MWLANS. The specific details found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for MWLANS
For more information on the general MWLANS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.14.3 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.14.3 for pricing.
National Security/Emergency Preparedness (NS/EP)
1. Overview
- National Security and Emergency Preparedness (NS/EP)/Telecommunications Priority Service (TSP) allows Agencies to establish priorities for circuit installation, restoration, and priority level changes in anticipation of, during, or after a national emergency. The service provider installs or restores circuits based on Agency priority level.
- Similar to FTS2001 NS/EP TSP
- Basic components required for service
- NS/EP TSP Priority Installations (NRC) - same as FTS2001 (FTS2001 SCIDs 1591, 1592, 1593, 21854, 21855)
- NS/EP TSP Priority Restorations (NRC) - same as FTS2001 (FTS2001 SCIDs 1594, 1598, 1599, 21858, 21859)
- NS/EP TSP Priority Restorations (MRC) - same as FTS2001 (FTS2001 SCIDs 1595, 1596, 1597, 21856, 21857)
- NS/EP TSP Priority Level for Design Change (NRC) - same as FTS2001 (FTS2001 SCIDs 1600, 1601, 21860)
- There are no features or SEDs for NS/EP TSP
2. Example
- Example: NS/EP TSP Priority Provisioning of a T1 circuit with Local Access Coordination
- TSP Priority Provisioning - Local Access Coordination (NRC): Choose CLIN 144004 (FTS2001 SCID 1591)
- TSP Restoration - Local Access Coordination (MRC and NRC): Choose CLIN 144002 (MRC) (FTS2001 SCIDs 1596 and 21857) and CLIN 144008 (NRC) (FTS2001 SCID 1598)
- TSP Priority Level for Design Change Local Access Coordination (NRC): Choose CLIN 144011 (NRC) - (FTS2001 SCID 1601)
Network Based IP-VPN Service (NBIPVPN)
2. NBIP-VPNS Technical Description
NBIP-VPNS Technical Summary
NBIP-VPNS provides secure, reliable transport of Agency applications across a contractor's multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) backbone infrastructure for geographically dispersed Agency locations. The service footprint covers CONUS, OCONUS and Non-Domestic locations. NBIP-VPNS is equivalent to FTS2001 services such as Private IP (PIP), Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS), and Very high performance Backbone Network Service (VBNS).
A virtual private network (VPN) is a network that is layered on top of an underlying transport network. The private nature of a VPN derives from the implementation of the VPN in an encapsulated form that is not visible to the underlying network. Virtual paths called 'tunnels' are established within the network. The main characteristic of a Network-based VPN is that all devices involved in building the VPN are systems owned by the contractor and located at the edge of the contractor's backbone. Tunnels usually terminate at the contractor's edge router.
The following diagram illustrates a layered architecture for NBIP-VPNS with its basic building blocks. The figure shows two independent network based VPNs interconnecting Agency sites with various forms of dial, broadband, and dedicated access to the contractor's network.
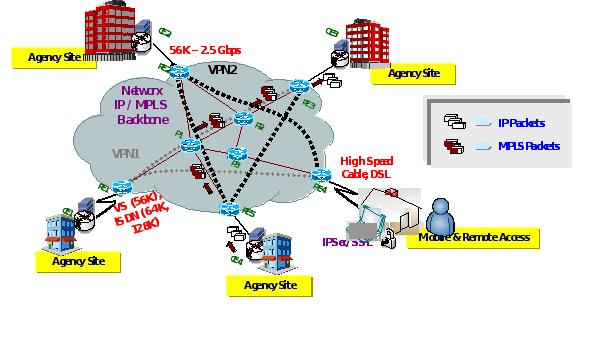
The basic building blocks are comprised of the following:
- CE1 - CE4 : Customer Edge Devices : Service Enabling Devices (SEDs)
- P1 - P3 : IP/MPLS Backbone Core Devices
- PE1 - PE5 : Provider Edge Devices
- VS (Voice Service) : Analog dialup at 56 Kbps
- ISDN : Circuit Switched Data Service (CSDS) at 64 Kbps and 128 Kbps
- High Speed Cable Access : 320 Kbps up to 10 Mbps
- SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) : Tunneling standard to facilitate flexible and secure access to the Agency network
- IPSec (IP Security): IPSec can be used in tunnel mode (entire packet is encrypted) or transport mode (only data is encrypted).
MPLS is a labeling scheme that is used by a network edge router to create paths across the network with specific constraints, such as acceptable packet delay. MPLS remains independent of the layer 2 and 3 protocols. IP packets are encapsulated, labeled, and switched between the source and destination PEs. Each CE and PE pair creates a local loop/access.
- VPN1 is a closed user group with PE1, PE3, and PE4 edge devices.
- VPN2 is a closed user group with PE2, PE3, PE4, and PE5 edge devices.
Note that an edge device can belong to multiple VPNs as illustrated by the PE3 and PE4 devices.
3. NBIP-VPNS Technical Detail
The NBIP-VPNS managed solution facilitates the shift of an Agency's capital and operational expenditure burdens to the Networx contractor. The contractor's core MPLS infrastructure can be used to create Agency specific topologies from partially-meshed to fully-meshed networks.
NBIP-VPNS supports a complete set of Agency site types:
- Intranet - provides secure tunnels between remote sites
- Extranet - enables trusted business partners to gain access to corporate information via secure/encrypted tunnels
- Remote Access - enables mobile/remote workers to gain access to secure corporate information via secure encrypted tunnels.
NBIP-VPNS allows Agencies to interconnect sites served by ATMS, FRS, PLS, and Ethernet services. The MPLS backbone creates virtual circuits between MPLS-enabled endpoints on the network, and provides the ability to establish Classes of Service (CoS) categorized by the type of traffic. The classification of traffic is defined at the Agency SED, and may be categorized as:
- Premium - Time-critical traffic such as voice, video, and VoIP
- Enhanced - Business-critical traffic such as database transactions
- Standard - Non-critical traffic such as email, http, ftp, etc.
End-to-end Quality of Service (QoS) can be provided through traffic classification and prioritization at the CE, PE, or core P devices (see the example figure). Agencies will receive customized NBIP-VPNS solutions that meet the Agency's specific requirements.
NBIP-VPNS features are available that include:
- Class of Service - Premium, Enhanced, and Standard as defined above
- High availability options for Customer Premises Equipment
- Internet Gateway Service - hardened trusted gateway between the internet and the IP-VPN service
- Interworking Services - transparent interworking across locations with ATMS, FRS, Ethernet, and the contractor's IPS
- Key Management - generation, distribution, storage, and security of encryption keys
- Security Services.
Basic service level agreements (SLAs) supported include:
- Availability
- Latency
- Time to Restore.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for NBIP-VPNS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for NBIP-VPNS.
For more information on the general NBIP-VPNS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.7.3 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.7.3 for pricing.
4. NBIP-VPNS Price Description
NBIP-VPNS Price Basics
NBIP-VPNS provides network-based private data transport between user locations. The pricing associated with NBIP-VPNS is based on a number of factors such as number of sites, bandwidth requirements, security services, and the type of access. CLINs are distinguished by access type:
- Embedded: One CLIN is ordered to obtain both access and transport with one rate.
- Independent (aka Access Services): A separate CLIN for the access is ordered from one contractor to connect an agency's site to another contractor's network.
- No access (i.e. Dedicated Access Arrangements (DAA)): A separate CLIN for the access is ordered along with transport service from the same contractor. This is the most commonly ordered option as shown in Example 1 below.
NBIP-VPNS is equivalent to FTS2001 services such as Private IP (PIP), Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS), and Very high performance Backbone Network Service (VBNS).
Price components required for full end-to-end service for Domestic and Non-Domestic NBIP-VPNS:
- NBIP-VPNS Transport monthly recurring charge per port
- DAA Originating and Terminating Wireline Access (MRC) and (NRC)
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- Class of Service (CoS)
- High Availability Options for CPE
- Internet Gateway Service
- Interworking Services
- Key Management
- Security Services.
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement NBIP-VPNS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
- Network Design and Engineering (NRC ICB), if necessary.
Example 1: NBIP-VPNS CONUS Dedicated T1
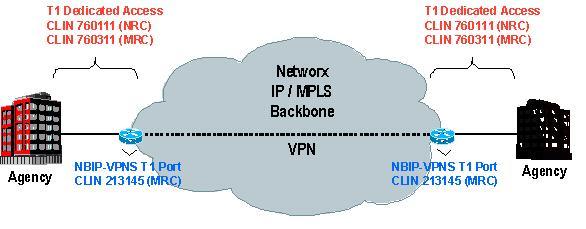
- NBIP-VPNS Transport: Choose CLIN 213145 (Port T1 MRC)
- Access NRC: Choose CLIN 760111 Routine DAA T1 NRC
- Access MRC: Choose CLIN 760311 Routine DAA T1 MRC
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs may differ between contractors.
- A Network Design and Engineering NRC may be applicable.
This document only addresses the NBIP-VPN service at contract award. Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for NBIP-VPNS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for NBIP-VPNS.
For more information on the general NBIP-VPNS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.7.3 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.7.3 for pricing.
Optical Wavelength Service (OWS)
1. Overview
OWS provides dedicated high speed optical transport networks to interconnect Agencies offices in different geographic regions. OWS is a new service that was not provided on FTS2001 contracts. Basic OWS is a point-to-point bi-directional, single link service provided by Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) equipment. However, networks with more flexible topologies such as multi-point to multi-point can be provided through emerging technologies.
OWS may be ordered in Metro areas or long haul CONUS wide, with OCONUS and Non-Domestic locations optional to offer. The Agency may opt to manage its own network or to obtain network management from its contractor. OWS is delivered to the customer's Service Delivery Point (SDP). The Agency can order OWS that will connect to and interoperate with:
- Contractor's metro and long haul networks
- Agency's Intranet
- Internet
- Other Agency networks.
The diagram below illustrates a CONUS wide contractor's Dense WDM (DWDM) transport network delivering optical carrier (OC) wavelengths. A Customer Network Management (CNM) feature is shown that could include alarm monitoring capabilities as well as capabilities for set up, modification, and tearing-down of connections.
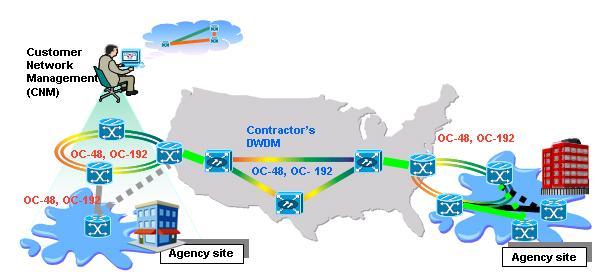
3. Technical Details
Government Agencies require dedicated broadband, framing-independent transport networks to interconnect their offices in different regions of the United States and internationally. In offering OWS, the contractor always provides the optronics equipment and fiber connectivity that comprise the transport network. Management of the network, however, may be performed by either the providing contractor or the Government Agency. In the latter case, Agencies will manage their dedicated networks via a Web portal or a remote User Interface (UI).
OWS is provided over Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) equipment where several wavelengths, sometimes referred to as lambdas, are multiplexed into a composite signal that is transmitted over a single fiber. An emerging technology known as Automatic Switched Transport Network (ASTN) may be offered as an option by the vendor. ASTN allows traffic paths to be established through the network through an ASTN agent. This agent is also known as an Optical Control Plane. The Optical Control Plane provisions the path through the network as requested by the customer edge-device (e.g., router) and allocates bandwidth for the user requested service, providing more flexibility in meeting user demand. ASTN further enables Agencies to order multi-point to multi-point connections, full mesh configuration, with routing constraints, and Quality of Service (QoS) options. OWS over ASTN also enables network-to-network interconnections to be established.
OWS provides advanced transport capabilities for Government Agencies. OWS allows Agencies to build high speed networks at OC-48 or OC-192 that require physical isolation of traffic to meet bandwidth intensive demands. It supports very fast service set-up/tear-down (i.e., in hours or minutes) and supports low latency and jitter. OWS enables collaborative, dynamic multi-terabit and grid-computing applications and supports fast restoration capabilities (in the sub-millisecond range)
Optional OWS features may be ordered that include:- Two levels of Customer Network Management
- Equipment Protection
- Geographical Diversity
- Protected Wavelengths
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for OWS. The specific details can be found within each Contractors Networx contract files and pricing notes for OWS
For more information on the general OWS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.5.4 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.5.4 for pricing.
5. Price Basics
OWS is a service that was not offered on the original FTS2001 contracts. OWS is provided over the following two transport technologies:
- Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM): OWS is provided over WDM equipment where several wavelengths, sometimes referred to as lambdas, are multiplexed into a composite signal that is transmitted over a single fiber.
- Automatic Switched Transport Network (ASTN): An emerging technology known as ASTN may be offered as an option by the vendor. ASTN allows traffic paths to be established through the network through an ASTN agent. This agent provisions the path through the network and allocates bandwidth for the user requested service, providing more flexibility in meeting user demand. ASTN further enables Agencies to order multi-point to multi-point connections.
The Monthly Recurring Charge (MRC) for transport consists of a fixed component plus a distance-dependent (per mile) component. CONUS-to-CONUS distance is calculated using the distance formula:
Distance (miles) = ROUNDUP(SQRT(((V1-V2)^2+(H1-H2)^2)/10),0)
Where (V1, H1) and (V2, H2) are the V and H coordinates of the locations, respectively
Distance involving OCONUS or non-domestic locations is calculated using airline miles. Note: The Networx Pricer automatically calculates the distance when given the originating and terminating locations.
Price components required for full end-to-end service for Domestic and Non-Domestic OWS:- OWS Transport monthly recurring charge with a fixed component and charge per mile
- Dedicated Access Arrangements (DAA) Originating and Terminating Wireline Access (MRC) and (NRC)
- Features ordered as needed
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement OWS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
Example 1: Domestic OWS WDM Routine Level for OC-48 wavelength
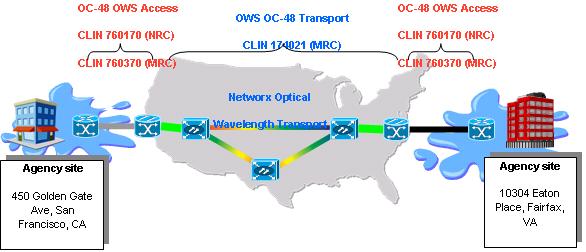
- OWS Transport: Choose CLIN 174021 WDM Routine OC48 - 2.5 Gbps - Domestic Long Haul Routine MRC per channel)
- Access MRC: Choose CLIN 760370 Routine DAA OWS OC-48 MRC (ICB) for both ends of the OC-48 Circuit. Prices for this CLIN are not available in the unit pricer. This circuit is priced as ICB (Individual Case Basis).
- Access NRC: Choose CLIN 760170 Routine DAA OWS OC-48 NRC (ICB) for both ends of the OC-48 Circuit. Prices for this CLIN are not available in the unit pricer. This circuit is priced as ICB (Individual Case Basis).
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs differ between vendors.
6. Price Additional Details
A fixed price is provided for Metro OWS, i.e., transport in a domestic metropolitan area. Thus, the Metro OWS price does not vary by metropolitan area.
Price components required for full end-to-end service for Metro OWS:
- OWS Transport monthly recurring charge (MRC) per channel
- DAA Originating and Terminating Wireline Access (MRC) and (NRC)
- Features ordered as needed
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement OWS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
Example 2: Metro OWS WDM Routine Level for OC-48 wavelength
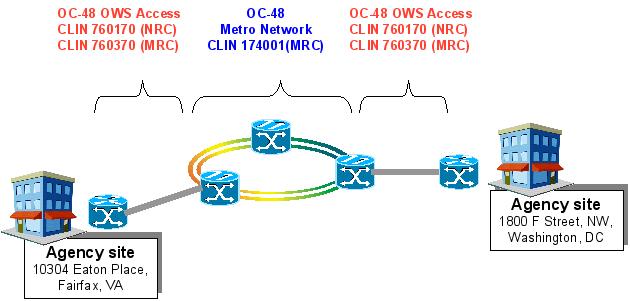
- OWS Transport: Choose CLIN 174001 WDM Routine OC48 - 2.5 Gbps - Metro MRC per channel)
- Access MRC: Choose CLIN 760370 Routine DAA OWS OC-48 MRC (ICB) for both ends of the OC-48 Circuit. Prices for this CLIN are not available in the unit pricer. This circuit is priced as ICB (Individual Case Basis).
- Access NRC: Choose CLIN 760170 Routine DAA OWS OC-48 NRC (ICB) for both ends of the OC-48 Circuit. Prices for this CLIN are not available in the unit pricer. This circuit is priced as ICB (Individual Case Basis).
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs differ between vendors.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for OWS. The specific details can be found within each Contractors Networx contract files and pricing notes for OWS.
For more information on the general OWS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.5.4 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.5.4 for pricing.
Premise Based IP-VPN Service (PBIPVPN)
2. Technical Description
Premises - Based IP VPN Service (PBIP-VPNS) Technical Summary
PBIP-VPNS provides secure, reliable transport of Agency applications across a contractor's multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) backbone infrastructure for geographically dispersed Agency locations. The service footprint covers CONUS, OCONUS and Non-Domestic locations. PBIP-VPNS is similar to FTS2001 services such as Private IP (PIP), Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS), and Very high performance Backbone Network Service (VBNS).
A virtual private network (VPN) is a network that is layered on top of an underlying transport network. The private nature of a VPN derives from the implementation of the VPN in an encapsulated form that is not visible to the underlying network. Virtual paths called "tunnels" are established within the network.
The following diagram illustrates a layered architecture for PBIP-VPNS with its basic building blocks. The figure shows two independent premises-based VPNs interconnecting Agency sites with various forms of dial, broadband, and dedicated access to the contractor's network.
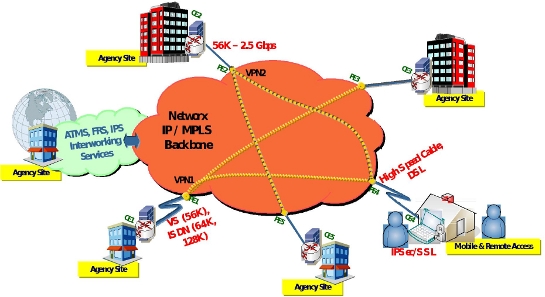
- CE1 - CE5 -> Customer Edge Devices
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs)
- PE1 - PE5 -> Provider Edge Devices
- VS (Voice Service) -> Analog dialup at 56 Kbps
- ISDN -> Circuit Switched Data Service (CSDS) at 64 Kbps and 128 Kbps
- High Speed Cable Access -> 320 Kbps up to 10 Mbps
- SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) -> Tunneling standard to facilitate flexible and secure access to the Agency network
- IPSec (IP Security) -> IPSec can be used in tunnel mode (entire packet is encrypted) or transport mode (only data is encrypted).
- Each CE and PE pair creates a local loop/access.
- VPN1 is a closed user group with PE1, PE3, and PE4 edge devices.
- VPN2 is a closed user group with PE2, PE4, and PE5 edge devices.
The basic building blocks are comprised of the following:
Note that an edge device can belong to multiple VPNs as illustrated by the PE4 device.
3. Technical Detail
Premises- Based IP VPN Service (PBIP-VPNS) Technical Detail
The PBIP-VPNS solution gives the Agency full end-to-end security control of the traffic; but carries a higher burden of capital and operational expenditure. The contractor's core MPLS infrastructure can be used to create Agency specific topologies from partially-meshed to fully-meshed networks.
The main characteristics of a premises-based VPN are:
- VPNs are typically IPSec tunnel-based, with customer edge (CE) devices encrypting and decrypting traffic before it enters and leaves the contractor's network.
- Because security is provided on an end-to-end basis, the contractor has no visibility into the IP tunnel.
- Contractor provides any-to-any connectivity via IP routing to build paths across the contractor's cloud.
- The CE may either be furnished by an Agency or by the contractor as part of a managed service.
PBIP-VPNS supports a complete set of Agency site types:
- Intranet - provides secure tunnels between remote sites
- Extranet - enables trusted business partners to gain access to corporate information via secure/encrypted tunnels
- Remote Access - enables mobile/remote workers to gain access to secure corporate information via secure encrypted tunnels
PBIP-VPNS allows Agencies to interconnect sites served by ATMS, FRS, PLS, and Ethernet services. The MPLS backbone creates virtual circuits between MPLS-enabled endpoints on the network and Agencies will receive customized PBIP-VPNS solutions that meet the Agency's specific requirements.
PBIP-VPNS features are available that include:
- High availability options for Customer Premises Equipment (CPE)
- Internet Gateway Service - hardened trusted gateway between the internet and the IP-VPN service
- Interworking Services - transparent interworking across locations with ATMS, FRS, Ethernet, and the contractor's IPS
- Key Management - generation, distribution, storage, and security of encryption keys
- Security Services
Basic service level agreements (SLAs) supported include:
- Availability
- Latency
- Time to Restore.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for PBIP-VPNS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for PBIP-VPNS.
For more information on the general PBIP-VPNS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.7.2 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.7.2 for pricing.
4. Price Description
Premises- Based IP VPN Service (PBIP-VPNS) Price Basics
PBIP-VPNS provides secure, reliable transport of Agency applications across a contractor's multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) backbone infrastructure for geographically dispersed Agency locations. Pricing for PBIP-VPNS is based on a number of factors such as number of sites, bandwidth requirements, security services, and the type of access.
PBIP-VPNS provides three basic solutions:
- Intranet - provides secure tunnels between remote sites
- Extranet - enables trusted business partners to gain access to corporate information via secure/encrypted tunnels
- Remote Access - enables mobile/remote workers to gain access to secure corporate information via secure encrypted tunnels
Price components required for full end-to-end service for Intranet and Extranet PBIP-VPNS:
- VPN Gateway Management (MRC ICB)
- PBIP-VPNS uses an underlying, separately priced, contractor-provided, IP network (see Section B.2.4.1 Internet Protocol Service (IPS) for pricing)
- DAA Originating and Terminating Wireline Access (MRC) and (NRC)
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- High Availability Options for CPE
- Internet Gateway Service
- Interworking Services
- Key Management
- Security Services
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement PBIP-VPNS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
- Network Design and Engineering Service (NRC ICB), if necessary
Example 1: PBIP-VPNS Intranet or Extranet
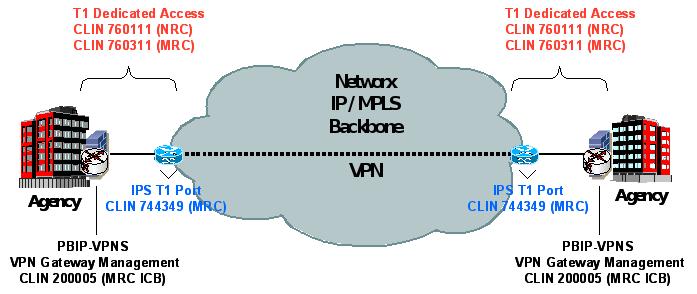
- PBIP-VPNS VPN Gateway Management: Choose CLIN 200005 (VPN Gateway Management). Prices for this CLIN are not available in the unit pricer. Prices are ICB.
- IPS Transport: Choose CLIN 744349 (Routine Dedicated T1 - CONUS MRC per port)
- Access NRC: Choose CLIN 760111 Routine DAA T1 NRC
- Access MRC: Choose CLIN 760311 Routine DAA T1 MRC
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs may differ between contractors.
- A Network Design and Engineering NRC may be applicable
5. Price Additional Detail
For a remote access solution, two types of access arrangements are possible:
- Independent Access - With Independent Access, an agency may use access from a different contract to connect with the contractor's IPS transport network. There are no additional charges for interfacing with independent access.
- Embedded Access - With Embedded Access, the access prices are included in the contractor's port prices.
Price components required for full end-to-end service for Remote Access PBIP-VPNS:
- VPN Gateway Management (MRC ICB)
- PBIP-VPNS uses an underlying, separately priced, contractor-provided, IP network (see Section B.2.4.1 Internet Protocol Service (IPS) for pricing)
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement PBIP-VPNS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
- Network Design and Engineering Service (NRC ICB), if necessary
Example 2: PBIP-VPNS Remote Access

- PBIP-VPNS VPN Gateway Management: Choose CLIN 200005 (VPN Gateway Management). Prices for this CLIN are not available in the unit pricer. Prices are ICB.
- IPS Transport: Choose CLIN 744011 (Routine Embedded-Cable High-speed (at 1.54 Mbps/384 kbps) - CONUS MRC per port)
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs may differ between contractors.
- A Network Design and Engineering NRC may be applicable
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for PBIP-VPNS. The specific details can be found within each Contractors Networx contract files and pricing notes for PBIP-VPNS.
For more information on the general PBIP-VPNS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.7.2 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.7.2 for pricing.
Private Line Service (PLS)
2. Technical Description
Private Line Service (PLS) Technical Summary
PLS provides dedicated connectivity on a non-switched basis between two or more designated Service Delivery Points (SDPs) for voice, data, video, and multimedia service applications at Agency-specified bandwidths. Because PLS is a dedicated service, the maximum bandwidth purchased its always available on an end-to-end basis. Connectivity between end points is permanently established until an Agency requests a service modification, move, or disconnect.
PLS may be ordered as domestic (CONUS and OCONUS), or non-domestic service. PLS supports data rates from subrate-DS0 to T3 to SONET OC192 (including E1, E3 and OCONUS equivalent analog circuits). The range of line speeds, route diversity and reliability options provided by PLS allows an Agency to satisfy a wide variety of requirements for mission critical applications.
The figure below shows an illustrative PLS configuration. PLS provides dedicated connections that can interoperate with Government specified SDPs such as PBXs, Multiplexers, Routers, Video codecs, and Group 4 Faxes.
PLS, because it is an industry standard offering, allows for connection to and interoperation with all other networks, including other Networx Universal and Networx Enterprise carriers networks. The figure illustrates a link provided by carrier A and terminated on its POP. In the example, a second link is provided by Carrier B, including the access link between the two networks. Coordination across the carrier networks may be required for interoperability.
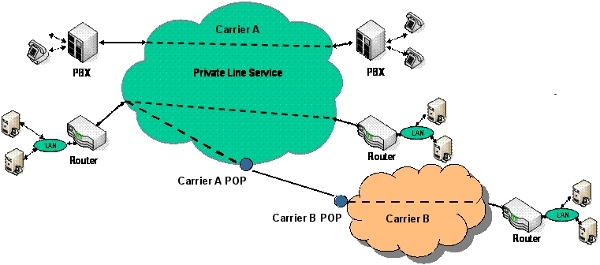
Illustrative PLS Configuration
3. Technical Detail
PLS is a legacy service that was offered on FTS2001 contracts that supports the full range of technical capabilities available on commercial offerings. PLS provides transparency to any transmission protocol used and ensures visibility to all bit sequences transmitted through the SDP. Data rates supported by PLS include:
- Subrate-DS0 and DS0.
- Channelized or Unchannelized T1, T3, E1 and E3.
- SONET OC-1 and OC1 Virtual Tributary.
- Channelized or Concatenated SONET OC-3, OC-12, OC-48, and OC-192.
- Analog circuits.
Non-domestic geographic coverage and offerings for PLS is specific to the different Networx service providers.
Mandatory PLS Features
Mandatory PLS features are detailed in the Networx Contracts Section C.2.5.1.2.1 and are briefly described below:
- Multipoint Connection
- In Branch Off mode where all SDPs are treated as one shared medium and each point can autonomously send and receive data.
- In Drop-and-Insert mode where channels of a channelized T1, T3, SONET OC-3, or SONET OC-12 service category can be dropped off and new channels can be simultaneously picked up or inserted.
Allows interconnection of three or more subscribers premises as follows:
- Special Routing
- Transport Diversity between connecting POPs. Provides two or more physically separated diverse routes for PLS circuits (each pair of diverse circuits constituting a relationship pair). The diverse routes do not share common telecommunications facilities or offices and a minimum separation of 30 feet is maintained throughout all diverse routes. If diversity is not available for a location, an acceptable negotiated solution will be proposed on an individual case basis.
- Transport Avoidance between connecting POPs. A capability will be provided for an Agency to specify a geographic location or route to avoid on the network. If that avoidance is not available in some locations, an acceptable negotiated solution will be proposed on an individual case basis.
Internal control (i.e., electronic flagging of routes) will be established for the PLS to prevent accidental dismantling of diversified/avoidance routes, especially during routine route optimization initiatives by the contractor.
Provides different routes for PLS circuits based on the following arrangements:
- 7.5 kHz Audio
Compression of a customer provided 7.5 kHz audio signal, delivered and received in analog form, for transmission over a DS0 channel.
Optional PLS features
PLS features that are optional to offer are:
- Voice grade conditioning for analog lines.
- Low Bit Rate Voice capability to allow voice at 32 Kbps for analog data at 4.8 Kbps in conformance to Adaptive Differential Pulse Code Modulation (ADPCM).
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for PLS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for PLS.
For more information on the general PLS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.5.1 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.5.1 for pricing.
4. Price Description
PLS Price Basics
PLS provides facilities for duplex (bi-directional) service between two or more specified end points; accordingly, PLS is priced without regard for direction of carried traffic. PLS is a legacy service that was offered on FTS2001 contracts under Dedicated Transport Service (DTS).
- PLS Transport is based on the Originating and Terminating locations and consist of the following pricing elements:
- Domestic to Domestic (same region): Monthly recurring charge with a fixed component and charge per mile. Distance between locations is calculated using airline miles between POPs
- CONUS to OCONUS: Monthly recurring charge with a fixed component, charge per mile from the CONUS POP to the CONUS gateway, and a fixed monthly recurring charge from the CONUS gateway to the OCONUS POP
- OCONUS to OCONUS (different region): Fixed monthly recurring charge based on originating and terminating Country/Jurisdiction IDs
- Domestic to Non-Domestic: Monthly recurring charge with a fixed component, charge per mile from the Domestic POP to the Domestic gateway, and a fixed monthly recurring charge from the Domestic gateway to the Non-Domestic POP
- Non-Domestic to Non-Domestic (different region): Fixed monthly recurring charge based on originating and terminating Country/Jurisdiction IDs
- Non-Domestic to Non-Domestic (same region): Fixed monthly recurring charge based on originating and terminating POP IDs
- DAA Originating and Terminating Wireline Access (MRC) and (NRC)
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- Multipoint Connection
- Special Routing
- 7.5 kHz Audio
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement PLS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
Price components required for full end-to-end service for Domestic and Non-Domestic PLS:
Note: The Networx Pricer automatically calculates the distance when given the originating and terminating locations.
Example 1: CONUS PLS Routine Level for T3 circuit
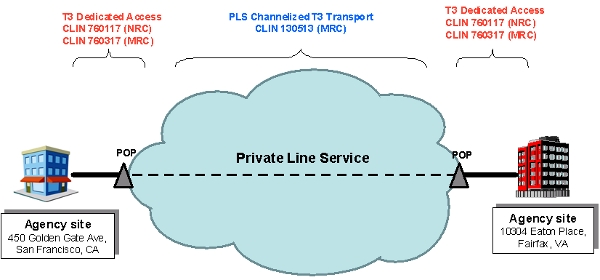
- PLS Transport: Choose CLIN 130516 (Full Channel Routine Channelized T3 MRC per circuit)
- Access NRC: Choose CLIN 760117 Routine DAA T3 NRC for both ends of the T3 circuit
- Access MRC: Choose CLIN 760317 Routine DAA T3 MRC for both ends of the T3 circuit
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs differ between vendors.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for PLS. The specific details can be found within each Contractors Networx contract files and pricing notes for PLS.
For more information on the general PLS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.5.1 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.5.1 for pricing.
Secure Managed E-mail Service (SMEMS)
1. Overview
The Networx contracts require a basic level of security management for its contractors that ensures compliance with Federal Government generally accepted security principles and practices, or better. The contracts employ adequate and reasonable means to ensure and protect the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of Networx services, Operational Support Systems (OSS), and Government information transported or stored in the contractor's Networx services infrastructure. These requirements are detailed in Section C.3.3.2 Security Management of the Networx contracts.
In addition to this mandatory level of security, the Networx contracts provide additional security services that may be ordered on a fee-for-service basis. These are:
- Managed Tiered Security Service (MTSS)
- Managed Firewall Service (MFS)
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Service (IDPS)
- Vulnerability Scanning Service (VSS)
- Anti-Virus Management Service (AVMS)
- Incident Response Service (INRS)
- Managed E-Authentication Service (MEAS)
- Secure Managed E-Mail Service (SMEMS)
The SMEMS offering is described below.
2. Technical Description
SMEMS Technical Summary
Email is one of the most important communication methods used by Agencies. However, its increasing use exposes Agency networks to a variety of security risks and unsolicited content, such as viruses, spam, and inappropriate material. Secure Managed Email Service (SMEMS) provides Agencies with a complete, fully managed email security solution.
Email security services implemented at Agency gateways and desktops usually attempt to handle events that have already breached the network. Any delay in applying security updates to this infrastructure exposes the network to rapid outbreaks and dynamic threats. SMEMS offers an additional layer of protection by proactively scanning and monitoring email traffic at the contractor's security platform, before it enters the Agency's network. The service supports email security functions such as Anti-Virus Scanning, Anti-Spam Filtering, and Content Control. The diagram below illustrates a sample SMEMS implementation. Illustrative hardware such as premises computers and servers are not provided as part of the SMEMS.
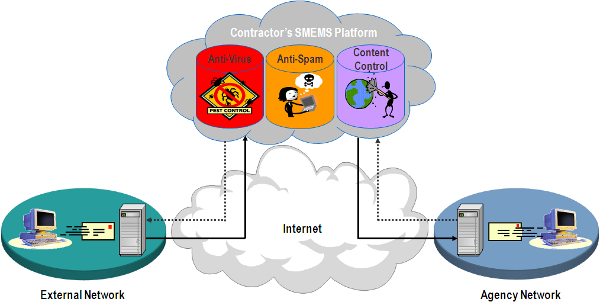
SMEMS builds on the FTS2001 contracts offerings. The service connects to and interoperates with the Agency's email system and networking environment. The service also supports connectivity to the Internet. SMEMS does not currently offer any features.
3. Technical Detail
SMEMS guards the Agency's network against growing security threats such as viruses, spam, unsolicited and inappropriate content. Security engines are continuously updated to maintain the effectiveness of the system. The contractor's fault tolerant and load-balanced platform can scan millions of email messages a day without noticeable delay to end-users. SMEMS works in conjunction with existing Agency email systems, and is implemented without additional investment in hardware and software at Agency sites.
SMEMS supports a range of technical capabilities that are available in commercial offerings. These include:
- Anti-Virus Scanning which monitors inbound and outbound messages and attachments for:
- Trojan horses, worms, macro viruses and other malicious files.
- Behaviors and characteristics that may indicate the presence of email viruses.
- Different strains of polymorphic viruses.
- Viruses in compressed files.
- Viruses in different languages (e.g., JAVA, ActiveX, Visual Basic).
- Anti-Spam Filtering which prevents unsolicited marketing and messages from entering the Agency's network, and having the effect of draining human, bandwidth and storage resources. The system shall support the following:
- Anti-spam methods including fingerprinting, blacklists, open relay blocking, honeypots, Bayesian probability, heuristic and rule-based filtering, as appropriate.
- Capability to distinguish between legitimate email and spam, reducing false negatives and false positives.
- Agency ability to customize spam lists, and specify domains, IP and email addresses which are to be allowed or blocked.
- Content Control which screens inbound and outbound email for content that may signal system abuse or violation of Agency communications policies. The systems shall support the following:
- Blocking of specific words, phrases, adult or sexually explicit material, and other inappropriate content.
- Preventing transmission of intellectual property and confidential information.
- Stopping files and attachments based on type, size, formats, number, and delivery time.
- Response to email infections and Agency policy violations, providing the following at a minimum:
- Alerts notifying the Systems/Network Administrator.
- Alerts notifying the sender and recipient of the message.
- Isolation of virus infected for cleaning, deletion, or post alert analysis and interpretation.
- A secure Web-based management interface which provides, but is not limited to, the following:
- Configuration tools allowing the Agency to set policies, rules and routing requirements.
- Email activity trends, such as daily, weekly, monthly, and yearly volumes and patterns.
- Email cleaned, deleted or rejected.
- Forwarding of weekly reports to designated Agency representative.
- Management of user and domain permissions.
- Potential threats flagged.
- Real-time service statistics and availability data.
- User and company domain activity.
- Viruses, spam, and other inappropriate content blocked.
- Email monitoring in real-time and on a 24x7 basis, for timely and accurate detection of harmful traffic and unwanted content.
These and other service capabilities are detailed in Section C.2.10.8.1.4 Technical Capabilities of the Networx contracts.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for SMEMS. The specific details can be found within each contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for SMEMS.
For more information on the general SMEMS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.10.8 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.10.8 for pricing.
4. Price Description
SMEMS Price Basics
SMEMS provides a complete, secure and fully managed email security solution. The service mitigates security holes and flaws before they are exploited. SMEMS is similar to FTS2001 Secure Managed Email.
Price components required for SMEMS are:
- Basic service (NRC and/or MRC per email account).
- No features available currently.
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement SMEMS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
Example 1: SMEMS
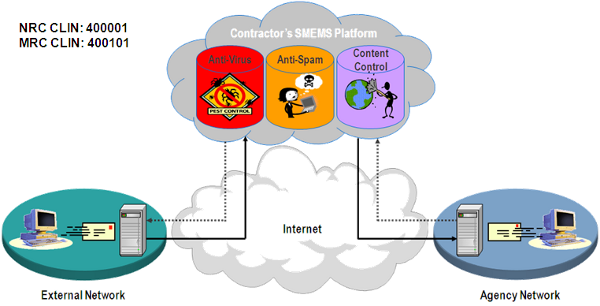
- Basic Service NRC: Choose CLIN 400001 (SMEMS NRC per email account).
- Basic Service MRC: Choose CLIN 400101 (SMEMS MRC per email account).
- SEDs may be required to implement SMEMS. Illustrative hardware is not provided as part of the SMEMS.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for SMEMS. The specific details can be found within each contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for SMEMS.
For more information on the general SMEMS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.10.8 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.10.8 for pricing.
Service-Enabling Devices (SEDS)
2. Technical Description
Service Enabling Devices (SED) Technical Summary
A SED is a unit of, or separately priced component within, contractor-provided and owned equipment used to meet the interface requirements for an individual Networx service. In addition, it can be used to implement access aggregation and integration to provide a lower service delivery cost to the Government. A SED may also be a unit of, or separately priced component within, contractor-provided and owned equipment and/or software used to enable the requirements associated with the Management & Applications Services and the Security Services.
A SED will only be offered as needed to provide delivery of a service that is acquired under the Networx contract.
Unless otherwise specifically agreed to by the Government, a SED includes all equipment (hardware, firmware, and software) needed within the contractor's network to provide a Networx service (e.g., any wireline access arrangement-implementing equipment, such as a SONET access arrangement Add/ Drop Multiplexer (ADM)). Any equipment at the contractor's Point of Presence (POP) or equipment otherwise within the contractor's backbone transport network (i.e., POP to POP) is part of the Networx service (access and/or transport service) and thus is not considered as a SED.
A SED could be of the following technology-based categories:
- Wireline SEDs, such as a Channel Service Unit/Data Service Unit (CSU/DSU), a router, or a multiplexer.
- Wireless SEDs, such as a cell phone.
- Satellite SEDs, such as a Very Small Aperture Terminal (VSAT).
- Management & Applications, and Security services SEDs, such a teleconferencing unit or an Anti-Virus software.
In addition, a SED could be physically a:
- Stand-Alone Unit - such as CSU/DSU, Cellular handset, Mobile handset, or a Satellite handset.
- Packaged Unit - that consists of a base unit and configurable components, such as routers, multiplexors, and VSATs.
- Base Unit - that consists of chassis, shelves, shelf-processors, cables, power supplies, etc.
- Configurable Components - that include plug-in, attachable, or loadable items, such as interface cards, memory and OS upgrades, other firmware or software items needed to configure the base unit.
- Accessories - additional components that enhance the use of a device, but that do not support the main function of the device (e.g., a spare battery, a carrying case for a cellular or mobile satellite handset, or an additional copy of a user manual).
The diagram below shows different types of SEDs for different Networx service types.
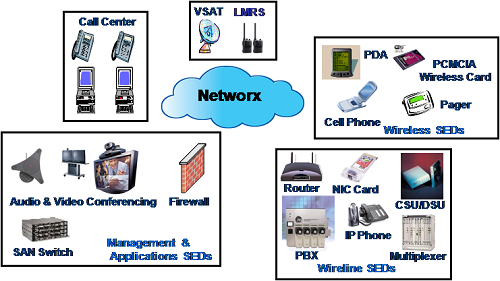
3. Technical Detail
SEDs are numerous and their technical details vary widely based on customers' diverse requirements for connecting to Networx services. Therefore, it is impractical to provide specific technical details in this document for all SEDs available on the Networx contract.
In addition, SEDs will continue to evolve over the life of the Networx contract, and newer SEDs will replace older SEDs.
For more information on the general SEDs specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.1.7 of the Networx contract for a technical description and Section B.4 for additional information and the pricing structure.
4. Price Description
Service Enabling Devices (SED) Price Basics
A Service Enabling Device (SED) is equipment used to meet the requirements for an individual Networx service. A SED is provided only as needed to deliver a service that is acquired under the Networx contracts. Unless otherwise specifically agreed to by the Government, all equipment (hardware, firmware, and software) needed within the contractor's network to provide service is part of the access and/or transport service and is not to be separately priced as a SED. Pricing for the same SED may vary by its installed geographic location (i.e., domestic (CONUS), domestic (by OCONUS Jurisdiction), and non-domestic (by Country/Jurisdiction)).
A SED is generally either (1) a stand-alone unit or (2) a packaged unit. However, for pricing purposes, a SED is identified by its separately priced components, as described below. SEDs pricing includes separate CLINs for the following SED Types:
- Stand-alone unit: A SED stand-alone unit is a self-contained, fully functioning device (e.g., a CSU/DSU or handset).
- Packaged SEDs: A SED packaged unit consists of a package of component elements including a separately-priced "base unit" (containing all minimally required elements) and a variable list of separately-priced additional configurable components. Examples of packaged units are routers, smart multiplexers, and VSATs.
- Base unit of packaged SEDs: The SED base unit includes only those underlying base components that are needed to support the common or shared functions of the equipment before the addition of the configurable components. Accordingly, the SED base unit price includes common use components such as chassis, shelves, interconnecting and power cables, internal power supply(s), mounting fixtures, antenna, CPU and both hardware and firm/software components of basic memory and operating system, as applicable.
- Configurable component: Configurable components are those separately priced components needed to equip the base unit of a packaged SED. Such configurable components include the plug-in, attachable, or loadable items such as line, circuit, network, and feature cards/blades, memory and/or operating system upgrades, and other firmware or software items needed to configure the base unit so that it can fully implement the required functionality of the packaged SED. Additional components may be added separately to upgrade or modify a previously installed packaged unit.
- Accessories: Accessories are separately-priced additional components that enhance the use of a device, but are not needed to implement the essential function(s) of the device (e.g., a spare battery or carrying case for a cellular or mobile satellite handset or an additional copy of a user manual).
Additionally, for pricing purposes, the priced components for a SED are placed in one of four separate technology-related pricing sections:
- Wireline SEDs - A wireline SED is a unit of contractor-provided wireline equipment, such as a CSU/DSU, router or multiplexer, necessary to complete a wireline Networx service. Wireline SEDs are composed of all necessary hardware, firmware, and software, and are associated with a fixed location.
- Wireless SEDs - A wireless SED is a unit of contractor-provided terrestrial wireless equipment, such as a cell phone or pager necessary to fully implement a wireless Networx service or to extend wireline service where a wireline termination is not possible. Wireless SEDs are composed of all necessary hardware, firmware, and software, and are generally mobile (i.e., not associated with a fixed location).
- Satellite service associated SEDs - A Satellite SED is a unit of contractor-provided uplink or downlink related equipment, such as a VSAT or handset, necessary to complete a Networx satellite service requirement. Satellite SEDs are composed of all necessary hardware, firmware, and software, and may or may not be associated with a fixed location.
- Management, Applications, and Security Service associated SEDs - A Management, Applications, and Security SEDs is a unit of contractor-provided equipment and/or software (e.g., teleconferencing unit, security fob, or Anti-Virus software) necessary to enable the requirements of a Networx Management and Applications, or Networx Security Service Type. These SEDs are composed of all necessary hardware, firmware, and/or software, and may or may not be associated with a fixed location.
Price components required for SEDs comprise some or all of the following:
- Charge for the SED consisting of one of the following two options:
- Device Non-Recurring Charge (DNRC) a one-time charge for use of a SED which is paid in a single installment, or
- Device Monthly Recurring Charge (DMRC) a monthly charge for a selected time period (24, 36, or 48, months). The DMRC is an amortized DNRC price over the selected time period. Early termination charges are incurred if the Agency doesn't meet the term commitments for the DMRC (see section B.4.8.2 for information on SEDs early termination charges). DMRCs apply only when the DNRC stand alone, base unit, or configurable component price is equal to or greater than $250.
- Maintenance MRC (MMRC) to cover ongoing maintenance, starting with the accepted installation or completed delivery of the SED(s).
- Install NRC to cover initial installation and outside moves of a SED connected at a fixed location.
- Inside Move NRC to cover inside moves of a SED(s) at a fixed location (i.e., an equipment move within same premises without change of the access arrangement).
- Upgrade NRC to cover on-site modification or upgrade of installed equipment at a fixed location.
Deinstallation of contractor-owned devices installed on the customer's premises (a fixed location), including storage, packaging for shipment, and/or transportation, are provided by the contractor at no additional charge to the Government.
Example 1: Wireline Cisco 2811 Router for a CONUS location:
There are two ways to find prices for the above SED:
- Browse the CLIN tree:
- Click "Browse Available CLINs."
- Open the "Service Enabling Devices" folder.
- Open the "Wireline (S_WRLN)" folder.
- Open the "Routers" folder.
- Select "S_WRLN Cisco 2811 CISCO2811 NRC."
- Select "CONUS" Area of the World (AOW).
- Use the search box:
- In the "Find CLIN" search box enter a description of the SED and hit "Enter". The more detailed information that is entered in the search box such as manufacturer, model number, and part number, there will be higher accuracy with the results of the search (in terms of finding the specific SED prices). In this example, enter "Cisco 2811 router" and then select "Cisco 2811 CISCO2811 NRC S_WRLN / Routers (990125)" from the produced list.
- Select "CONUS" Area of the World (AOW).
In this example, all Networx Universal and Enterprise contractors provide the following SED prices for CLIN 990125 (Cisco 2811) with the noted exceptions:
- DNRC.
- DMRC.
- 24 month (not offered by all contractors).
- 36 month.
- 48 month (not offered by all contractors).
- MMRC.
- Install NRC.
- Inside Move NRC.
- Upgrade NRC.
For more information on the general SEDs specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.1.7 of the Networx contract for a technical description and Section B.4 for additional information on the pricing structure.
Storage Service (SS)
2. Technical Description
Storage Services (SS) provide Agencies with highly available, robust, and resilient storage services so that Agency data can be stored and accessed securely without interruption through reliable, disaster-tolerant systems. Three storage services are available to Agencies through Networx:
- Backup and Restore (BBKUP&R). Enables Agencies to backup copies of their data at the contractor's data centers. The government's data is restored as required by the Agency.
- Network Attached Storage (NAS). Enables Agencies to securely store data organized as files on a device or an array of devices at the contractor's data centers.
- Storage Area Networks (SANs). Enables Agencies to securely store large amounts of data on a high-speed shared area network dedicated to storage at the contractor's data centers.
An Agency may also need additional services such as, but not limited to, assessment and development of Agency storage strategy, engineering and detailed design, and support of Agency Continuity of Operations (COOP).
The Agency can order SS that will connect to and interoperate with the contractor's data centers, the Agency's data center networks and/or back-up sites. Interoperability and connectivity with Agency SANs and LANs is provided. Interconnection of storage sites and Agency sites may be accomplished by the use of underlying transport services supported by the Networx contracts (e.g., SONETS, DFS, OWS, PLS, and Ethernet). SS is a new service that was not provided on the FTS2001 contracts.
The diagram below illustrates the three SS types. The connectivity between the Agency sites and the contractor's data centers is via the contractor's network.
The 3 types of SS: BBKUP&R, NAS, and SANs
3. Technical Detail
Government Agencies rely on Networx contractors to store critical data and SS enables them to acquire storage media and storage networks without having to invest in infrastructure. The SS through Networx allows Agencies to utilize storage space whether off-site; using transportable media or even if the media can be remotely accessed (BBKUP&R) through automation tools.
The SS supports state-of-the-art, commercially available technologies and transport protocols. The contractors are required to partition their infrastructure installed in their data centers and assign specific partitions for specific Agency. The contractor must support storage services that meet Agency security certification and accreditation (C&A) requirements, including storage services for classified data if needed by the Agency.
The flexibility provided by the storage services ranges from managing the storage infrastructure in their data centers in accordance with the contractor's policies up to customizing the service to allow compatibility with Agency storage management policies, procedures, and tools.
With Backup and Restore (BBKUP&R), the contractor enables backup of Agency designated files and databases automatically, including files that are open at the time of the backup. The following functions are also provided:
- 1. Daily automated data backup, and more frequent schedules if needed by an Agency.
- 2. Daily incremental and full weekly backups of data, and more frequent schedules if needed by an Agency.
- 3. Data secured in a geographically separate location as required by an Agency. The contractor provides storage facilities that meet Agency security requirements.
- 4. Retention of full monthly backup data for at least three months, and for longer if needed by the Agency.
- 5. Restoration of the backup data performed as needed by the Agency.
- 6. Remote Data Replication (RDR) services available in geographically separate locations. Replication supported may be manually or automatically initiated by the Agency.
- 7. Remote Data Mirroring (RDM) services provided to enable two or more locations, such as Agency data centers and COOP sites, to store and share the same data.
With NAS and SAN services, Agencies are provided with scalable and robust storage infrastructures that meet Agency's requirements protected by rigorous security policies and procedures.
With NAS, storage devices "plug-and-play" into existing LANs, at the contractor's data centers, with a minimum of effort. NAS is suitable for read-intensive applications. NAS uses an IP network architecture and provides file systems rather than raw storage volumes.
SANs are high-speed, special-purpose networks (or sub networks), similar to LANs, which connect all the servers and clients to a shared pool of storage devices. They enable the sharing and exchange of large amounts of data dynamically, regardless of the operating system or application. They interconnect different kinds of data storage devices with associated data servers on behalf of a larger network of users. SANs located at the contractor's data centers are partitioned to be shared by multiple agencies.
SS enables Agencies to separate storage traffic from the rest of the network traffic thus improving network performance and simplifying network management.
There are no Features associated to the Networx Storage Services. The supported interfaces at the storage device and network levels range from 125 Mbps up to 10 Gbps supporting a range of protocols such as Gigabit Ethernet, Fibre Channel, etc.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for SS. The specific details can be found within each contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for SS.
For more information on the general SS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.11.10 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.11.10 for pricing.
4. Price Description
SS Price Basics
SS allows users to securely access data stored in the Networx contractors. data centers. Three types of SS are available:
- Backup and Restore (BBKUP&R). Enables Agencies to backup copies of their data at the contractor's data centers. The government's data is restored as required by the Agency.
- Network Attached Storage (NAS). Enables Agencies to securely store data organized as files on a device or an array of devices at the contractor's data centers.
- Storage Area Networks (SANs). Enables Agencies to securely store large amounts of data on a high-speed shared area network dedicated to storage at the contractor's data centers.
SS was not offered on the original FTS2001 contracts.
SS Price Details (BBKUP&R)
Usage charges are charged at the corresponding unit price per GB for the volume used.
- Underlying access and transport services, such as SONETS, DFS, OWS, PLS or Ethernet, to provide connectivity.
- Basic Service (NRC per server).
- Usage (Usage per GB).
- No features available currently.
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement SS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
SS Price Details (NAS and SAN)
The basic service charge includes up to 2 Terabytes of storage per month. Usage-based charges only apply to monthly storage in excess of two Terabytes, and are charged on a per Gigabyte basis.
Price components required for SS NAS and SAN:
- Underlying access and transport services, such as SONETS, DFS, OWS, PLS or Ethernet, to provide connectivity.
- Basic Service (NRC and/or MRC per service).
- Usage (Usage per GB).
- No features available currently.
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement SS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between
Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
- Transport: Choose Networx telecommunications service such as OWS.
- Basic Service NRC: Choose CLIN 500002 (Managed Network Attached Storage (NAS) NRC per service).
- Basic Service MRC: Choose CLIN 500102 (Managed Network Attached Storage (NAS) MRC per service).
- Usage: Choose CLIN 500501 (Managed Network Attached Storage Usage per GB).
- SEDs may be required to implement SS.
- Transport: Choose Networx telecommunications service such as PLS.
- Basic Service NRC: Choose CLIN 500003 (Managed Storage Area Network (SAN) NRC per service).
- Basic Service MRC: Choose CLIN 500103 (Managed Storage Area Network (SAN) MRC per service).
- Usage: Choose CLIN 500601 (Managed Storage Area Networks Usage per GB).
- SEDs may be required to implement SS.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for SS. The specific details can be found within each contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for SS.
For more information on the general SS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.11.10 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.11.10 for pricing.
Synchronous Optical Network Service (SONETS)
2. Technical Description
SONETS Technical Summary
SONETS is a Networx service that enables Agencies to build optical transport networks that are high bandwidth, with a high level of reliability and traffic isolation. These transport networks are built using facilities from the contractor's optical backbones. SONETS provides proactive performance monitoring and enables self-healing functions with robust network management.
SONET is the U.S. standard for fiber optic synchronous transmission rates from 51.84 Mbps (OC-1) to beyond 13.27 Gbps (OC-256). The International Telecommunications Union version of the standard is the Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH), which begins at 155 Mbps. SONETS is capable of interoperating with SDH in CONUS by providing gateway functions to transport SDH traffic over a SONET infrastructure.
The diagram below illustrates a CONUS wide optical transport network built over a contractor's optical backbone that interconnects Agency's headquarters with branch offices. The Agency's optical network depicted is able to deliver bandwidth via electrical User to Network Interfaces (UNIs) i.e. DS1, DS3, E1, E3 and optical carrier (OC) interfaces i.e. OC-3 up to OC-192.
The contractor's optical backbone in the example below is built by multiple SONET rings designed with two different protection methods (e.g., UPSR, BLSR). The core rings use Bidirectional Switched Ring (BLSR) protection and the metro/access rings uses Unidirectional Path Switched Ring (
Example SONETS Implementation
SONETS may be ordered in Metro areas or long haul CONUS wide, with OCONUS and Non-Domestic locations optional to offer. As specified in Section C.2.5.2.1.3 of the Networx contracts, the Agency can order SONETS that will connect to and interoperate with:
- Government specified terminations (e.g., Service Delivery point (SDP)-to-SDP, Point of Presence (POP)-to-POP).
- All other networks including other Networx contractors networks where industry standards are used.
3. Technical Detail
General
Basic SONETS is a point-to-point bi-directional, single link service. Private networks with more complex topologies such as rings and mesh can also be provided with Next Generation SONETS capabilities.
SONETS transport technologies have evolved from a strict Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) channel allocation to more flexible bandwidth allocation methods provided by Next Generation SONET technologies. These include Link Adjustment Capacity Scheme (LCAS), Generic Framing Procedure (GFP) and Virtual Concatenation (VCAT). Basic SONET has always enabled Agencies to interconnect dissimilar networks such as Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM), Frame Relay (FR), and IP. However, with the additional protocols supported by Next Gen SONET (LCAS, GFP and VCAT), bandwidth efficiency has been considerably improved.
SONETS Technical Capabilities
Agencies subscribing to SONETS may opt for a single connection point-to-point which will be a dedicated connection between two sites with a dedicated, built-in protection channel that will not be used by any other customer's traffic. The Networx contractors support other network topologies such as rings and mesh. More detailed descriptions of SONETS capabilities are provided in Section C.2.5.2.1.4 of the Networx contracts.
SONETS Features
SONETS features that may be orderable are detailed in Section C.2.5.2.2.1 of the Networx contracts and are listed below:
- Bandwidth On Demand (BoD - Optional to offer).
- Channelization (SONET interfaces to Agency CPE that seamlessly interface with the Contractor's SONET network for data transport).
- Dedicated Metro Ring.
- DS1 Rate Synchronization Services (Optional to offer).
- Equipment Protection1:1 and 1+1 - CPE (Protection to user network interfaces at the SDP, where the protection channel is bridged to a failed working channel).
- Network Protection.
- Framing for Electrical Interfaces.
- Geographic Diversity protection.
- Local and Remote Node Multiplexing.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for SONETS. The specific details can be found within each Contractors Networx contract files and pricing notes for SONETS.
For more information on the general SONETS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.5.2 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.5.2 for pricing.
4. Price Description
SONETS Price Basics
SONETS is highly reliable transport that provides proactive performance monitoring thus preventing single and multiple failures, and further enables self-healing functions and robust network management. SONETS is a service that was not offered on the original FTS2001 contracts. SONETS is available as:
- Fixed Bandwidth (FB): Transport based on a fixed amount of bandwidth
- Bandwidth-on-Demand (BoD): Transport based on measured bandwidth usage (BoD is optional for Networx contractors. It is currently not offered but may be offered in the future.)
The MRC for transport consists of a fixed component plus a distance-dependent (per mile) component. The mileage charge for SONETS transport is based on the total mileage between the contractor's designated connecting POPs for any two customer locations. CONUS-to-CONUS distance is calculated using the distance formula:
- Distance (miles) = ROUNDUP(SQRT(((V1-V2)^2+(H1-H2)^2)/10),0)
- Where (V1, H1) and (V2, H2) are the V and H coordinates of the locations, respectively
Distance involving OCONUS or non-domestic locations is calculated using airline miles. Note: The Networx Pricer automatically calculates the distance when given the originating and terminating locations.
Price components required for full end-to-end service for Domestic and Non-Domestic FB SONETS:
- SONETS Transport monthly recurring charge with a fixed component and charge per mile.
- DAA Originating and Terminating Wireline Access (MRC) and (NRC)
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency
- Channelization
- Dedicated Metro Ring is priced on an Individual Case Basis (ICB). CLINs with ICB prices are not available in the unit pricer
- Equipment Protection 1:1 - CPE
- Equipment Protection 1+1 - CPE
- Equipment protection - Network Side
- Framing for Electrical Interfaces
- Geographic Diverse protection
- Local and Remote Node Multiplexing
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement SONETS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
- SONETS Transport: Choose CLIN 154013 Routine Fixed Bandwidth (FB) SONET OC-3 MRC
- Access NRC: Choose CLIN 760118 Routine DAA OC-3 NRC (ICB) for both ends of the OC-3 Circuit. Prices for this CLIN are not available in the unit pricer. Prices are ICB.
- Access MRC: Choose CLIN 760318 Routine DAA OC-3 MRC (ICB) for both ends of the OC-3 Circuit. Prices for this CLIN are not available in the unit pricer. Prices are provided by the contractor after a street address has been provided and a case number has been assigned.
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs differ between vendors.
Example 1: Domestic SONETS FB OC-3
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for SONETS. The specific details can be found within each Contractors Networx contract files and pricing notes for SONETS.
For more information on the general SONETS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.5.2 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.5.2 for pricing.
Teleworking Services (TWS)
1. Technical Description
TeleWorking Services (TWS) Technical Summary
Agencies use Networx TeleWorking Services (TWS) to enable employees to perform assigned work duties remotely from their primary office location. TWS offer Agencies services ranging from providing a teleworker's basic telecommunications connectivity to providing a fully managed service comprising a comprehensive set of features including training for the teleworker.
TWS enables geographically dispersed Agency staff to perform their assigned job duties through the use of electronically supported communications and collaboration capabilities. TWS is available in CONUS, OCONUS, and Non-Domestic locations.
TWS effectively enhances the overall Agency mission and business processes. This service offers employees greater flexibility in their working location and hours. There is evidence of an improvement in employee morale as workers avoid the long commutes and lost time. TWS meets the Federal telework mandates including the Public Law 106-346 Section 359.
The illustrative TeleWorking scenario below shows teleworker's at a remote office in New York, a small home office in Maine, and a mobile location in Colorado, all in direct voice and data communication with their central office in Washington D.C. Teleworkers typically establish a connection via a Virtual Private Network (VPN) tunnel through software provided by the Networx contractor.
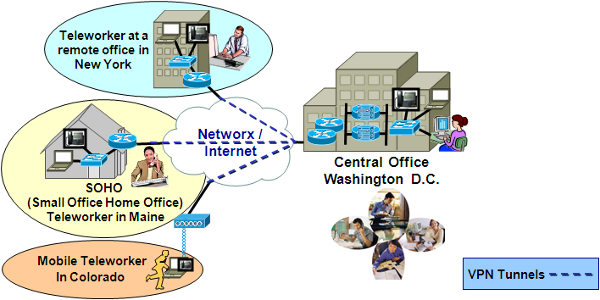
TeleWorking Scenario
2. Technical Detail
TWS is an application layer service that uses underlying network services to enable remote communications. It connects geographically dispersed teleworkers and interoperates with the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) and the Internet. It will interface with the following Networx services:
- Voice Services (Section C.2.2 of the Networx contracts).
- Internet Services (Section C.2.4 of the Networx contracts).
- Private Line Services (Optional) (Section C.2.5.1 of the Networx contracts).
- Combined Services (Section C.2.6 of the Networx contracts).
- Virtual Private Network Services (Section C.2.7 of the Networx contracts).
Technical Capabilities
(TWS) technical capabilities are described in detail in Section C.2.12.1.1.4 of the Networx contracts and are summarized below:
- Two tiers of TWS
- Tier 1 Basic - The Agency manages the service. The contractor provides basic connectivity and related components necessary to establish telework capabilities for the subscriber.
- Tier 2 Enhanced - The contractor designs and implements a custom service for the subscribing Agency.
- Connectivity to enable data and voice services for a remote teleworker location.
- Secure services with authentication and encryption capabilities before granting access to authorized users.
- Audit trails, management utilities, class of service capabilities, multiple protocols, and multiple domains and dynamic/static addressing.
- Capability to deliver TWS to specified endpoint devices such as analog telephones, FAX devices, IP phones, etc.
Features
TWS features are described in detail in Section C.2.12.1.2.1 of the Networx contracts and are summarized below:- Anti-Virus Management.
- Follow Me Service (Optional).
- Instant Messaging (Optional).
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention.
- Managed Firewall.
- Managed Moves, Adds, and Changes Support.
- Teleworker Firewall that is premise based at the TWS endpoint location.
- Video Conferencing (Optional).
- Voice Mail.
- Voice Service with call waiting, caller ID, Caller ID Block, and three way conference calling.
- Vulnerability Scanning.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for TWS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for TWS.
For more information on the general TWS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.12.1 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.12.1 for pricing.
3. Price Description
TWS Price Basics
(TWS) provides remote communications to Agency's networks and applications using underlying Networx services. TWS offers two tiers of service ranging from basic connectivity to a custom service:
- Tier 1 - Basic: The Agency manages the service. The contractor provides basic connectivity and related components necessary to establish telework capabilities for the subscriber.
- Tier 2 - Enhanced: The contractor designs and implements a custom service for the subscribing Agency. Prices for Tier 2 are on an Individual Case Basis (ICB) and are not available on the unit pricer.
TWS was not offered on the original FTS2001 contracts.
- Underlying transport services to provide connectivity
- Basic service (NRC and/or MRC per seat)
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- Anti Virus Management*
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention*
- Managed Firewall*
- Managed Moves, Add, and Changed Support
- Teleworker Firewall
- Voice Mail
- Voice Service*
- Vulnerability Scanning*
- Video Conferencing*
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement TWS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
Price components required for TWS:
* These features are not available under TWS on the unit pricer. Please see the individual services for pricing.
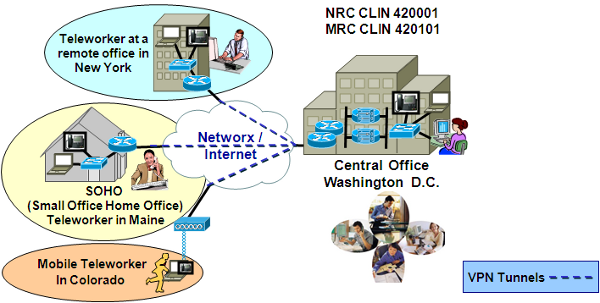
- Underlying Transport: Choose Networx telecommunications service such as IPS
- TWS Basic Service NRC: Choose CLIN 420001 (Basic: Tier I, NRC per seat)
- TWS Basic Service MRC: Choose CLIN 420101 (Basic: Tier I, MRC per seat)
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs may differ between contractors.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for (TWS). The specific details can be found within each contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for (TWS).
For more information on the general TWS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.12.1 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.12.1 for pricing.
Toll Free Services (TFS)
2. Technical Description
TFS is an inbound voice service which provides a toll free number (no charge to caller) with advanced features and routing capabilities that can be used by an Agency to provide enhanced customer service. TFS capabilities include voice applications, network based Interactive Voice Response (IVR) announcements, call routing to the appropriate party, and caller self service options to effectively manage inbound calls for delivering services to the Agency's callers.
TFS may be ordered as a domestic (CONUS and OCONUS) or non-domestic service with numbering consistent with toll free codes standards in the country in which the call originates.
The diagram below shows a typical TFS configuration. TFS can be used for individuals, help desks and call centers, to provide access to recorded announcements, access to voice mail service, or to provide a telephone number for an individual. TFS connects to and interoperates with the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) including both wireline and wireless transport. TFS utilizes the underlying Voice Service (VS) for connectivity and is offered for both dedicated and switched terminating access arrangements.
Typical TFS Configuration
3. Technical Detail
TFS provides a similar capability to FTS2001 Toll-Free Service. TFS will support the full range of technical capabilities that are available in commercial offerings. These include an intelligent call routing capability to meet an Agency's specific needs. An Agency can use presently assigned toll free numbers or request "vanity" toll free numbers (e.g., 1-800-CALL GSA) which will be provided if available. TFS supports portability of the assigned toll free number and can deliver inbound calls to a single site or to multiple sites. A brief summary of the other TFS technical capabilities is presented below:
- Universal International Toll Free Number service (UIFN) enabling the Agency to request a single, unique toll free number that is the same throughout the world (Where available commercially from participating countries)
- Busy signal or recorded announcements for all calls encountering network congestion and/or terminating egress congestion. The Agency determines the choice of announcements.
- A capability for customized network intercept to the recorded announcements and messages when a call cannot be completed. The announcement can be recorded by the contractor or remotely by the subscribing Agency in English and Spanish languages (other languages are optional).
- Dialed Number Identification Service (DNIS) that enables multiple toll free numbers to be routed and uniquely identified on a shared trunk group.
- Automatic Number Identification (ANI) to assist Agencies with identifying malicious or emergency calls and the help desk.
TFS also provides a wide range of service features that are listed below and described in the Networx Contracts Section C.2.2.3.2.1 Toll-Free Service Features:
- Agency based routing database
- Alternate Routing (also known as "Cascade" routing)
- ANI
- ANI Based Routing
- Announced Connect
- Announcements
- Call Prompter
- Call Redirection
- Computer Telephony Integration (CTI)
- Custom Call Records
- Day of Week Routing
- Day of Year Routing (Holiday Routing)
- In Route Announcements
- Interactive Voice Response (IVR)
- Make Busy Arrangement
- Network Call Distributor
- Network Queuing (Optional)
- NPA/NXX Routing
- Office Locator Database Service
- Operator Connect Bridging
- Percentage Call Allocation
- Real Time Reporting
- Routing Control
- Service Assurance Routing
- Speech Recognition
- Tailored Call Coverage
- Time of Day Routing
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for TFS. The specific details can be found within each Contractors Networx contract files and pricing notes for TFS.
For more information on the general TFS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.2.3 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.2.3 for pricing.
4. Price Description
Toll-Free Service (TFS) Price Basics
TFS provides a similar capability to FTS2001 Toll-Free Service. TFS provides basic inbound toll free calling with added capabilities to enable Agencies to effectively manage inbound calls. It includes options for termination of calls for the toll free number over either dedicated access or switched access arrangements. Calls can be either:
- Domestic to Domestic or
- Non-Domestic to Domestic
Price components required for full end-to-end service for Domestic and Non-Domestic to Domestic TFS:
- For switched access termination
- TFS Transport per-six second increment charge
- Access: Originating and terminating access costs are included in transport price
- For dedicated access termination
- TFS Transport per-six second increment charge
- Access: DAA Originating and Terminating Wireline Access (MRC) and (NRC)
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- Agency based routing database
- Alternate Routing (also known as "Cascade" routing)
- ANI
- ANI Based Routing
- Announced Connect
- Announcements
- Call Prompter
- Call Redirection
- *Computer Telephony Integration (CTI)
- Custom Call Records
- Day of Week Routing
- Day of Year Routing (Holiday Routing)
- In Route Announcements
- *Interactive Voice Response (IVR)
- Make Busy Arrangement
- *Network Call Distributor
- Network Queuing (Optional)
- NPA/NXX Routing
- Office Locator Database Service
- Operator Connect Bridging
- Percentage Call Allocation
- Real Time Reporting
- Routing Control
- Service Assurance Routing
- *Speech Recognition
- Tailored Call Coverage
- Time of Day Routing
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement TFS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
* Some or all price components are priced on an Individual Case Basis (ICB). CLINs with ICB prices are not available in the unit pricer.
Example 1: TFS with Switched Access Termination
- TFS Transport: Choose CLIN 34001 (TFS Transport Usage Price - Switched access termination per six-second increment)
- Access: For calls terminated over a switched access arrangement, the originating and terminating access costs are included in the transport pricing.
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs differ between vendors.
Example 2: TFS with Dedicated Access Termination
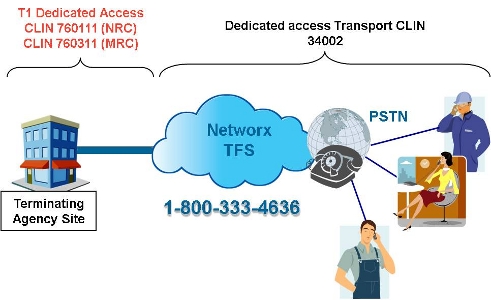
- TFS Transport: Choose CLIN 34002 (TFS Transport Usage Price - Dedicated access termination per six-second increment)
- Access NRC: Choose CLIN 760111 Routine DAA T1 NRC for the terminating end of the T1 dedicated access circuit
- Access MRC: Choose CLIN 760311 Routine DAA T1 MRC for the terminating end of the T1 dedicated access circuit
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs differ between vendors.
5. Price Additional Detail
A payphone add-on charge applies to toll-free calls placed from payphones. The payphone add-on charge does not apply to calls placed from payphones paid for by inserting coins during the progress of the call.
Flat rate pricing is provided on a per Service Delivery Point (SDP) basis, for call between locations in CONUS, Alaska, and Hawaii. Flat rate pricing packages are available based upon blocks of minutes used per month. Overage usage charges occur if the maximum monthly minutes are exceeded.
Price components required for full end-to-end service for Flat Rate TFS:
- For switched access termination
- TFS Transport flat rate MRC (inclusive of a pre-determined number of maximum allowable minutes per month)
- Overage usage per additional six-second increment for minutes of use above the maximum allowed per month
- Access: Originating and terminating access costs are included in transport price
- For dedicated access termination
- TFS Transport flat rate MRC (inclusive of a pre-determined number of maximum allowable minutes per month)
- Overage usage per additional six-second increment for minutes of use above the maximum allowed per month
- Access: DAA Originating and Terminating Wireline Access (MRC) and (NRC)
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement TFS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
Example 3: Flat Rate TFS for up to 10,000 minutes
- TFS Transport: Choose CLIN 34202 (TFS Flat Rate - 10,000 minutes - Switched access termination per package)
- Overage: Choose CLIN 34402 (TFS Overage - 10,000 minutes - Switched access termination)
- Access: For calls terminated over a switched access arrangement, the originating and terminating access costs are included in the transport pricing.
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs differ between vendors.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for TFS. The specific details can be found within each Contractors Networx contract files and pricing notes for TFS.
For more information on the general OWS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.2.3 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.2.3 for pricing.
Video Teleconferencing Service (VTS)
1. Technical Description
Video Teleconferencing Service (VTS) Technical Summary
VTS supports diverse Agency video teleconferencing needs, such as conferencing, distance learning, remote testimony, and other applications. This service enables participants at different locations worldwide to simulate face to face meetings and conduct interactive dialogue with instant sharing of various applications and documents. VTS supports desktop-PC, portable roll about, and fixed conference room for point-to-point and multi-point conferencing with audio conference add-on capabilities.
VTS is an application-layer service that uses underlying network service(s) to carry video traffic. VTS can operate over circuit-switched networks and Internet Protocol (IP) networks, including the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) and other Networx contractor's networks. Networx Circuit Switched Data Service (CSDS), Network-Based IP VPN Service (NBIP-VPNS), and Private Line Service (PLS) can provide connectivity to the contractor's multipoint video conferencing bridge. VTS provides appropriate adapters and gateways for coding conversion, video format conversion, rate adaptation, protocol conversion, and dissimilar networks.
The diagram below shows the various capabilities of VTS, such as point-to-point and multi-point video conference, reservation, and gateway capabilities.
2. Technical Detail
VTS is similar to Video Teleconferencing Service on the FTS2001 contracts. It supports the full range of technical capabilities that are available in commercial offerings. These capabilities include:
- On-demand and reservation-based video teleconferencing.
- Two way video, one way video with interactive voice, and/or the instant sharing of various types of documents/data files among VTS participants as an adjunct to the video teleconferencing session.
- Document sharing (data conferencing) which enables conference participants to interactively view, edit, and share or transfer data files and documents.
- Audio conference add-on capability to support non-video conference participants in a VTS call.
- Different modes of VTS operations:
- Dial Out mode: Centralized arrangements where the conference bridge operator initiates a call and dials each participant at least 15 minutes prior to the conference start time.
- Meet Me (Dial In) mode: Each participant is responsible for individually initiating a call and dialing into the conference bridge.
- Mixed Dial mode: A combination or mix of both dial out and meet me (dial in) callers.
- During a multi-point conference, the addition of a party to, or the deletion of a party from, the conference will be indicated by a tone or by a verbal or visual announcement.
- Multipoint video conference capabilities:
- Voice Activation. The video signal transmitted to all VTS conference call locations is automatically switched by voice activation when the speaker's audio signal exceeds a preset level for a specified amount of time.
- Continuous Presence. Multiple VTS locations may be viewed simultaneously on the same video screen. If the number of locations participating in the video conference exceeds the number being viewed via continuous presence, the selection of the video from a participating location that is displayed can be coordinated between the VTS operator and the participants.
- Chairperson Control. The chairperson, in control of the VTS, sends his or her own video or selects a return video from one of the participating locations to be sent to all participating locations. The chairperson has the capability of transferring control of the video teleconference to another presenter at his or her location.
- Lecture Control (Broadcast Video with Audio Return Only). The video from the lecturer's location is transmitted to all VTS participants. Audio, but no video, is returned to the lecturer's location from all other participating locations. The lecturer can select one or all of the audio signals for transmission to all participants.
- Reservation system capabilities:
- Schedule a multi-point or point-to-point VTS conference within 30 minutes after the advance reservation request, and to schedule a VTS conference up to one year in advance by voice, fax, or electronic means.
- VTS users can cancel a video teleconference prior to the scheduled start time of the video teleconference.
- Based on availability of bridging capacity and required network functions, request a delay in the scheduled termination time of a VTS conference, which is already in progress, is granted if the request is made at least 20 minutes before the scheduled terminating time of the VTS.
- Ability for VTS authorized users to schedule one or more video teleconferences by time and day of week either as a single event or recurring event on a daily, weekly, monthly or other periodic basis.
- Allows users with operating at different (disparate) data rates/speeds to connect and conference at their preferred speed.
- Ability to add participants or join a conference.
- Ability for VTS users to request operator assistance to resolve technical issues during a video conference.
These and other service capabilities are detailed in Section C.2.8.1.1.4 Technical Capabilities of the Networx contracts.
VTS also offers features that complement the basic service. These features are described in Section C.2.8.1.2 Features of the Networx contracts and are listed below:
- Attended Service.
- Certification.
- Coding Conversion (Transcoding).
- Rate Adaptation.
- Security - Sensitive but Unclassified (SBU).
- Security - Classified [Optional].
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for VTS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract and pricing notes for VTS.
For more information on the general VTS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.8.1 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.8.1 for pricing.3. Price Description
VTS Price Basics
VTS enables participants at different locations to simulate face-to-face meetings and conduct interactive dialogue with instant sharing of documents and applications. VTS conferences are available among two or more locations. VTS' audio conference add-on capability supports non-video conference users via a VTS call. Data connectivity is required for VTS. VTS provides the following components:
- Dedicated VTS - The prices for dedicated VTS are in addition to any applicable charges for the underlying access and transport service used for video teleconferencing.
- Dial-in VTS - Participants individually dial into the conference bridge. The prices for dial-in VTS are in addition to any applicable charges for the underlying access and transport service used for video teleconferencing.
- Dial-out VTS - Conference bridge operator initiates call to each participant. The prices for dial-out VTS include the transport and terminating access charges to the user.
Conferences canceled prior to scheduled start time are not billable. After the scheduled start time, all reserved ports and features are billed for the entire reserved duration whether actually used or not. An ongoing conference that is interrupted through no fault of any of the active participating locations is billed at the next lower completed billing increment, and if such an ongoing conference is interrupted in the first billable time increment, there is no billing for any time of that conference session. VTS is similar to Video Teleconferencing Service on the FTS2001 contracts.
- Price components required for full end-to-end basic service for VTS:
- Underlying transport services, such as IPS, CSDS, PLS, or NBIP-VPNS, to provide video/data connectivity
- Basic service consisting of one of the following:
- Dedicated VTS (MRC per port)
- Dial-in VTS (usage charges per minute per port)
- Dial-out VTS (usage charges per minute per port)
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- Attended service
- Certification
- Coding Conversion (Transcoding)
- Rate Adaptation
- Security - Sensitive but Unclassified
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement VTS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
Example 1: Dial-In VTS 384 kbps IPS Origination

- Underlying Transport: Choose Networx telecommunications service such as IPS or NBIP-VPNS
- VTS Basic Service: Choose CLIN 251112 (Dial-in 384 kbps or lower (but higher than 128 kbps) video bandwidth originating at IP site, per minute per port)
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs may differ between contractors.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for VTS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for VTS.
For more information on the general VTS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.8.1 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.8.1 for pricing.
Voice Service (VS)
1. Technical Description
Voice Service (VS) Technical Summary
VS is a service comprised of voice circuits typically capable of carrying one telephone conversation or its digital equivalent. In CONUS analog voice circuits have been replaced with digital equivalent circuits with a 64 kbps standard for both Time Division Multiplex (TDM) and Internet Protocol (IP) based backbone circuits. VS supports outgoing voice calls by direct station-to-station dialing from on-net and off-net locations worldwide, including calling cards.
VS calls can be initiated from many types of telephony equipment, including single-line and multi-line key sets. VS calls typically traverse trunks to PBX and Centrex equipment and terminate in a variety of telephony equipment which may include secure telephone units and connection to Inmarsat mobile satellite devices.
The diagram below shows VS connectivity from on-net locations, such as Agencies served by PBXs and Centrex Central Offices. In addition, VS is interoperable with the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) and all Networx contractors VS networks.
VS Connectivity from On-Net Locations
2. Technical Detail
VS supports the full range of technical capabilities that are available in commercial offerings. It is similar to Switched Voice Service (SVS) on the FTS2001 contracts. These capabilities include:
- Uniform numbering plan:
- Unique directory number for all on-net Government locations, including support of existing FTS2001 numbers.
- PSTN (including both wireline and wireless networks) numbers and any future changes to PSTN numbers
- Non-commercial Agency specific private 700 numbers
- Allow transparency and interconnectivity between the Networx contractor's network and other networks. The contractor provides gateways between the networks as needed.
- Support originating and terminating on-net calls. Incoming off-net calls from the PSTN are blocked unless an Agency specific request for the service gateway has been received and implemented.
- Networx contractor's network-specific private numbers, including access to contractor's operators, trouble reporting, or other special applications.
- Network intercept to a recorded announcement is provided as an inherent network capability when a call cannot be completed, for example:
- Number disconnected (disconnected numbers are not reassigned for at least 90 days for those situations where the contractor controls number assignment).
- Time-out during dialing.
- Network congestion.
- Denial of access to off-net and non-domestic calls.
- Denial of access to features.
- User-to-user signaling via ISDN D-channel during a call.
- Voice quality at least equal to 64 kbps PCM (standard: ITU G.711) for both TDM and
- VoIP based VS backbone networks.
These and other service capabilities are detailed in Section C.2.2.1.1.4 Technical Capabilities of the Networx contracts.
VS also offer features that complement the basic service. These features are described in Section C.2.2.1.2 Features of the Networx contracts.
- Agency-Recorded Message Announcements.
- Authorization Codes.
- Calling Cards (Post-paid and Pre-paid).
- Caller Identification (ID).
- Call Screening for users (class of service and restrictions).
- Customized Network Announcement Intercept Scripts.
- Internal Agency Accounting Code.
- Off-Net Information Calls.
- Operator Services.
- Support for Government travel cards.
- Suppression of Calling Number Delivery.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for VS. The specific details can be found within each contractor's Networx contract and pricing notes for VS.
For more information on the general VS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.2.1 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.2.1 for pricing.
3. Price Description
Voice Service (VS) Price Basics
VS provides a similar capability to FTS2001 Switched Voice Service. VS supports outgoing voice calls by direct station-to-station dialing from on-net and off-net locations, including calling cards. Calls can be either:
- CONUS to CONUS
- CONUS to OCONUS/Non-Domestic
- OCONUS/Non-Domestic to CONUS
- OCONUS/Non-Domestic to OCONUS/Non-Domestic
Price components required for full end-to-end service for VS:
- For switched access origination
- VS Transport per-six second increment charge.
- Access: Originating and terminating access costs are included in transport price.
- For dedicated access origination
- VS Transport per-six second increment charge.
- Access: DAA Originating and Terminating Wireline Access (MRC) and (NRC).
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- Agency-Recorded Message Announcements.
- Authorization Codes/Calling Cards.
- Caller Identification (ID).
- Call Screening for users.
- Internal Agency Accounting Code.
- Off-Net Information Calls.
- Operator Services.
- Suppression of Calling Number Delivery.
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement VS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
Example 1: VS with Switched Access Origination
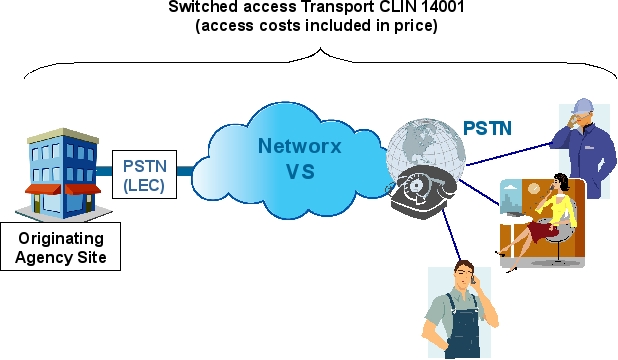
- VS Transport: Choose CLIN 14001 (VS Transport Usage Price - Switched access origination per six-second increment)
- Access: For calls originated over a switched access arrangement, the originating and terminating access costs are included in the transport pricing.
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs differ between vendors.
Example 2: VS with Dedicated Access Origination
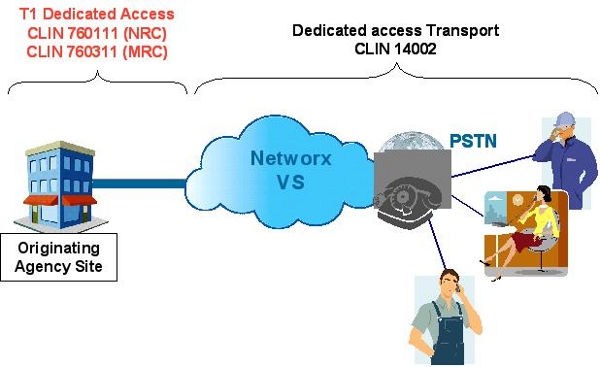
- VS Transport: Choose CLIN 14002 (VS Transport Usage Price - Dedicated access origination per six-second increment)
- Access NRC: Choose CLIN 760111 Routine DAA T1 NRC for the originating end of the T1 dedicated access circuit
- Access MRC: Choose CLIN 760311 Routine DAA T1 MRC for the originating end of the T1 dedicated access circuit
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs differ between vendors.
4. Price Additional Detail
For calls that terminate to a mobile phone or other wireless device (e.g., pagers) non-domestically, a per six-second increment additional add-on charge applies. These charges vary by terminating country.
Flat rate pricing is provided on a per Service Delivery Point (SDP) basis, for call between locations in CONUS, Alaska, and Hawaii. Flat rate pricing packages are available based upon blocks of minutes used per month. Overage usage charges occur if the maximum monthly minutes are exceeded.
Price components required for full end-to-end service for Flat Rate VS:
- For switched access origination
- VS Transport flat rate MRC (inclusive of a pre-determined number of maximum allowable minutes per month)
- Overage usage per additional six-second increment for minutes of use above the maximum allowed per month
- Access: Originating and terminating access costs are included in transport price
- For dedicated access origination
- VS Transport flat rate MRC (inclusive of a pre-determined number of maximum allowable minutes per month)
- Overage usage per additional six-second increment for minutes of use above the maximum allowed per month
- Access: DAA Originating and Terminating Wireline Access (MRC) and (NRC)
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement VS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation, and a MRC for maintenance.]
Example 3: Flat Rate VS for up to 10,000 minutes
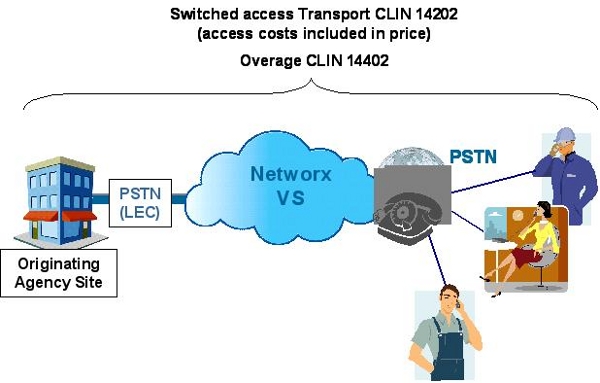
- VS Transport: Choose CLIN 14202 (VS Flat Rate - 10,000 minutes - Switched access origination per package)
- Overage: Choose CLIN 14402 (VS Overage - 10,000 minutes - Switched access origination)
- Access: For calls originated over a switched access arrangement, the originating and terminating access costs are included in the transport pricing.
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs differ between vendors.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for VS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for VS.
For more information on the general VS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.2.1 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.2.1 for pricing.
VoIP Transport Service (VOIPTS)
3. Technical Summary
VOIPTS provides transport of Agency voice communications as data packets over a contractor's Internet Protocol (IP) network as a cost effective alternative to legacy voice systems and architectures. VOIPTS allows voice calls, originating from on-net locations to be connected to both on-net and off-net locations by direct dialing.
VOIPTS facilitates connections to and interoperability with the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN), including both wireline and wireless networks, in both domestic and non-domestic locations. The primary cost saving application for VOIPTS is to replace dedicated tielines between Agency PBX's. As shown in the figure below, VOIPTS gateways enable interoperability between Voice over IP (VoIP) networks and non-IP networks and devices. Gateway functions include:
- Access Gateway-Provides access to the contractor's network via an Ethernet port from an Agency's local area network (LAN) or other IP equipment.
- Trunking Gateway-Provides access and interoperability between the IP network and the Agency's Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) based equipment (PBX's etc).
- PSTN Gateway-Provides transparent access to and interoperability with the domestic and non-domestic PSTN.
Example of VOIPTS Implementation
The service has the capability for calls to be re-routed to the PSTN if VOIPTS fails or is unavailable to complete calls. VOIPTS provides cost savings by the capability to bypass the PSTN entirely.
4. Technical Detail
VOIPTS continues and extends a service that was offered on FTS2001 contracts. The service technical capabilities are detailed in Section C.2.7.8.1.4 of the Networx contracts which include the following:
- Capability for VOIPTS subscribers to establish and receive telephone calls between on-net locations and originate calls to off-net locations.
- A routing prioritization scheme (class of service) scheme that assigns a higher priority to time sensitive VOIPTS packets than to non-time sensitive packets.
- Interoperability with public and private Agency network dial plans.
- Gateways for interoperability between diverse networks (illustrated in the above figure) that comply with the subscribing Agency's interface requirements.
- Flexible alternate routing capability (overflow and failover routing) to rout off-net calls to the PSTN if VOIPTS is unavailable.
- Capability to interoperate with Agency firewalls and security layers.
- Secure contractor's web site for VOIPTS performance and management reports.
- Call routing capability between phone numbers and IP addresses or URLs.
- Security practices and safeguards to minimize susceptibility to security issues and prevent unauthorized access.
VOIPTS is a basic service which does not have additional orderable features.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for VOIPTS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for VOIPTS.
For more information on the general VOIPTS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.7.8 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.7.8 for pricing.
5. Price Description
VOIPTS Price Basics
VOIPTS enables Agencies to leverage the WAN data network to transport voice communications between Agency locations. VOIPTS uses an underlying, separately priced, contractor provided IP network to provide on-net calling. On-net calling is free of usage charges up to the performance capability of the VOIPTS interface hardware. Management of the network is provided by the underlying network service. Calls to off-net locations are delivered via a contractor provided PSTN gateway. The price structure consists of outbound usage to off-net locations and is priced in six second increments.
VOIPTS continues and extends a service that was offered on FTS2001 contracts.
Price components required for full end-to-end service for Domestic and Non-Domestic VOIPTS:
- Underlying contractor provided IP network, such as NBIP-VPNS, to provide on-net calling
- DAA Originating and Terminating Wireline Access (MRC) and (NRC)
- VOIPTS Transport outbound usage charge to off-net locations per six-second increment
- No features available currently
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement VOIPTS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
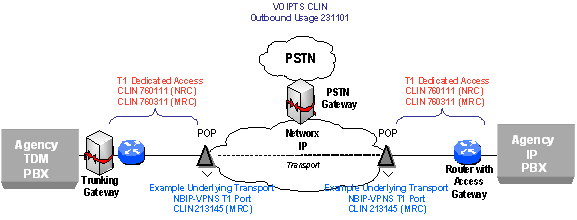
- Underlying transport: Choose Networx telecommunications services such as NBIP-VPNS (e.g., NBIP-VPNS CLIN 213145 T1 MRC per port)
- Access NRC: Choose CLIN 760111 Routine DAA T1 NRC
- Access MRC: Choose CLIN 760311 Routine DAA T1 MRC
- VOIPTS Transport: Choose CLIN 231101 (Outbound usage charge to off-net location per six-second increment)
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs may differ between contractors.
This document only addresses the VOIPTS service at contract award. Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for VOIPTS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for VOIPTS.
For more information on the general VOIPTS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.7.8 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.7.8 for pricing.
Vulnerability Scanning Service (VSS)
1. Overview
The Networx contracts require a basic level of security management for its contractors that ensures compliance with Federal Government generally accepted security principles and practices, or better. The contracts employ adequate and reasonable means to ensure and protect the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of Networx services, Operational Support Systems (OSS), and Government information transported or stored in the contractor's Networx services infrastructure. These requirements are detailed in Section C.3.3.2 Security Management of the Networx contracts.
In addition to this mandatory level of security, the Networx contracts provide additional security services that may be ordered on a fee-for-service basis. These are:
- 1.Managed Tiered Security Service (MTSS)
- 2.Managed Firewall Service (MFS)
- 3.Intrusion Detection and Prevention Service (IDPS)
- 4.Vulnerability Scanning Service (VSS)
- 5.Anti-Virus Management Service (AVMS)
- 6.Incident Response Service (INRS)
- 7.Managed E-Authentication Service (MEAS)
- 8.Secure Managed E-Mail Service (SMEMS)
The VSS offering is described below.
2. Technical Description
VSS Technical Summary
VSS allows Agencies to conduct effective and proactive assessments of critical networking environments, and correct vulnerabilities before they are exploited. VSS searches for security holes, flaws, and exploits on Agency systems, networks and applications. VSS helps to guard the Agency network infrastructure against emerging threats.
VSS builds on the FTS2001 contracts offerings. The service connects to and interoperates with the Agency networking environment, including Demilitarized Zones (DMZs) and secure LANs as required by the Agency. The service also supports Internet connectivity.
The Agency may order one or more of the following:
- External Vulnerability Scanning which tests Internet connected nodes in the network, including Web environments
- Internal Vulnerability Scanning which looks for local/host flaws and internal threats, usually inside the firewall
The diagram below illustrates a sample VSS implementation. Illustrative hardware such as edge routers, firewalls and Agency servers are not provided as part of the VSS.
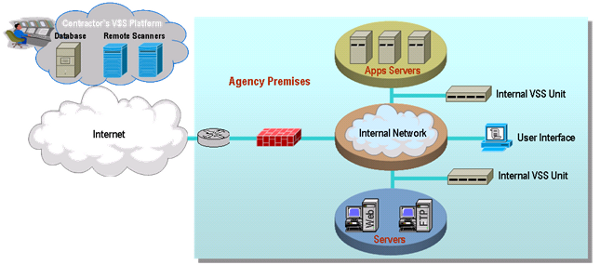
VSS also provides an Application Programming Interface (API) feature. This allows the Agency to integrate the service into its own tools and applications, as required, using for example, a standard Extensible Markup Language (XML) API. This enables Agency security personnel to assess the vulnerabilities of hosts, export vulnerability data, etc.
VSS Technical Detail
VSS tests for vulnerabilities by comparing scanned information to threat data contained in a database. VSS can also simulate a real intrusion in a controlled environment, in order to gauge a network's susceptibility to attacks. The service performs external scans by remotely probing a network for vulnerabilities that generally come from the outside; and internal scans which detect flaws originating from the inside.
VSS supports a range of technical capabilities that are available in commercial offerings. The contractor establishes, implements, and maintains the vulnerability scanning service, which operates on a 24x7 basis. The systems periodically probe networks, including operating systems and application software, for potential openings, security holes, and improper configuration. VSS explores vulnerabilities in, but not limited to, the following areas as applicable:
- Backdoors.
- Brute Force Attacks.
- Network Sniffing.
- Protocol Spoofing.
- Trojan Horses.
The VSS contractor proactively identifies network vulnerabilities, and proposes appropriate countermeasures, fixes, patches, and workarounds. The contractor notifies the Agency of vulnerabilities discovered, and also provides secure Web access to vulnerability information, scan summaries, device/host reports, and trend analyses. VSS provides scan scheduling flexibility to the Agency in order to minimize any interruptions in normal business activities. The service also supports non-destructive and non-intrusive vulnerability scans that will not crash the systems being analyzed, or disrupt Agency operations. The scans will not provoke a debilitating denial of service condition on the Agency system being probed. The VSS scanning engine is regularly updated with new vulnerabilities information in order to maintain effectiveness of the service. These and other VSS service capabilities are detailed in Section C.2.10.3.1.4 Technical Capabilities of the Networx contracts.
VSS is required to support the User-to-Network Interfaces (UNIs) defined in applicable Networx services, for example:
C.2.4.1 Internet Protocol Service (IPS). C.2.7.2 Premises-based IP VPN Services (PBIP-VPNS). C.2.7.3 Network-based IP VPN Services (NBIP-VPNS).
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for VSS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for VSS.
For more information on the general VSS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.10.3 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.10.3 for pricing.
3. Price Description
VSS Price Basics
VSS provides external and internal vulnerability assessments of the Agency's networking environment. The service mitigates security holes and flaws before they are exploited. VSS provides the following pricing options:
- Unlimited Scans consist of unlimited scans within a month for a predetermined number of IP addresses. The NRC includes the design, implementation, and configuration of VSS. The MRC comprises the management and ongoing scanning/monitoring support.
- Usage consists of a predefined number of scans to be distributed over any IP addresses as defined by the Agency at the time the scan is conducted. A scan comprises one scan of one IP address one time.
VSS builds on the FTS2001 contracts offerings.
Price components required for service are:
- Underlying transport services, such as IPS to provide connectivity
- Basic service (NRC and/or MRC) consisting of either:
- VSS Unlimited Scans (NRC + MRC per IP address or per block of IP address)
- VSS Usage (NRC per scan or per block of scans)
- VSS Application Programming Interface feature ordered as needed by the Agency
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement VSS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
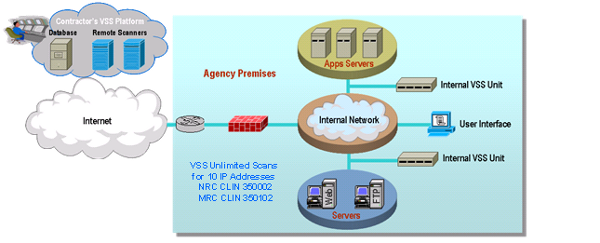
- Transport: Choose Networx telecommunications services such as IPS
- Unlimited Scans NRC: Choose CLIN 350002 (Unlimited Scans for 10 specified IP addresses NRC per block of 10 IP addresses)
- Unlimited Scans MRC: Choose CLIN 350102 (Unlimited Scans for 10 specified IP addresses MRC per block of 10 IP addresses)
- SEDs may be required to implement VSS. Illustrative hardware is not provided as part of the VSS.
Example 2: VSS Usage for 50 scans
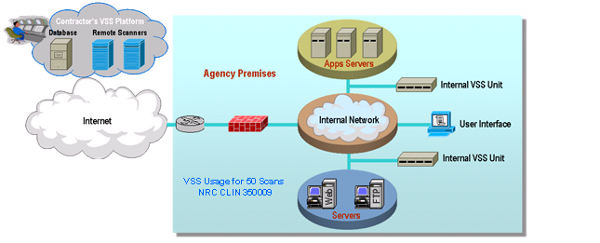
- Transport: Choose Networx telecommunications services such as IPS
- Usage NRC: Choose CLIN 350009 (50 scans NRC per block of 50 scans)
- SEDs may be required to implement VSS. Illustrative hardware is not provided as part of the VSS.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for VSS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for VSS.
For more information on the general VSS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.10.3 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.10.3 for pricing.
Web Conferencing Service (WCS)
2. Technical Description
WCS Technical Summary
WCS enable agencies to enhance traditional conferencing by allowing remote participants to interactively collaborate to share information, documents, and applications over the Internet with a commercially available web browser. The scope of collaboration is wide and allows the participants real-time interactive collaboration in a private and secure WCS session for activities such as Sharing Presentations/Documents, File Transfers, Polling, Online Surveys, Voting, Slide Annotation, White Board, and chat - public and private.
WCS is typically used in conjunction with an audio and/or video conference and enables Agencies to provide participants with secure, user friendly and interactive real time collaboration capabilities. Agencies can utilize WCS to effectively disseminate information quickly and easily, reduce the cost of training and educational programs, and permit individuals and groups to participate in activities they otherwise would be unable to attend due to a variety of conflicts.
The figure below shows a typical WCS application.

Networx Web Conference Service
3. Technical Detail
WCS is an application layer service provided over an Internet connection that has no geographic coverage constraints. The service is accessible via a Universal Resource Locator (URL) address and will be compatible with commercially available Internet web browser software packages. WCS will interoperate with the Internet and subscribing Agencies IP network(s). Agency Internet access to WCS is not included as part of the service.
WCS was not offered on the original FTS2001 contracts but some similar conferencing capabilities are covered in other FTS2001 services. WCS will provide point-to-point and multi-point web conferences supported with customized greeting, authentication, password protection and Online Help. WCS will traverse and successfully interoperate with Agency firewalls and security layers.
Capabilities
WCS provides a wide range of Technical Capabilities available to the authorized users and a detailed description of these is covered in the Section C.2.8.3.1 4 of the Networx Contracts. Listed below is a very brief summary of the capabilities provided to the participants.
- Authentication and password protection; a customized greeting (or message) screen, and Online Help.
- Test and verification of the web browser on Participant's computer or Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) to ensure that it is compatible with WCS. The appropriate plug-ins required to deliver WCS to the subscriber will be provided.
- Support for dynamic content, i.e., the ability to use Audio Visual Interleave (AVI's) files, flash, animated gif, and dynamic html pages.
- Conference Request on demand, via scheduled reservation with a single point of contact, within 30 minutes prior to the requested conference time.
- Scheduling or cancelling one or more web conferences, within at least one year in advance, either as a single event or recurring event on a daily, weekly, monthly, or other periodic basis.
- E-mail notification with a meeting invitation and RSVP to conference participants.
- Ability to extend the scheduled conference time and to add participants as requested.
- Capacity to support at least 31 simultaneous participants in an individual web conference.
- Immediate response to an operator request for assistance to resolve any technical or WCS service issues or problems.
- Ability for the participants to view the name list of other participants attending the WCS.
- Ability for the conference leader to control and share a remote participant's desktop application.
- Group web surfing ability for the conference leader to enable him to guide and navigate WCS participants to a web page.
- Ability for multiple Presenters on a WCS meeting or event.
- Ability for the conference leader to lock and unlock access to the meeting. When the meeting is locked, no additional participants can join the active conference. [Optional]
- Ability for conference leaders to print the presentation used during the WCS or save it to a file. Participants shall have the same capability if permitted by the conference leader.
Features
WCS also provides service features listed below and described in the Networx Contracts Section C.2.8.3.2.1 Toll-Free Service Features:
- Streaming Audio - Ability to deliver one way audio synchronized with any data portions of the web conference.
- Streaming Video - Ability to deliver one way video synchronized with any data portions of the web conference.
- Web Based Presentation Replay - Ability to replay (or playback) web based presentations. The replay shall be available for a minimum of 30 days after the initial conference with options for extending the period.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for WCS. The specific details can be found within each Contractors Networx contract files and pricing notes for WCS.
For more information on the general WCS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.8.3 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.8.3 for pricing.
4. Price Description
WCS Price Basics
WCS enables real time collaboration between participants using a commercially available web browser and is typically used in conjunction with an audio or video connection. WCS provides the following pricing options:
- A usage charge per minute per port
- A subscription service consisting of a Monthly Recurring Charge (MRC) per subscription with a set number of participants (5,10,20, or 30 participants)
Underlying transport services (i.e. VS for audio, IPS for Internet connection) to provide connectivity are separately priced. Audio Conferencing Service (ACS) and Video Teleconferencing Service (VTS) may also be required for audio and video conferencing and are separately priced.
WCS was not offered on the original FTS2001 contracts but some similar conferencing capabilities are covered in other FTS2001 services.
- Price components required for WCS Usage:
- Underlying transport services, such as IPS or VS, to provide connectivity (Audio Conferencing Service (ACS) and Video Teleconferencing Service (VTS) may also be required for audio and video conferencing)
- Basic service (usage charges per minute per port)
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency:
- Streaming audio
- Streaming video
- Web Based Presentation Replay
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement WCS. [Please note that SEDs under Networx replace the FTS2001 User-to-Network Interfaces and Access Adaptation Functions (UNIs/AAFs). SEDs may differ between Networx providers. The pricing structure for SEDs provides for either a one-time payment or monthly term payments for purchase, plus a NRC for installation and a MRC for maintenance.]
Example 1: WCS Usage

- Underlying Transport: Choose Networx telecommunications service such as IPS
- WCS Basic Service: Choose CLIN 270302 (usage per minute per port)
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs may differ between contractors.
WCS Price Additional Detail
WCS Subscription: If a WCS subscription is purchased, there is no usage charge. The WCS subscription service offers unlimited web conferences for up to a specified number of concurrent participants (5, 10, 20, or 30 participants), priced on a monthly basis.
Price components required for WCS Subscription:

- Underlying transport services, such as IPS or VS, to provide connectivity (Audio Conferencing Service (ACS) and Video
- Teleconferencing Service (VTS) may also be required for audio and video conferencing)
- Basic service (MRC per block of participants)
- Features ordered as needed by the Agency
- Service Enabling Devices (SEDs) may be required to implement WCS
Example 2: WCS Subscription for five (5) participants
- Underlying Transport: Choose Networx telecommunications service such as IPS
- WCS Basic Service: Choose CLIN 270101 (WCS Subscription Service per block of 5 participants)
- SEDs must be chosen based on equipment required at each location. CLINs may differ between contractors.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for WCS. The specific details can be found within each Contractors Networx contract files and pricing notes for WCS.
For more information on the general WCS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.8.3 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.8.3 for pricing.